Window functions in Tableau
Time Series Analysis in Tableau

Chris Hui
VP of Product, Tracked
What is a window?
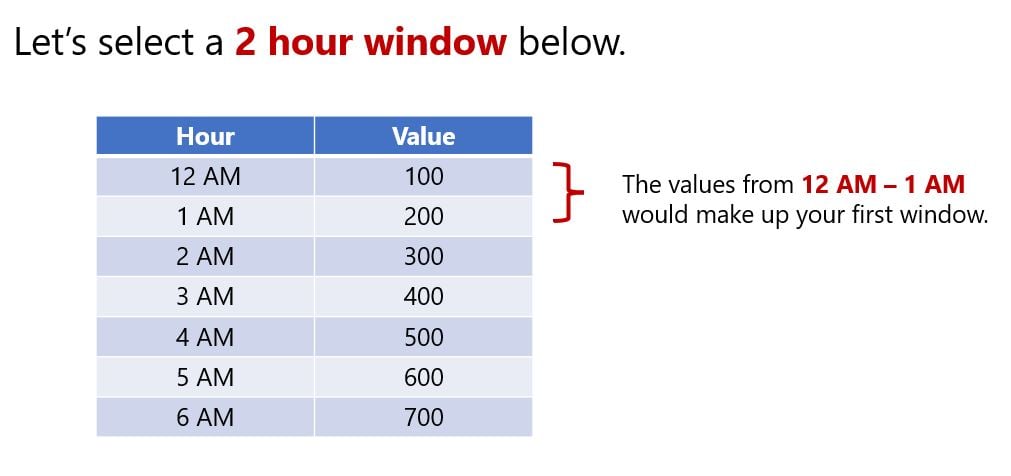
- Windows refer to specific partitions you want to analyze
- Used specifically as an argument for window functions
- Window size is determined based off the start window and end window
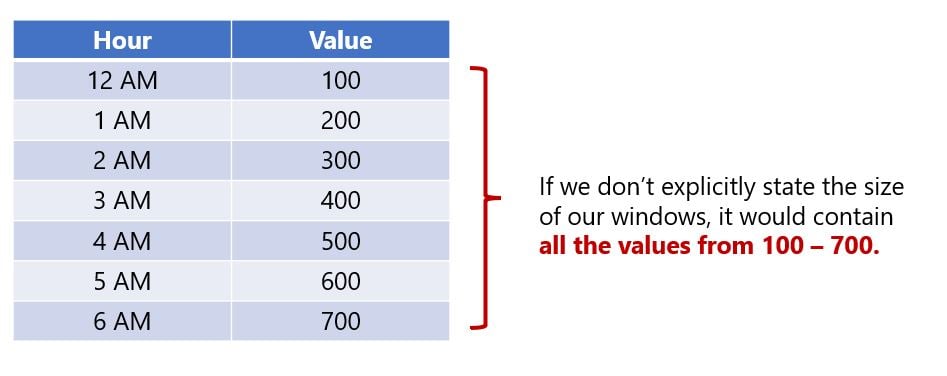
- Provided no start or end window is supplied, the entire measures range of values is treated as one window
What is a window function?
