Date transformations and visualizations
Time Series Analysis in Tableau

Chris Hui
VP of Product, Tracked
Splitting up data in Tableau
Data can be encoded via delimiters that can be split apart into their own fields (e.g. AUS-001)
Tableau has two distinct splitting options: Split or Custom split
Split: separates the data based off the most common delimiter
Splitting up data in Tableau
Data can be encoded via delimiters that can be split apart into their own fields (e.g. AUS-001)
Tableau has two distinct splitting options: Split or Custom split
Split: separates the data based off the most common delimiter
| Cust Order Key | Split 1 | Split 2 | Split 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AA-B1-C1 | AA | B1 | C1 |
| AA-B2-C2 | AA | B2 | C2 |
| AA-B3-C3 | AA | B3 | C3 |
Splitting up data in Tableau
Data can be encoded via delimiters that can be split apart into their own fields (e.g. AUS-001)
Tableau has two distinct splitting options: Split or Custom split
Split: separates the data based off the most common delimiter
- Custom split: separates the data based off custom delimiters specified
| Cust Order Key | Split 1 | Split 2 | Split 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AA-B1-C1 | AA | B1 | C1 |
| AA-B2-C2 | AA | B2 | C2 |
| AA-B3-C3 | AA | B3 | C3 |
$$
| Cust Order Key | Split 1 | Split 2 | Split 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AA-B1-C1.DD | AA | B1 | C1.DD |
| AA-B2-C2.DD | AA | B2 | C2.DD |
| AA-B3-C3.DD | AA | B3 | C3.DD |
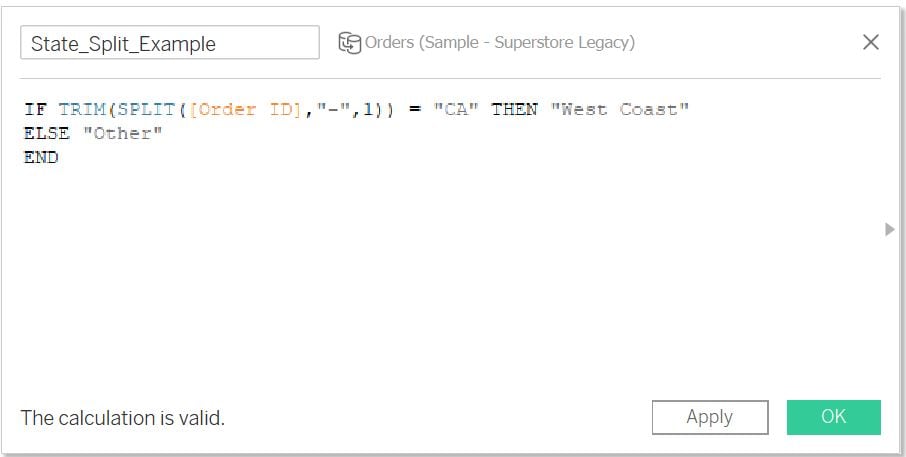
Calculated splits in Tableau
SPLIT()is helpful when you need to split up one or more delimiters in a textual fieldThe tokens (text) are returned either left to right (positive), or right to left (negative) dependent on position
Splitting functions are generally nested and combined with functions like:
IF()/TRIM()/CASE

Validating dates
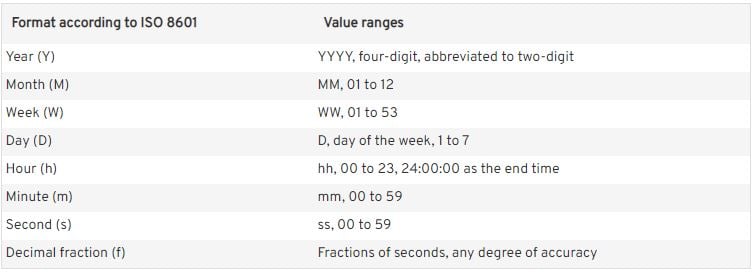
By design, Tableau adheres to and recognizes ISO-8601 and Standard Gregorian date formats
However dates can sometimes appear in a textual / string format
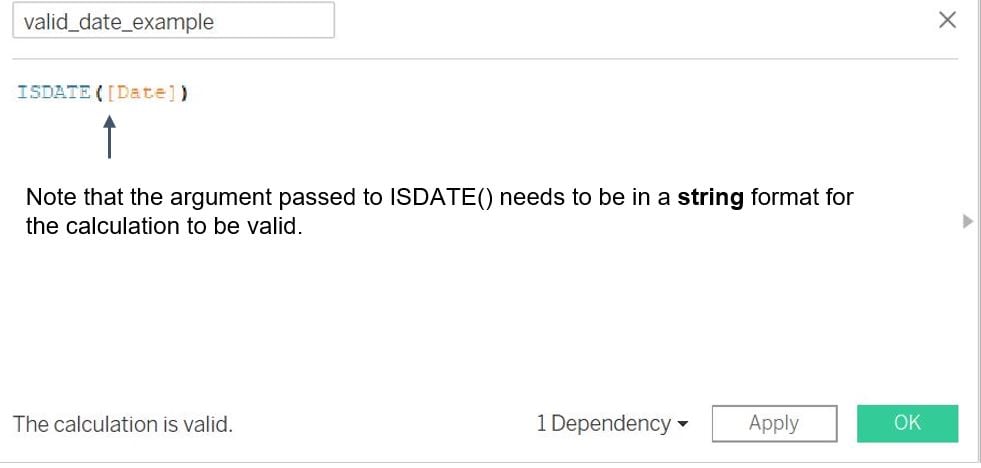
The
