Data quality terms and concepts
Introduction to Data Quality

Chrissy Bloom
Head of Enterprise Data Strategy & Governance
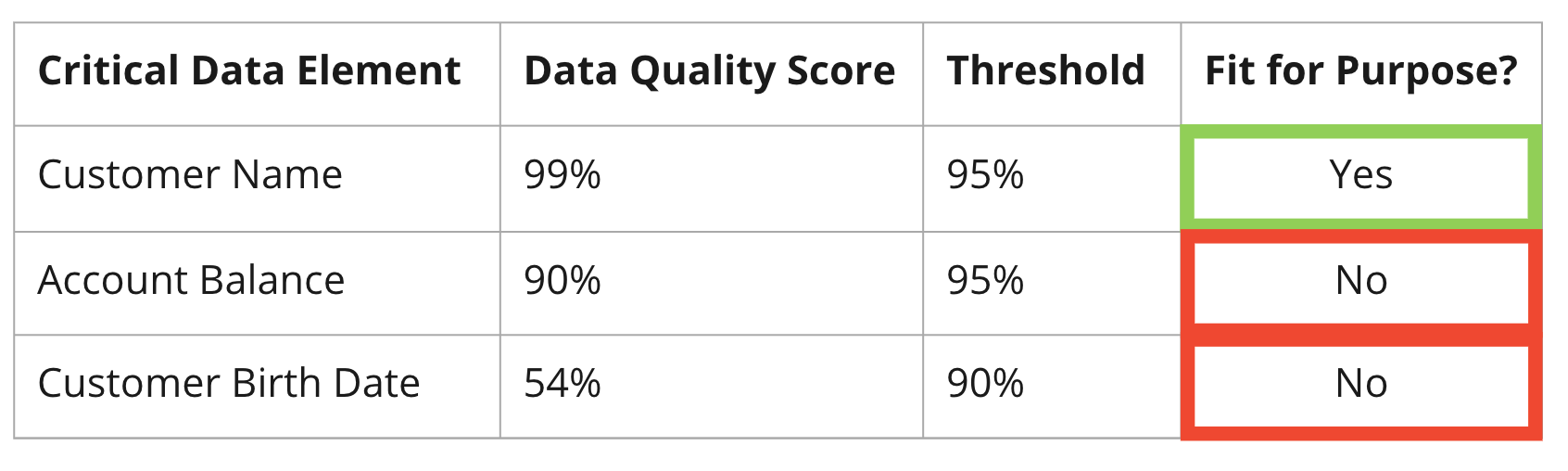
Defining data quality
- Data Quality: a measurement of the degree to which data is fit for purpose
- Good data quality = trust in data
- Better business decisions
- Better equipped business processes
- Often good data quality is assumed
- Data quality needs to be measured and monitored to ensure that data is fit for use.
Defining data quality dimensions
Data Quality Dimension: a measurement of a specific attribute of a data's quality
- Use data quality dimensions to quantify how fit for purpose data is.