Known as moving calculations that smooth data over specified time windows
- Examples include: window sums, moving averages and moving standard deviations
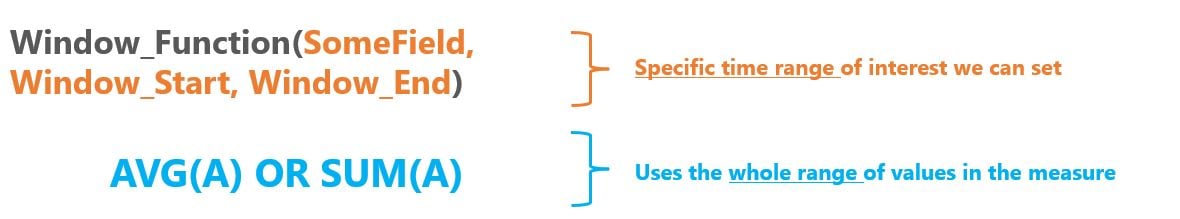
- Composed of a measure, start size, and end size
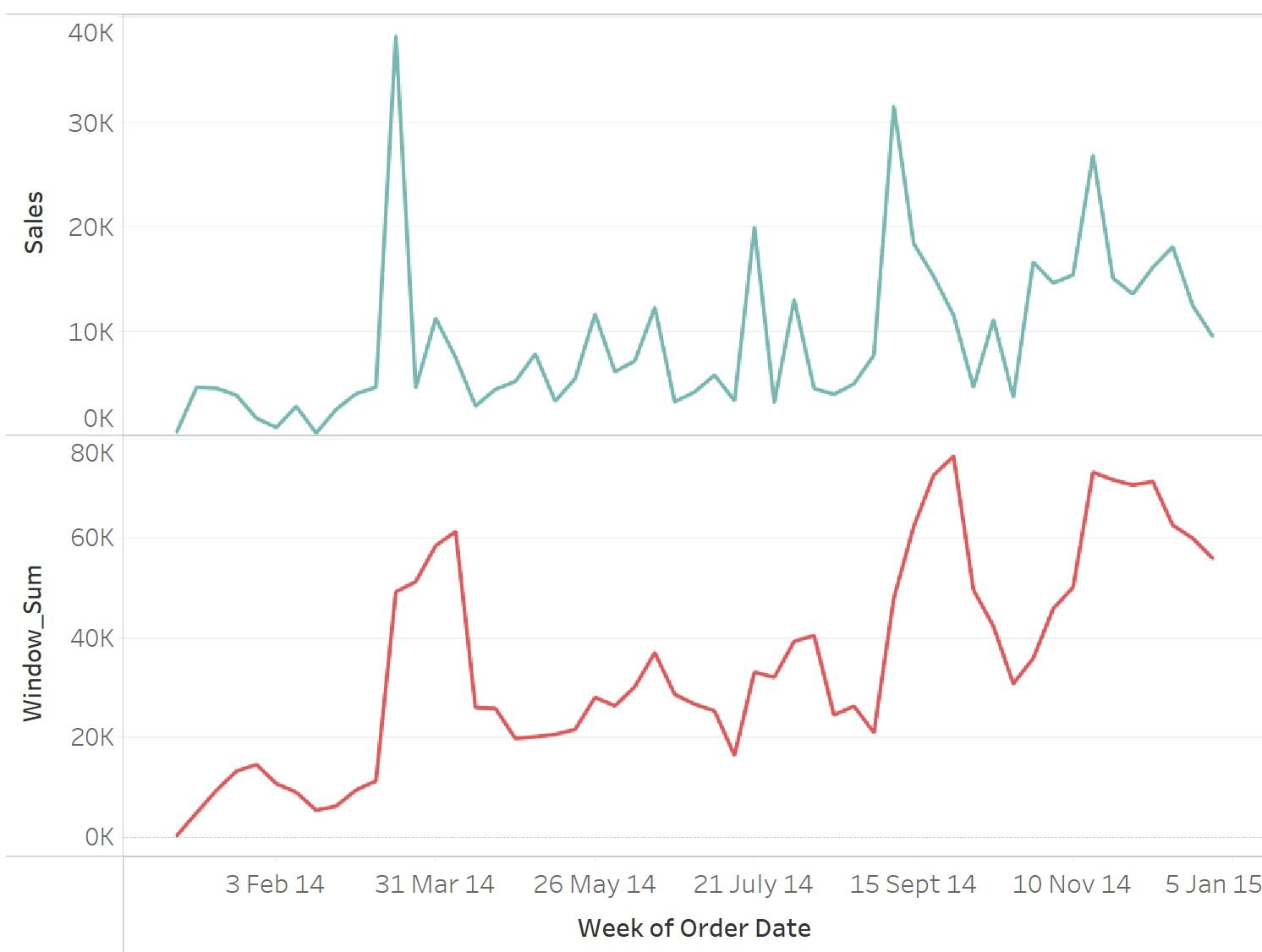
How does window sizing work?
