Hypothesis formulation and distributions
A/B Testing in Python

Moe Lotfy, PhD
Principal Data Science Manager
Defining hypotheses
A hypothesis is:
- a statement explaining an event
- a starting point for further investigation
- an idea we want to test
A strong hypothesis:
- is testable, declarative, concise, and logical
- enables systematic iteration
- is easier to generalize and confirm understanding
- results in actionable/focused recommendations
Hypothesis format
General framing format:
- Based on X, we believe that if we do Y
- Then Z will happen
- As measured by metric(s) M
Example of the alternative hypothesis:
- Based on user experience research, we believe that if we update our checkout page design
- Then the percentage of purchasing customers will increase
- As measured by purchase rate
- Null hypothesis: ...the percentage of purchasing customers will not change...
Calculating sample statistics
# Calculate the number of users in groups A and B
n_A = checkout[checkout['checkout_page'] == 'A']['purchased'].count()
n_B = checkout[checkout['checkout_page'] == 'B']['purchased'].count()
print('Group A users:',n_A)
print('Group B users:',n_B)
Group A users: 3000
Group B users: 3000
# Calculate the mean purchase rates of groups A and B
p_A = checkout[checkout['checkout_page'] == 'A']['purchased'].mean()
p_B = checkout[checkout['checkout_page'] == 'B']['purchased'].mean()
print('Group A mean purchase rate:',p_A)
print('Group B mean purchase rate:',p_B)
Group A mean purchase rate: 0.820
Group B mean purchase rate: 0.847
Simulating and plotting distributions
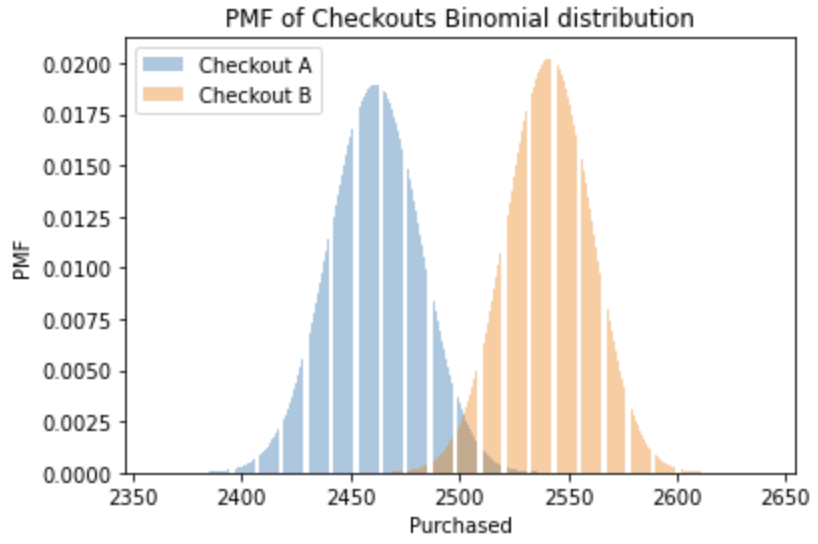
The number of purchasers in n trials with purchasing probability p is Binomially distributed.
# Import binom from scipy library
from scipy.stats import binom
# Create x-axis range and Binomial distributions A and B
x = np.arange(n_A*p_A - 100, n_B*p_B + 100)
binom_a = binom.pmf(x, n_A, p_A)