- Completeness
- Validity
- Uniqueness
- Consistency
- Timeliness
- Accuracy
Completeness as a data quality dimension
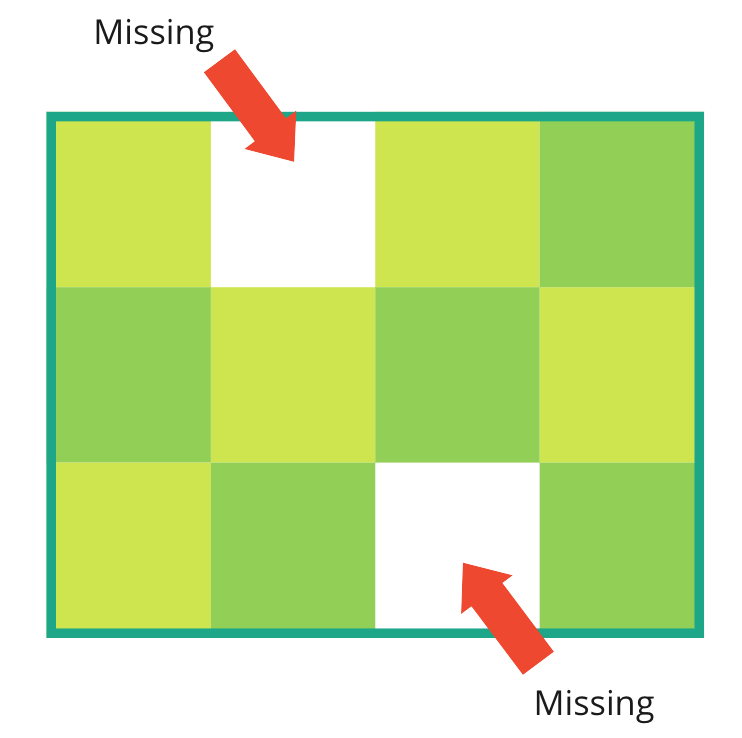
Completeness:
- Dataset level: measures the degree to which all expected records in a dataset are present.
- Data element level: measures the degree to which all records have data populated when expected.
- Business issues due to incomplete data:
- Numbers may be skewed
- Customers may be affected
Completeness example
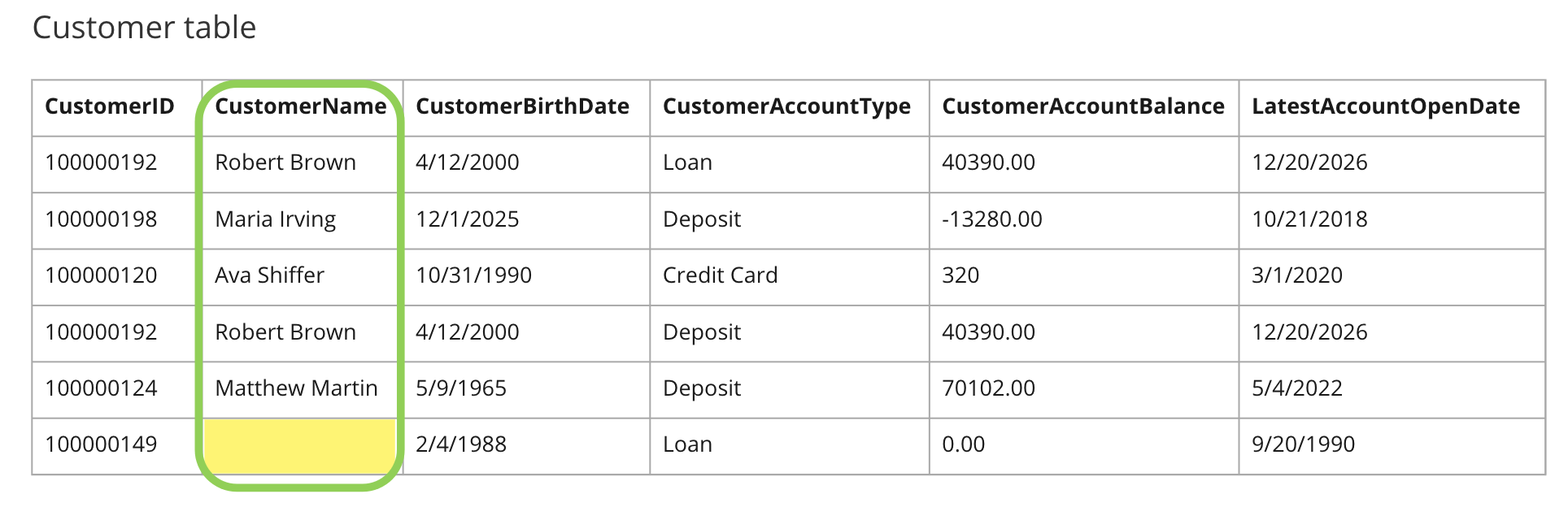
All records must have a value populated in the CustomerName field.