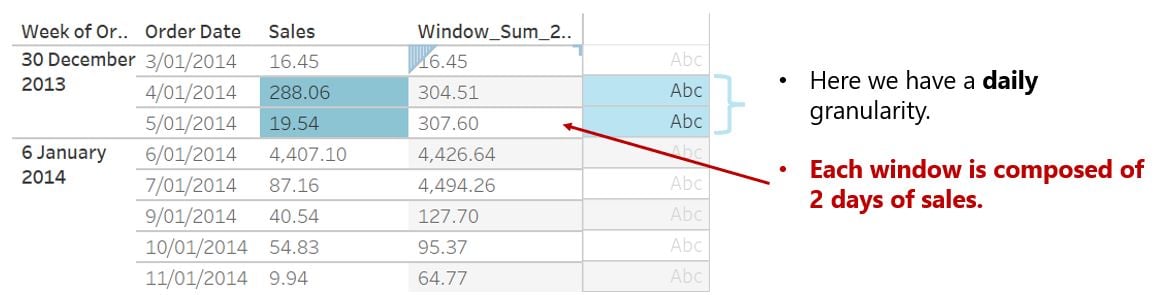
- Sizing of your window refers to the number of data points to be included
- Once the window sizing is set, it applies this for each subsequent row wise calculation
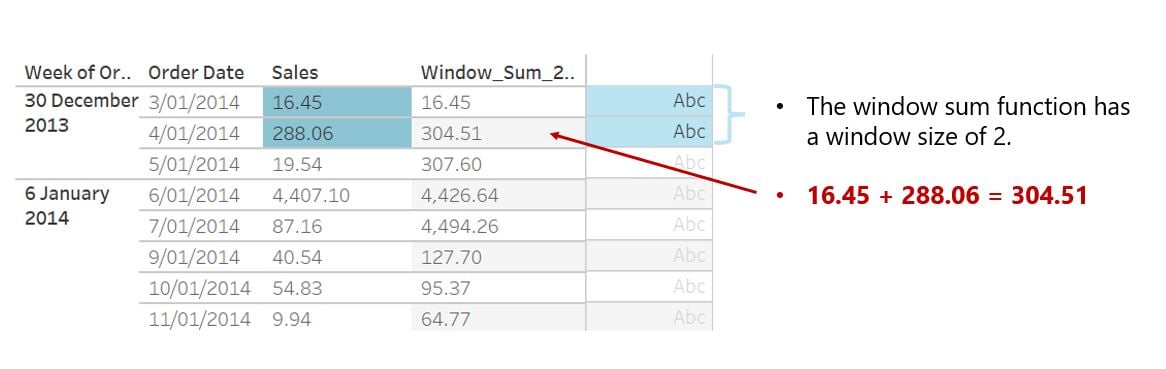
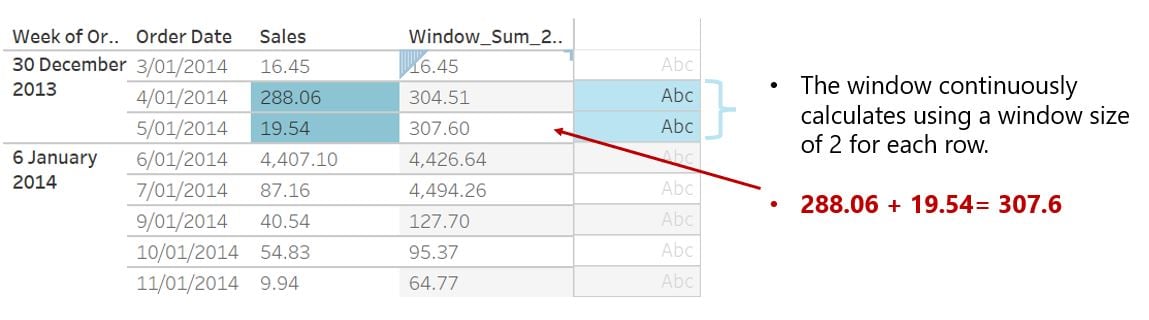
How does granularity impact window sizing?