ISDATE()function can be utilized to return True for all entries recognized as dates and False otherwise
To parse or not to parse?
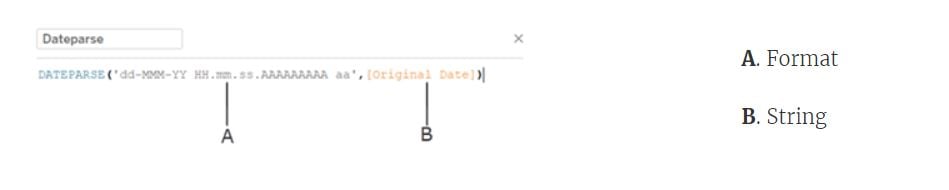
DATEPARSE()converts non-standard string fields to date time objects through explicit parsing of the date formatIt can be utilized for all date strings that are recognized as strings as opposed to dates
MM-YY-DD might makes sense to us, but not to Tableau, unless you specify this with
DATEPARSE()
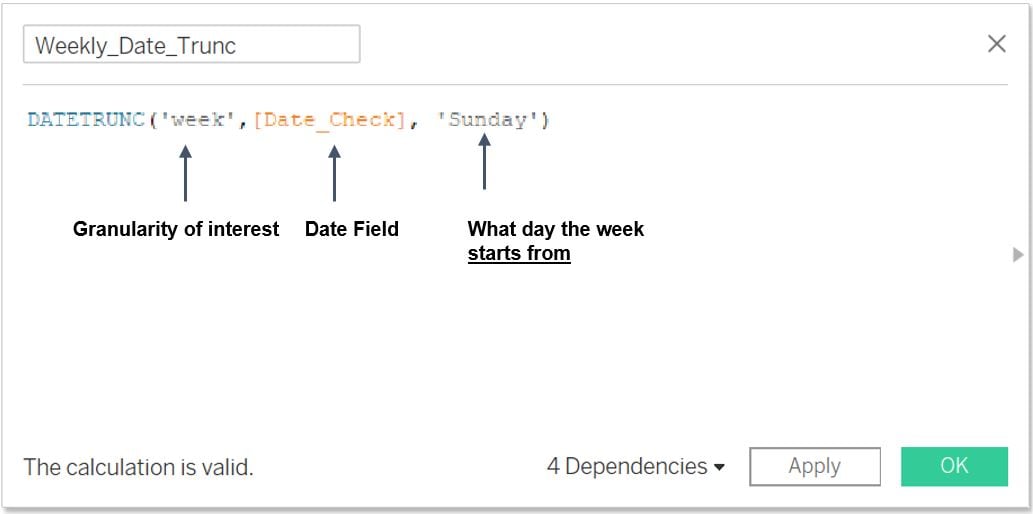
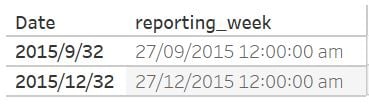
Cleansing with date truncation
ISDATE()andDATEPARSE()are useful to identify invalid dates, but not correcting these datesDATETRUNC()returns the lowest value for each date partition, dependent of the day specification (i.e. Week start on Monday)
DATETRUNC()is useful for verifying re-occurring reporting periods for errors (e.g. Weekly)
The dataset
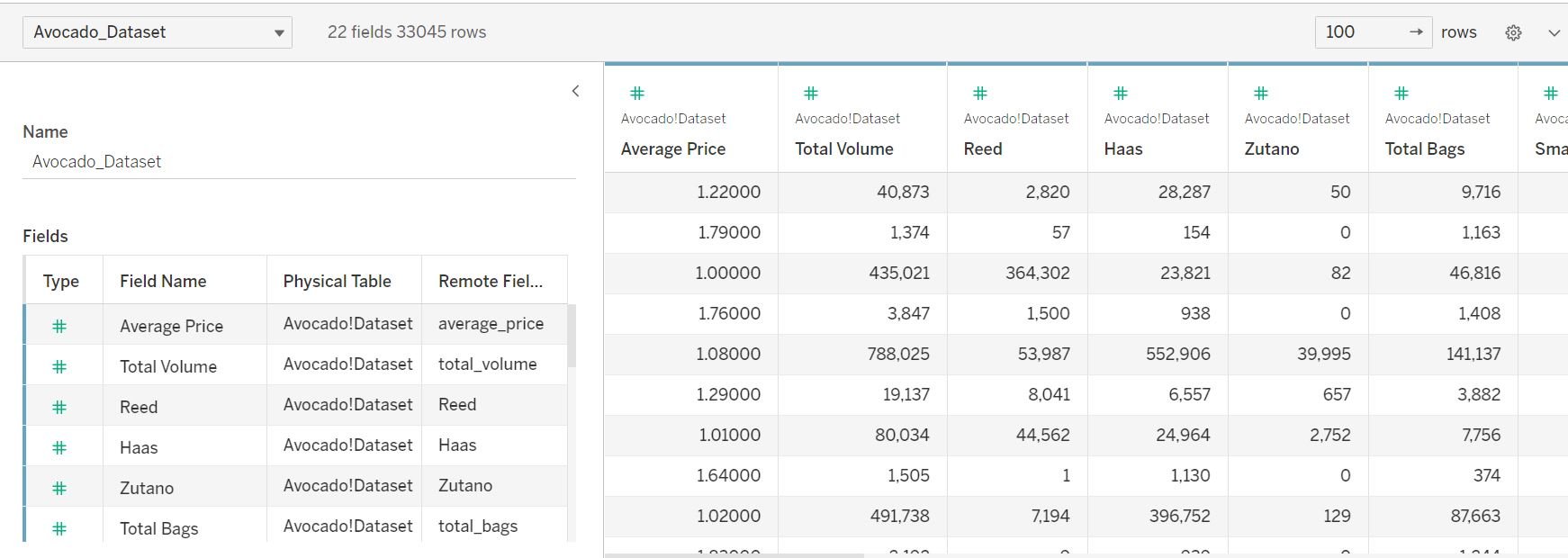
- Univariate and multivariate analysis of Avocado Varieties
- Seasonal variations and pricing distributions
- Trend analysis & percentiles

Let's practice!
Time Series Analysis in Tableau