Validity as a data quality dimension
Validity: measures the degree to which the values in a data element are valid
- Requires business context
- Define list or criteria for valid values
- Numeric measurement of validity = count of valid/total count
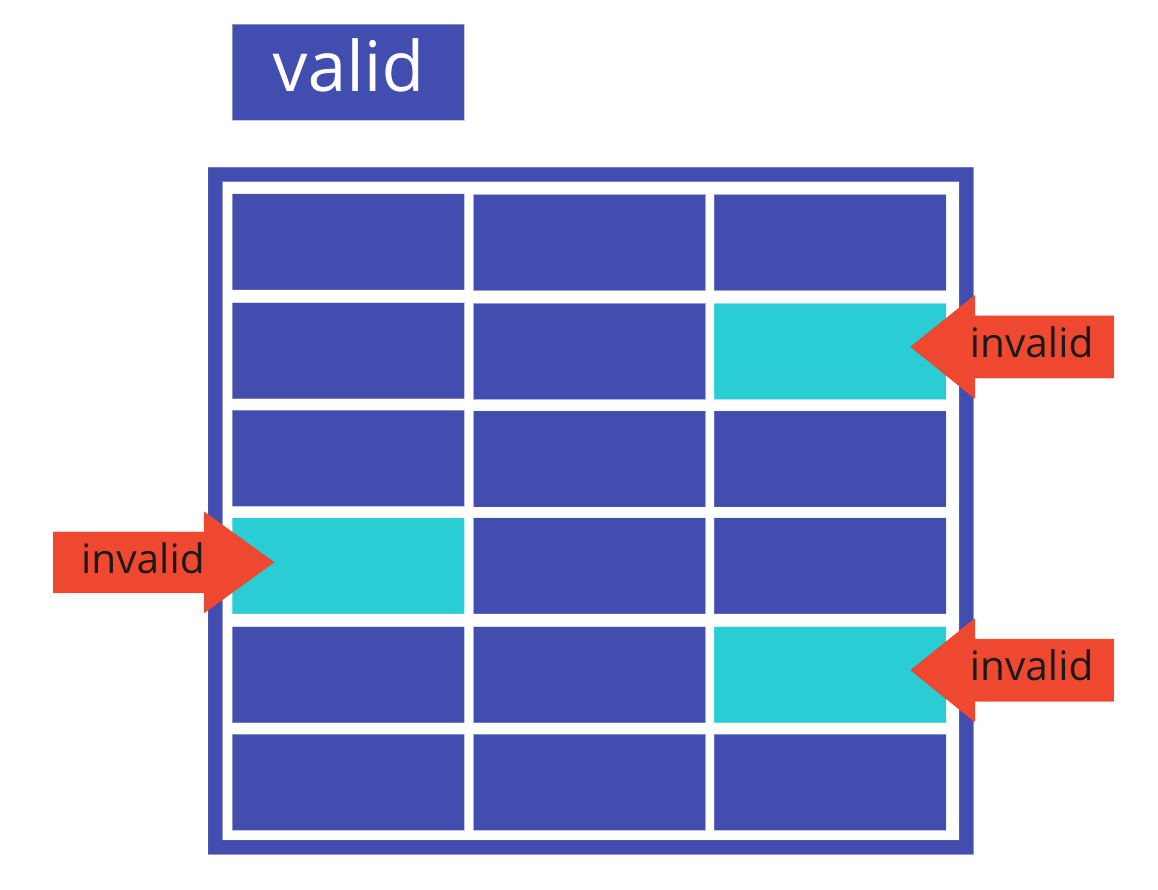
Validity example
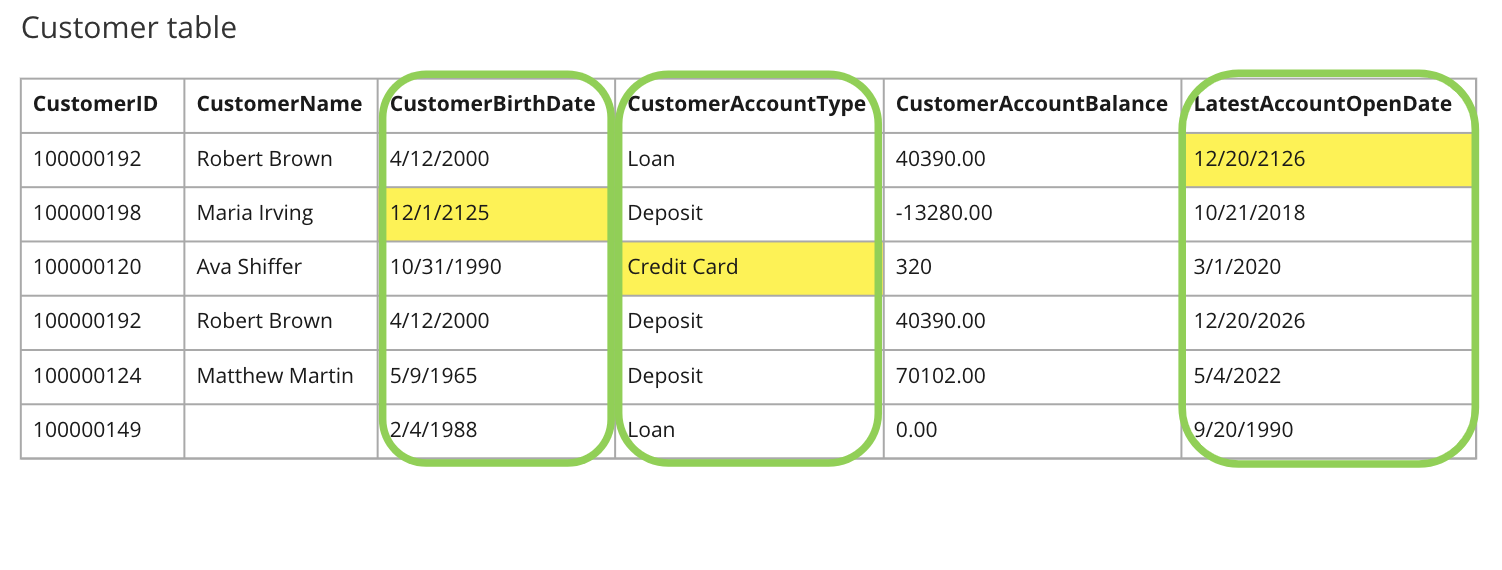
