Logging experiments on MLFlow
End-to-End Machine Learning

Joshua Stapleton
Machine Learning Engineer
MLFlow
Without MLflow...
- Many untracked, disorganized experiment runs
- Dissimilar, or incomparable runs
- Unreproducible, lost runs
With MLflow...
- Tracked, organized experiment runs
- Comparison between standardized runs
- Reproducible runs
- Share, deploy models
Creating experiments
mlflow.set_experiment()
- Sets experiment name
- Provides workspace for experiment runs
Usage:
import mlflow
# Set an experiment name, which is a workspace for your runs
mlflow.set_experiment("Heart Disease Classification")
Running experiments
# Start a new run in this experiment with mlflow.start_run(): # Train a model, get the prediction accuracy logistic_model = LogisticRegression()# Log parameters, eg: mlflow.log_param("n_estimators", logistic_model.n_estimators)# Log metrics (accuracy in this case) mlflow.log_metric("accuracy", logistic_model.accuracy)# Print out metrics print("Model accuracy: %.3f" % accuracy)
Model accuracy: 0.96
Retrieving experiments
mlflow.get_run(run_id)
- Metadata for specific run
mlflow.search_runs()
- Returns DataFrame of metrics for multiple runs
Usage:
# Fetch the run data and print params
run_data = mlflow.get_run(run_id)
print(run_data.data.params)
print(run_data.data.metrics)