- Granularity directly impacts the result of window aggregation function
- Aggregations are computed first, before window size
What's the purpose of a window function?
- Creates aggregate views of your data based on specific time windows
- Normal aggregation functions use the whole range of your data (i.e. no specification)
Example window functions:
WINDOW_SUM()WINDOW_AVG()WINDOW_STDEV()
WINDOW_CORR()WINDOW_MEDIAN()
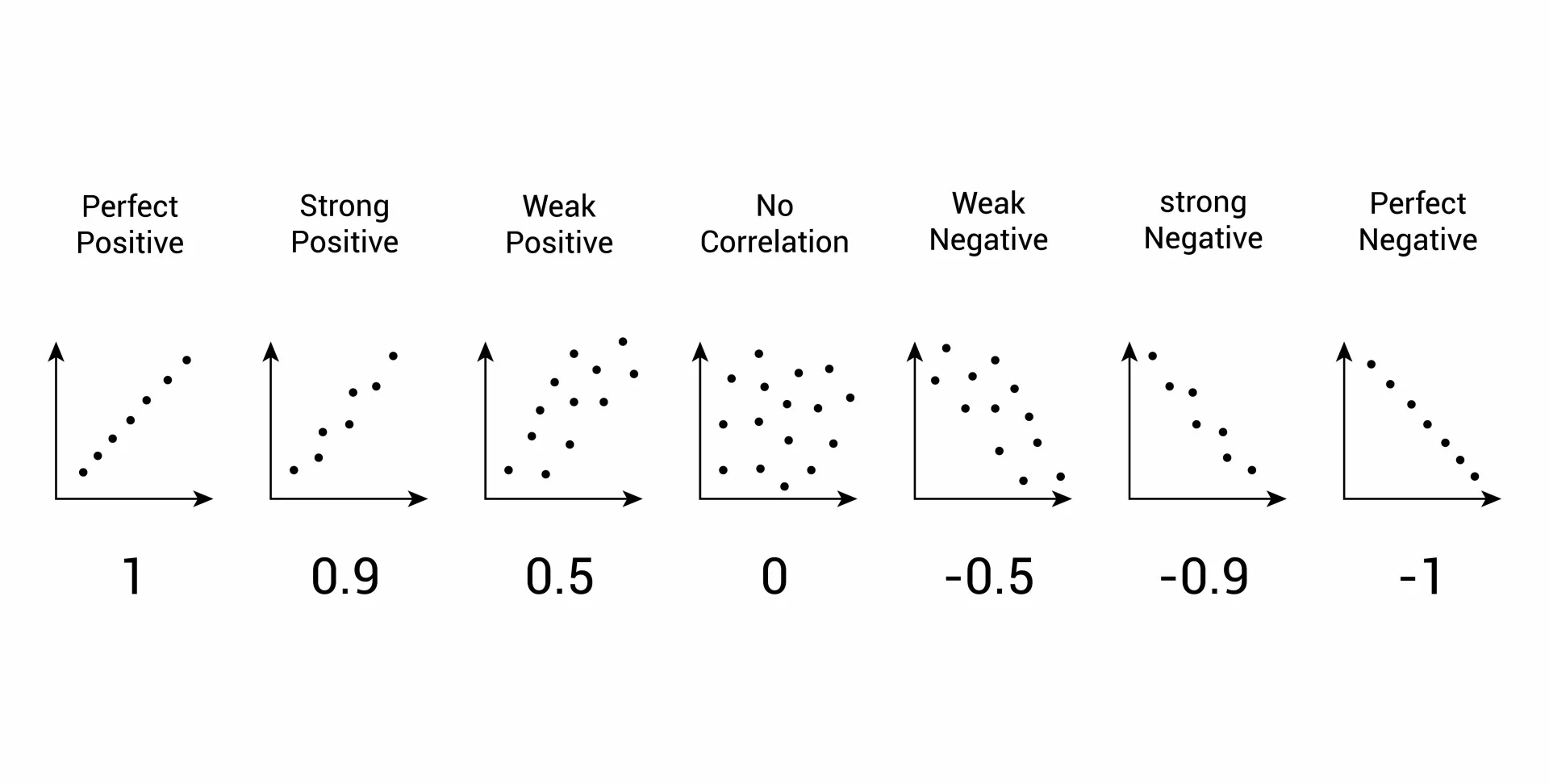
What's correlation?