- CustomerBirthDate value must be a date in the future.
- CustomerAccountType value must be either Loan or Deposit.
- LatestAccountOpenDate value must be a date in the past.
Uniqueness as a data quality dimension
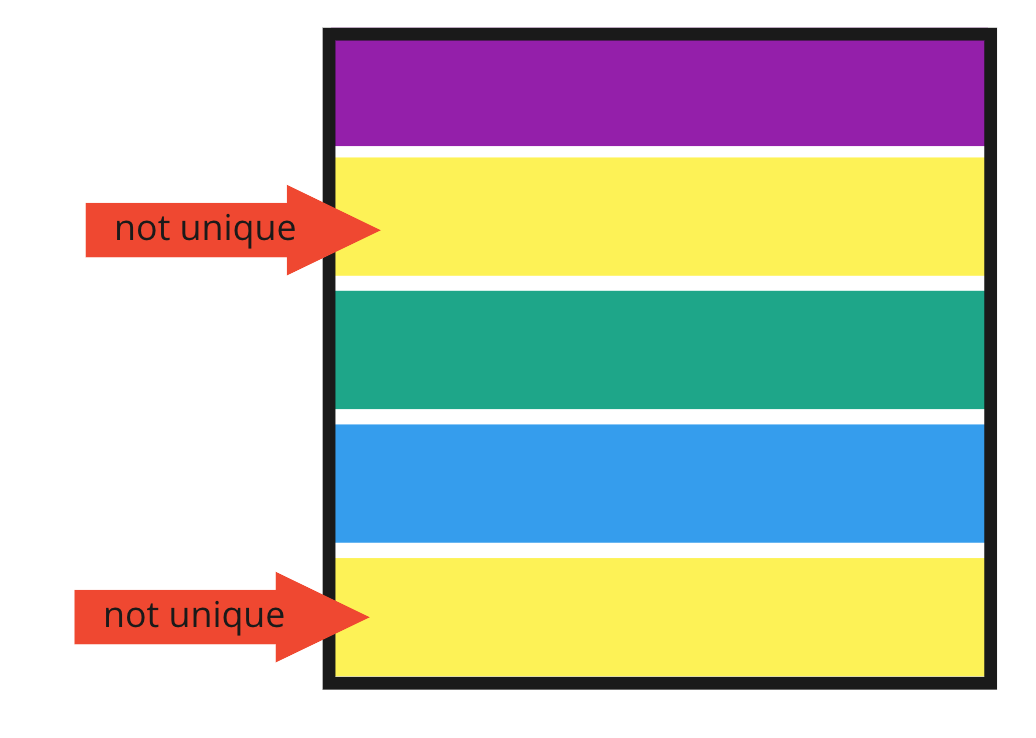
Uniqueness: measures the degree to which the records in a dataset are not duplicated