# Search all runs in experiment
exp_id = run_data.info.experiment_id
runs_df = mlflow.search_runs(exp_id)
{'epochs': '20', 'accuracy': 0.95}
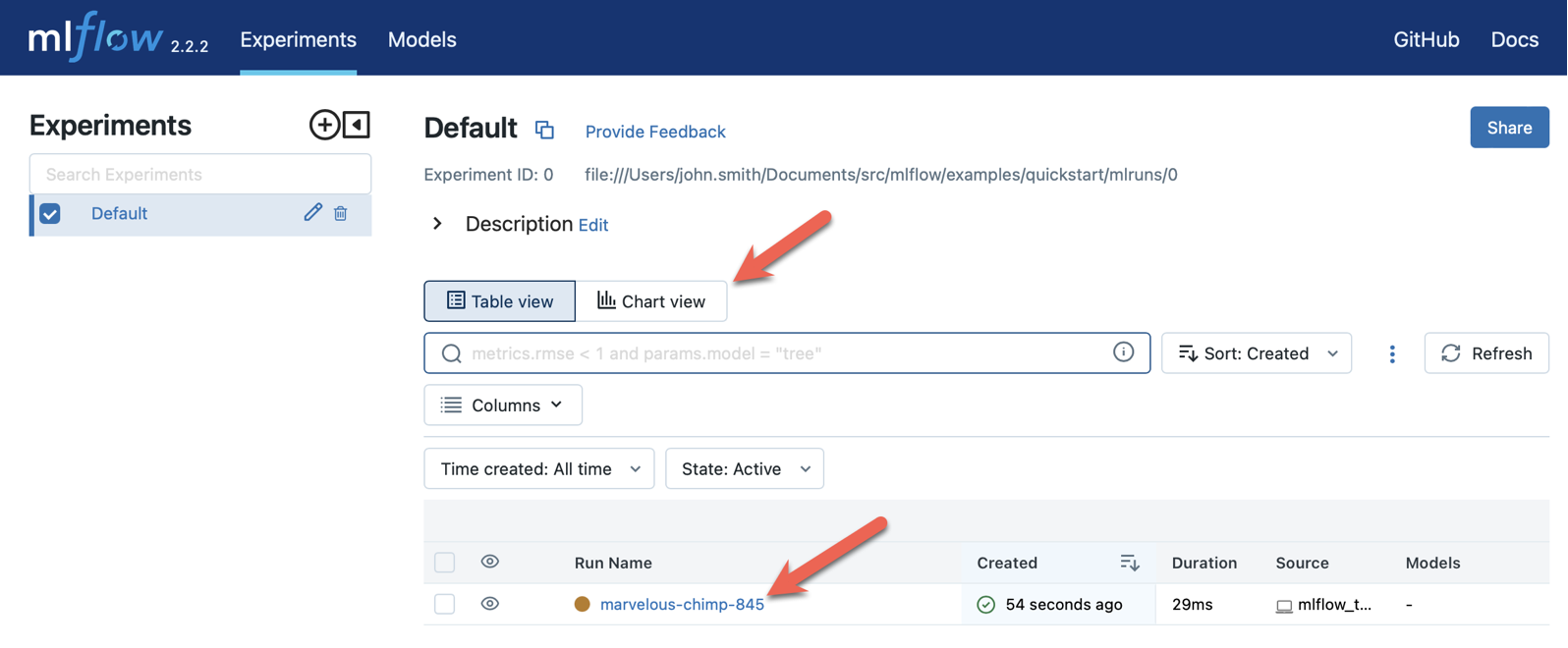
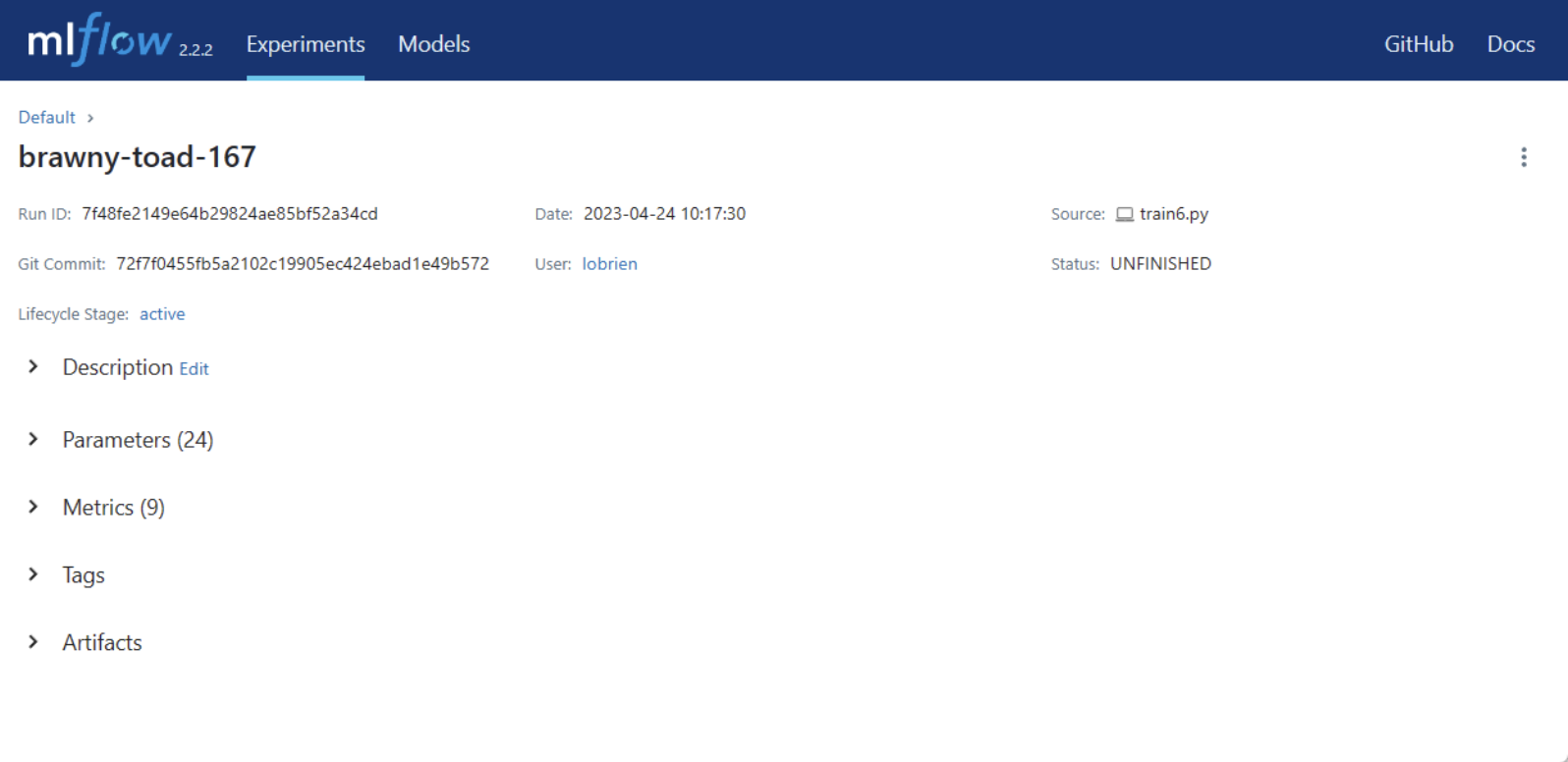
MLFlow UI
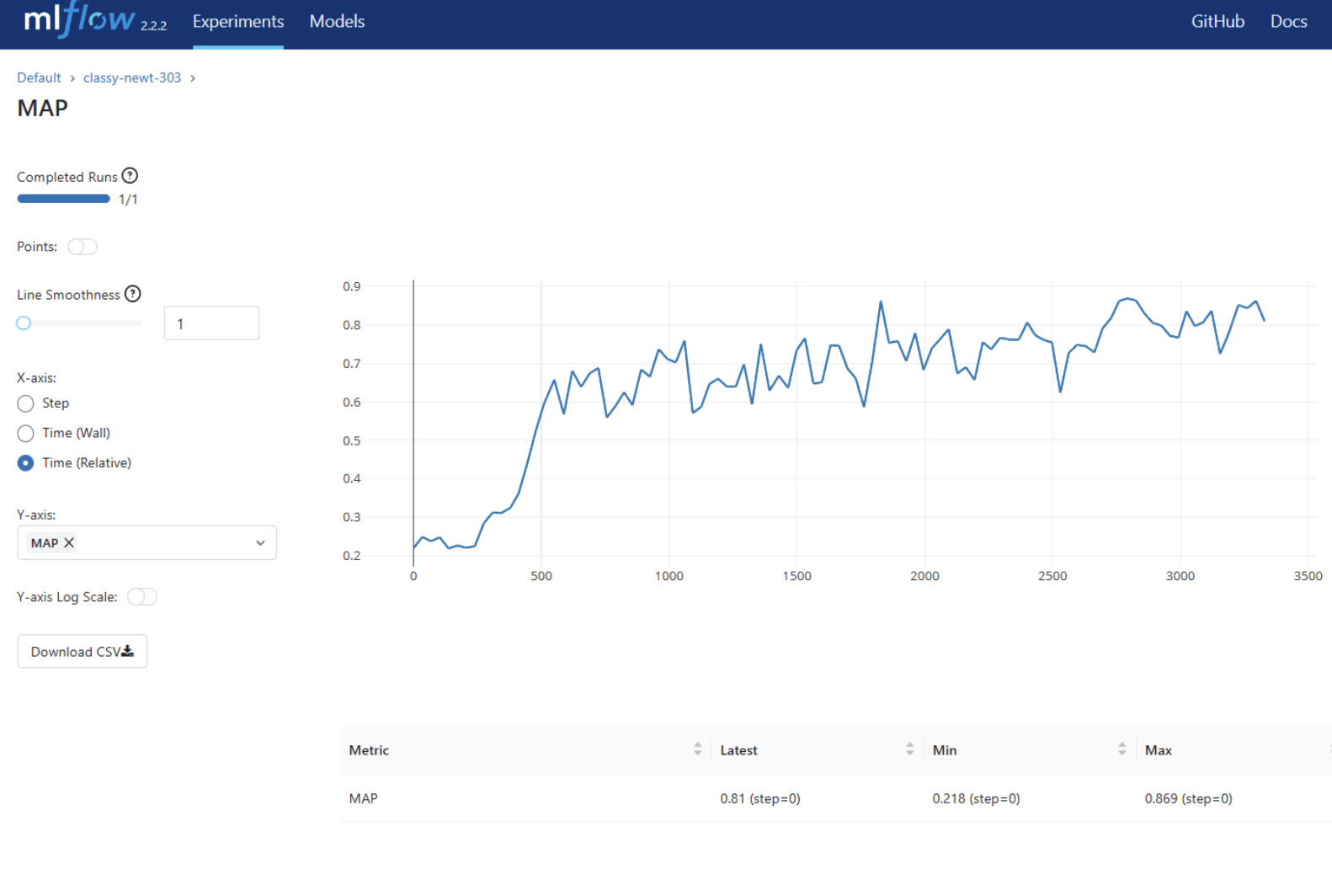
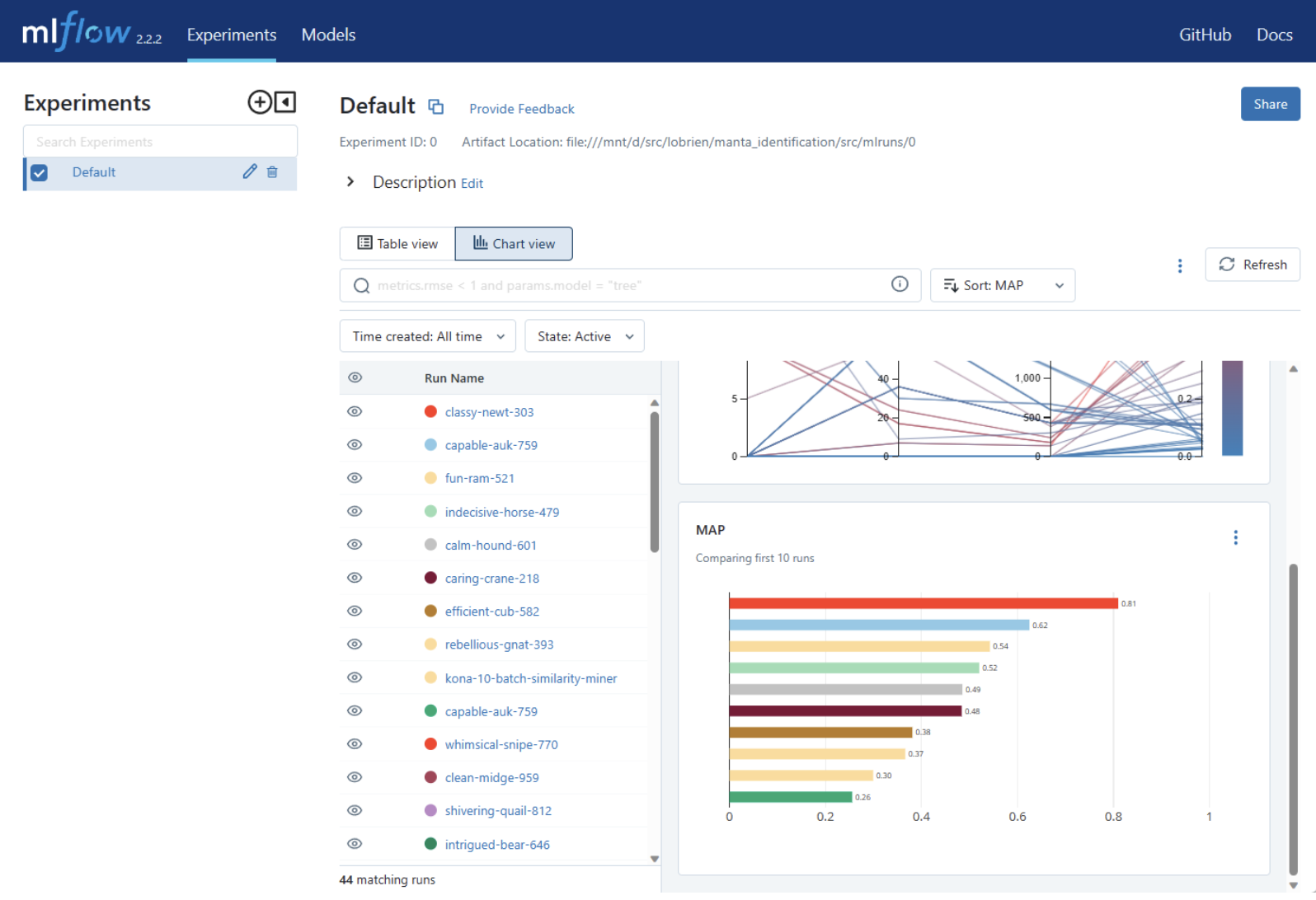
MLFlow UI (cont.)
MLflow resources
- Introduction to MLflow
- MLflow's official website

Let's practice!
End-to-End Machine Learning