Measures the extent to which two variables may be related
Correlation coefficient (r) measures the strength and direction of the relationship
Values range from -1 to 1
A positive value means that as one variable increase, the other also increases
Inversely, a negative direction means when one variable increases, the other decreases
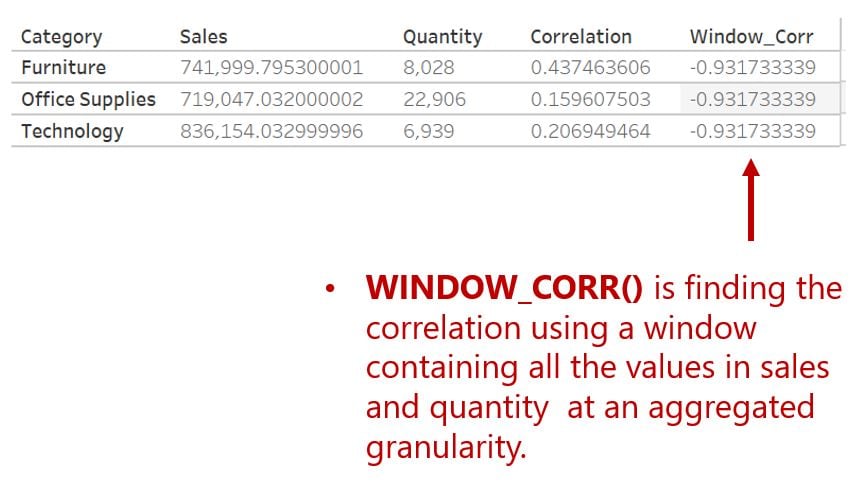
How do window correlations work?
Calculate the pearson correlation coefficient for the whole view between two aggregated variables
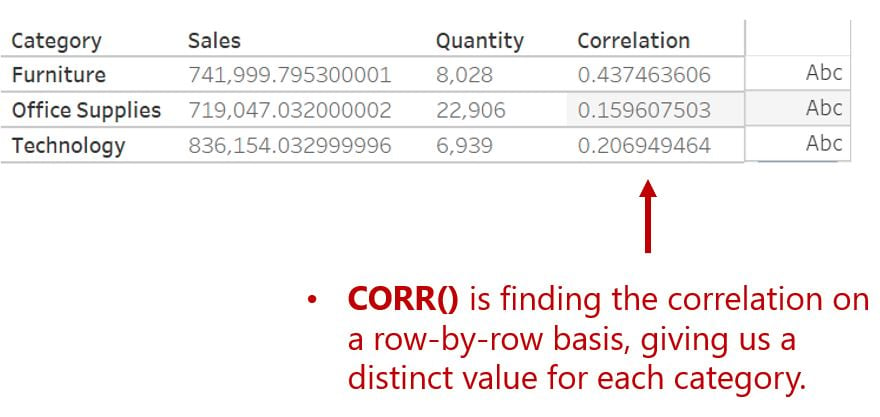
In contrast to the
CORR()function that requires non-aggregated variables
Introducing the dataset
- Analyzing water trading activity and the seasonal transactions that occur
- Time series techniques to identify abnormal pricing patterns:
- Moving averages
- Window correlations

1 https://theswaddle.com/water-is-now-a-traded-commodity-can-it-still-be-a-human-right-too/
Let's practice!
Time Series Analysis in Tableau