- Requires business context to define criteria for determining unique records
- May need to look for duplicates in one or multiple columns to identify errors
Uniqueness example
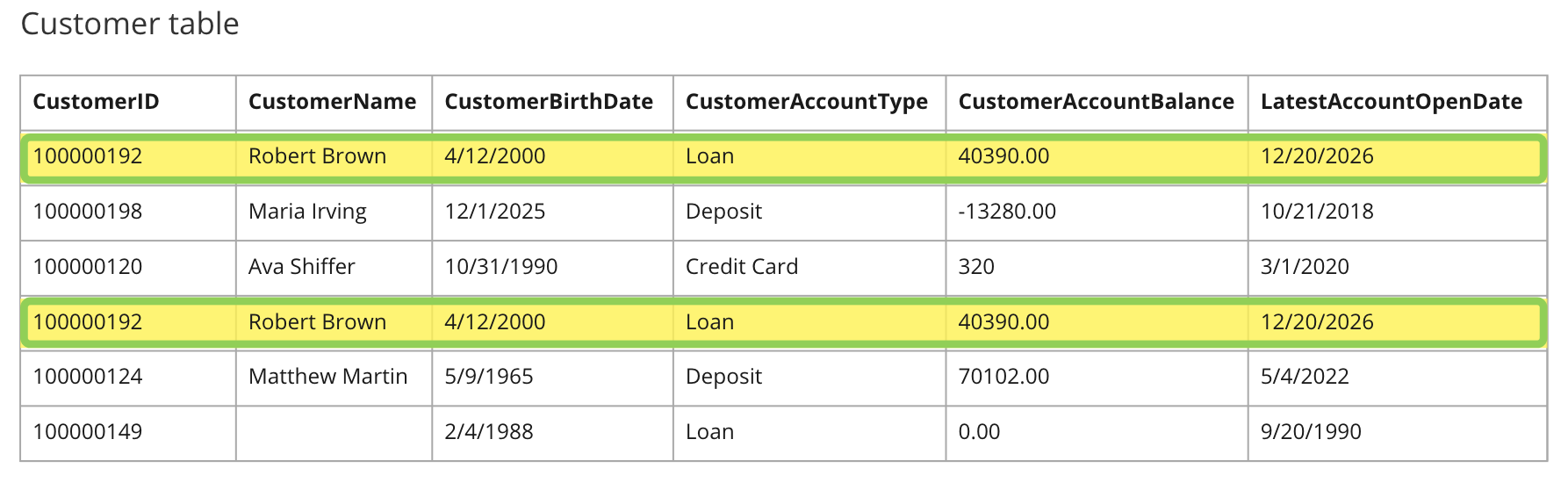
All records must have a unique CustomerID and CustomerName.
Let's practice!
Introduction to Data Quality

