MLflow Tracking
Introduction to MLflow

Weston Bassler
Senior MLOps Engineer
Tracking data about models

1 istock.com
What is MLflow Tracking?
- Model Metrics
- F1, Recall, Accuracy, MSE, etc...
- Parameters
- library specific
- code
train.py
- other artifacts
- tokenizers, pickle, etc...
Training runs
- How MLflow is organized
- New run equals new model training
- A run is placed within an experiment
- Invoked via
mlflow.start_run()

1 unsplash.com
Starting a training run
import mlflow
# Start a run
mlflow.start_run()
<ActiveRun: >
# End a run
mlflow.end_run()
Setting a training run variable
import mlflow # Set experiment mlflow.set_experiment("My Experiment") # Start a run run = mlflow.start_run()# Print run info run.info
<RunInfo: artifact_uri='./mlruns/0/9de5df4d19994546b03dce09aefb58af/artifacts',
end_time=None, experiment_id='31', lifecycle_stage='active',
run_id='9de5df4d19994546b03dce09aefb58af', run_name='big-owl-145',
run_uuid='9de5df4d19994546b03dce09aefb58af', start_time=1676838126924,
status='RUNNING', user_id='user'>
Logging to MLflow Tracking
Metrics
log_metric("accuracy", 0.90)log_metrics({"accuracy": 0.90, "loss": 0.50})
Parameters
log_param("n_jobs", 1)log_params({"n_jobs": 1, "fit_intercept": False})
Artifacts
log_artifact("file.py")log_artifacts("./directory/")
Logging a run
import mlflow # Set Experiment mlflow.set_experiment("LR Experiment")# Start a run mlflow.start_run()# Model Training Code here lr = LogisticRegression(n_jobs=1) # Model evaluation Code here lr.fit(X, y) score = lr.score(X, y)
# Log a metric
mlflow.log_metric("score", score)
# Log a parameter
mlflow.log_param("n_jobs", 1)
# Log an artifact
mlflow.log_artifact("train_code.py")
Open MLflow UI
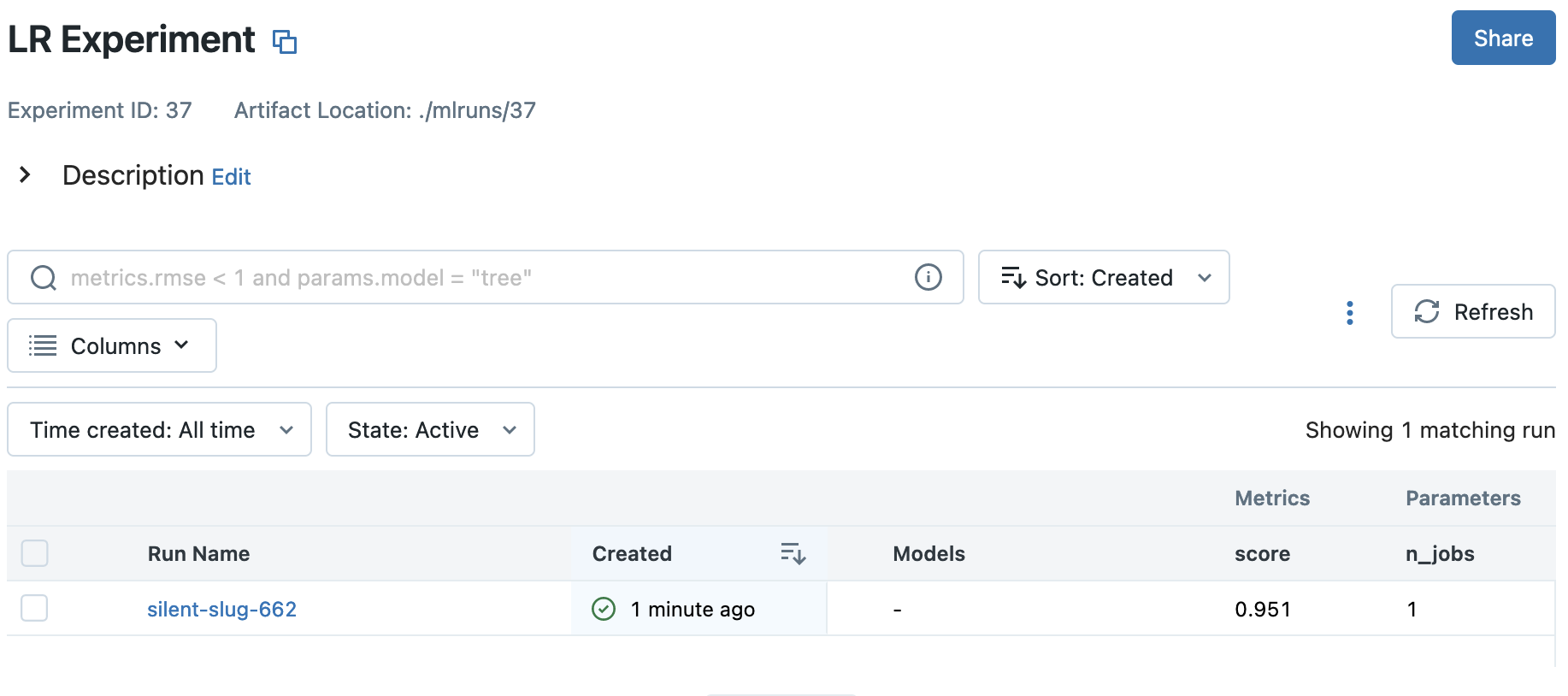
Tracking UI experiment view
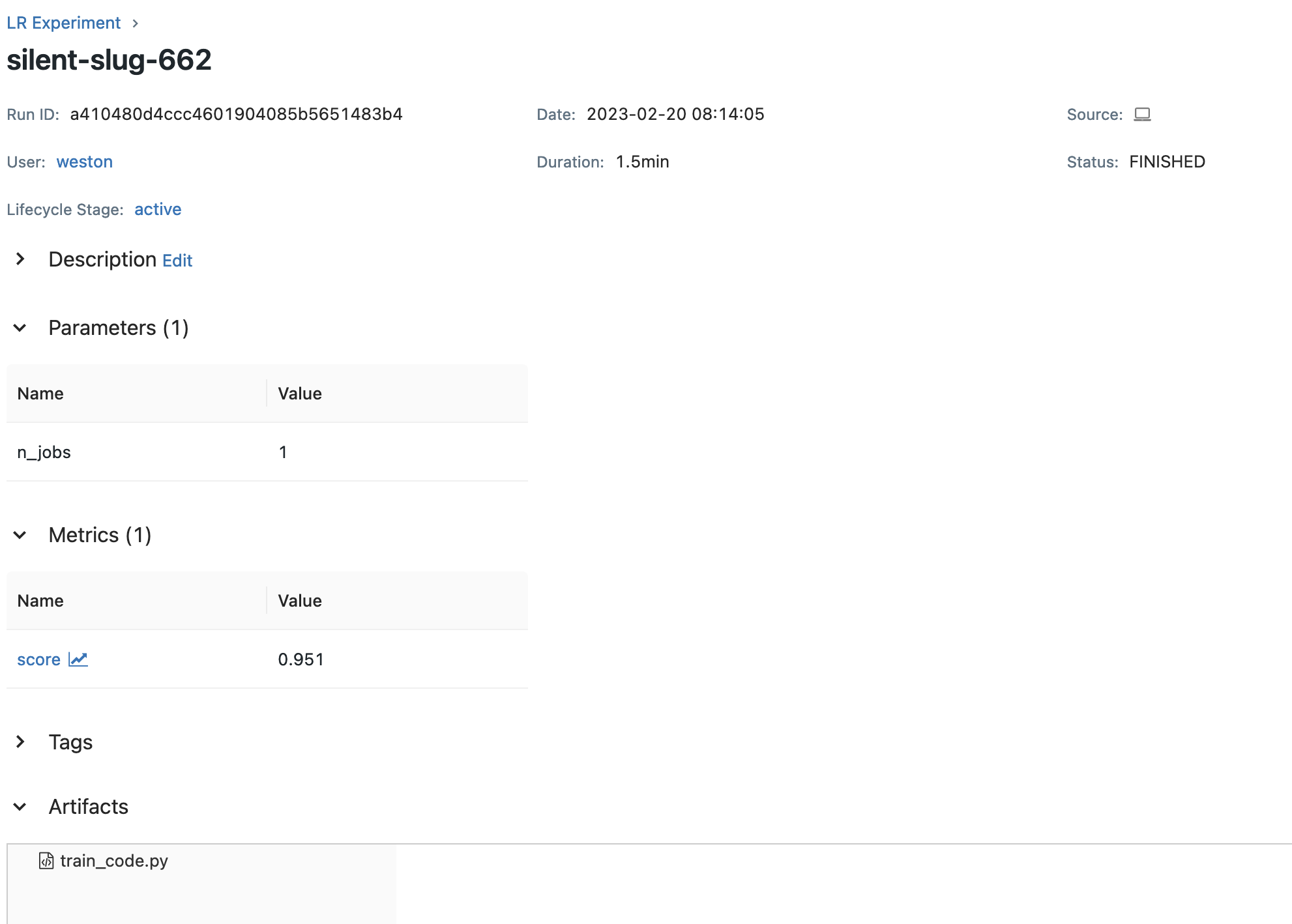
Tracking UI run view
Let's practice!
Introduction to MLflow