Encoding categorical data using supervised learning
Feature Engineering in R

Jorge Zazueta
Research Professor and Head of the Modeling Group at the School of Economics, UASLP
Introducing supervised encoding
Supervised encoding, in contrast, uses the outcome values to derive numeric features from nominal predictors.
Introducing supervised encoding
Supervised encoding uses the outcome values to derive numeric features from nominal predictors.
Some supervised encoding functions available in the embed package
| Function | Definition |
|---|---|
| step_lencode_glm() | Uses likelihood encodings to convert a nominal predictor into a single set of scores derived from a generalized linear model. |
| step_lencode_bayes() | Applies Bayesian likelihood encodings to convert a nominal predictor into a single set of scores derived from a generalized linear model estimated using Bayesian analysis. |
| step_lencode_mixed() | Converts nominal predictors into a single set of scores derived from a generalized linear mixed model. |
Predicting grant application success
We are interested in predicting grant application success based solely on sponsor code.
lr_model <- logistic_reg() # declare model
lr_recipe_glm <- # Set recipe glm
recipe(class ~ sponsor_code,
data = grants_train) %>%
step_lencode_glm(sponsor_code,
# Declare outcome variable
outcome = vars(class))
lr_workflow_glm <- # Create Workflow
workflow() %>%
add_model(lr_model) %>%
add_recipe(lr_recipe_glm)
Workflow summary
lr_workflow_glm
-- Workflow ------------------------------------
Preprocessor: Recipe
Model: logistic_reg()
-- Preprocessor --------------------------------
1 Recipe Step
- step_lencode_glm()
-- Model --------------------------------------
Logistic Regression Model Specification (classification)
Computational engine: glm
Fitting, augmenting, and assessing
We fit and evaluate our model
lr_fit_glm <- # Fit
lr_workflow_glm %>%
fit(grants_train)
lr_aug_glm <- # Augment
lr_fit_glm %>%
augment(grants_test)
glm_model <- lr_aug_glm %>% # Assess
class_evaluate(truth = class,
estimate = .pred_class,
.pred_successful)
Performance results are stored in glm_model
glm_model
# A tibble: 2 × 3
.metric .estimator .estimate
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 accuracy binary 0.728
2 roc_auc binary 0.684
Binding models together
We build bayes_modeland mixed_model to compare the performance of the corresponding steps.
# Define model names
model <- c("glm", "glm",
"bayes","bayes",
"mixed", "mixed")
# Bind models in a tibble
models <-
bind_rows(glm_model,
bayes_model,
mixed_model)%>%
add_column(model = model)%>%
select(-.estimator) %>%
spread(model,.estimate)
A convenient performance table
models
# A tibble: 2 × 4
.metric bayes glm mixed
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
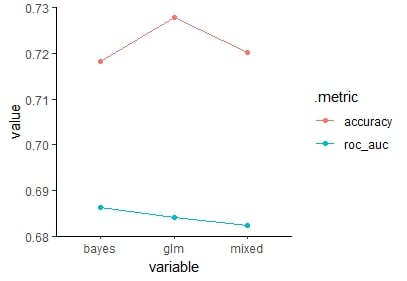
1 accuracy 0.718 0.728 0.720
2 roc_auc 0.686 0.684 0.682
Visualizing our results
Visualize results in a parallel coordinates chart from the Gally package.
# Libraries
library(GGally)
# Parallel coordinates chart
ggparcoord(models,
columns = 2:4,
groupColumn = 1,
scale="globalminmax",
showPoints = TRUE)
Parallel coordinates chart of accuracy and roc_auc comparing all models.
Let's practice!
Feature Engineering in R

