Monitoring and visualization
End-to-End Machine Learning

Joshua Stapleton
Machine Learning Engineer
What's next?
- Trained, optimized, deployed, predicted... what next?
- Monitoring
- Logging results
- Visualizing performance
Logging with python
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Setting up basic logging configuration
logging.basicConfig(filename='predictions.log', level=logging.INFO)
# Make predictions on the test set and log the results
for i in range(X_test.shape[0]):
instance = X_test[i,:].reshape(1, -1)
prediction = model.predict(instance)
logging.info(f'Inst. {i} - PredClass: {prediction[0]}, RealClass: {y_test[i]}')
Logging with python (cont.)
# Function to visualize the predictions from log
with open(logfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
predicted_classes = [int(line.split("Predicted Class: ")[1].split(",")[0]) \
for line in lines]
# Perform data analysis, visualization, etc.
...
- Use Python logging to trace model performance
Visualization
- Inspect performance over time
- Transform raw data of inputs / predictions into insights
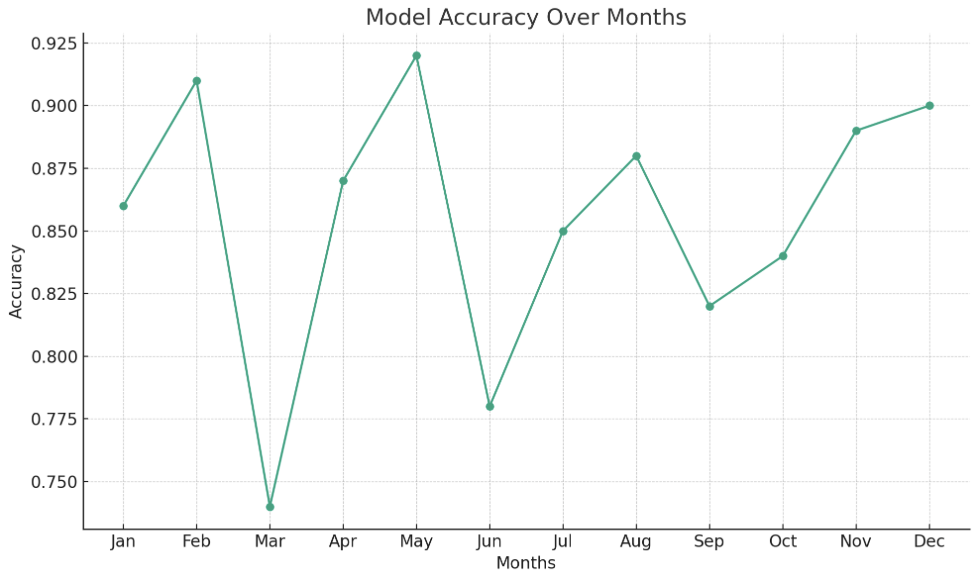
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# Sample data: Random accuracy values for 12 months months = ["Jan", "Feb", "Mar", ...] accuracies = [0.86, 0.91, 0.74, ...]plt.plot(months, accuracies, '-o') plt.title("Model Accuracy Over Months") plt.xlabel("Months") plt.ylabel("Accuracy") plt.show()
Visualization example
Logging
Recording of events
- Tracking variable values, Function calls
- Information that informs execution + performance
Monitoring helps track:
- Usage, Performance, Errors/anomalies
2023-08-04 09:15:20 [INFO] Model version 1.2.7 started2023-08-04 09:15:45 [INFO] Preprocessing input data for prediction2023-08-04 09:15:47 [DEBUG] Input data shape: (1, 12)2023-08-04 09:15:48 [INFO] Making prediction2023-08-04 09:15:50 [DEBUG] Output prediction: [0.78]...
Visualization examples
- Helpful metric for our model: balanced accuracy over time
- Spot trends, see if performance degrades
- See if retraining is necessary
- Choose helpful metrics for our use-case
Example:
- Balanced accuracy changes relative to expected, real-world rate
- Potentially indicative of problem
- Choose and evaluate
Let's practice!
End-to-End Machine Learning