binom_b = binom.pmf(x, n_B, p_B)
# Plot Binomial distributions A and B
plt.bar(x, binom_a, alpha=0.4, label='Checkout A')
plt.bar(x, binom_b, alpha=0.4, label='Checkout B')
plt.xlabel('Purchased')
plt.ylabel('PMF')
plt.title('PMF of Checkouts Binomial distribution')
plt.show()
Central limit theorem
For a sufficiently large sample size, the distribution of the sample means, p, will be
- normally distributed around the true population mean
- with a standard deviation = standard error of the mean
- irrespective of the distribution of the underlying data
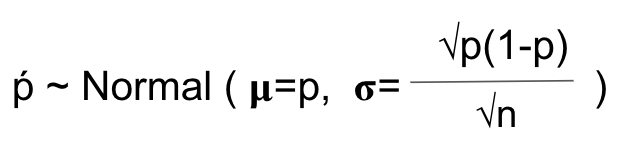
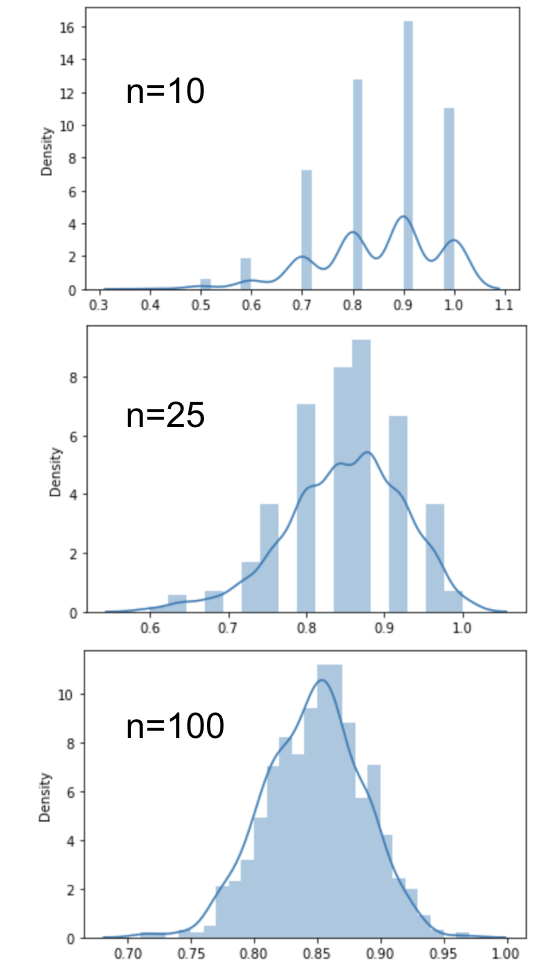
Central limit theorem in python
# Set random seed for repeatability
np.random.seed(47)
# Create an empty list to hold means
sampled_means = []
# Create loop to simulate 1000 sample means
for i in range(1000):
# Take a sample of n=100
sample = checkout['purchased'].sample(100,replace=True)
# Get the sample mean and append to list
sample_mean = np.mean(sample)
sampled_means.append(sample_mean)
# Plot distribution
sns.displot(sampled_means, kde=True)
plt.show()
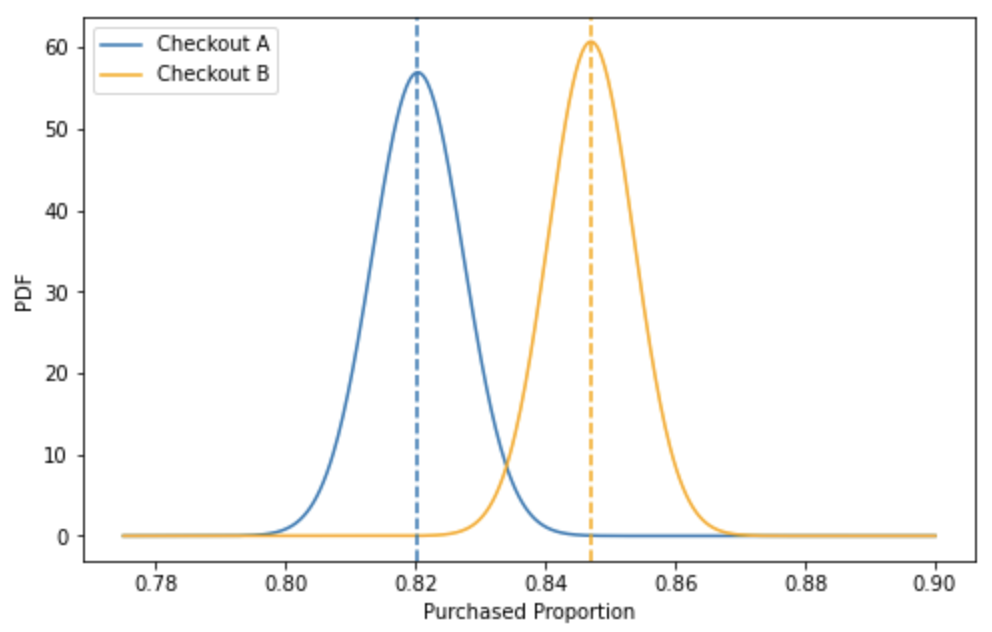
Hypothesis mathematical representation
# Import norm from scipy library
from scipy.stats import norm
# Create x-axis range and normal distributions A and B
x = np.linspace(0.775, 0.9, 500)
norm_a = norm.pdf(x, p_A, np.sqrt(p_A*(1-p_A) / n_A))
norm_b = norm.pdf(x, p_B, np.sqrt(p_B*(1-p_B) / n_B))
# Plot normal distributions A and B
sns.lineplot(x=x, y=norm_a, ax=ax, label='Checkout A')
sns.lineplot(x=x, y=norm_b, color='orange', \
ax=ax, label= 'Checkout B')
ax.axvline(p_A, linestyle='--')
ax.axvline(p_B, linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('Purchased Proportion')
plt.ylabel('PDF')
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.show()
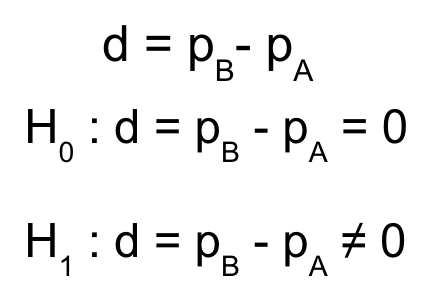
Let's practice!
A/B Testing in Python

