Date transformations and visualizations
Time Series Analysis in Tableau

Chris Hui
VP of Product, Tracked
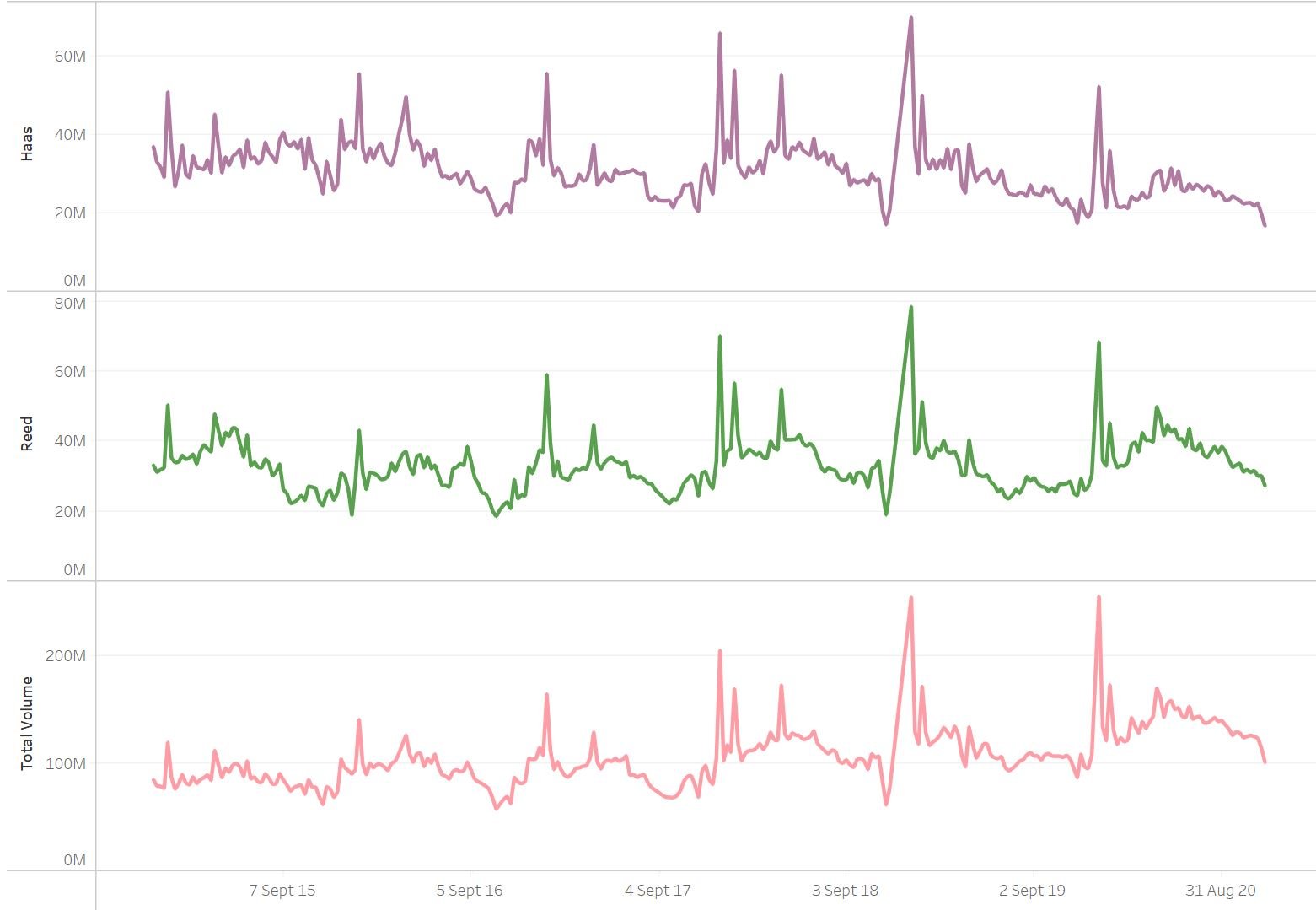
What's seasonality?
Seasonality is when time series data experiences regular and predictable changes that recur every calendar year
Examples include tourism or fruiting seasons that have variable prices based off timing
Seasonal behaviour allows business to effectively plan around peaks and troughs to optimize their business
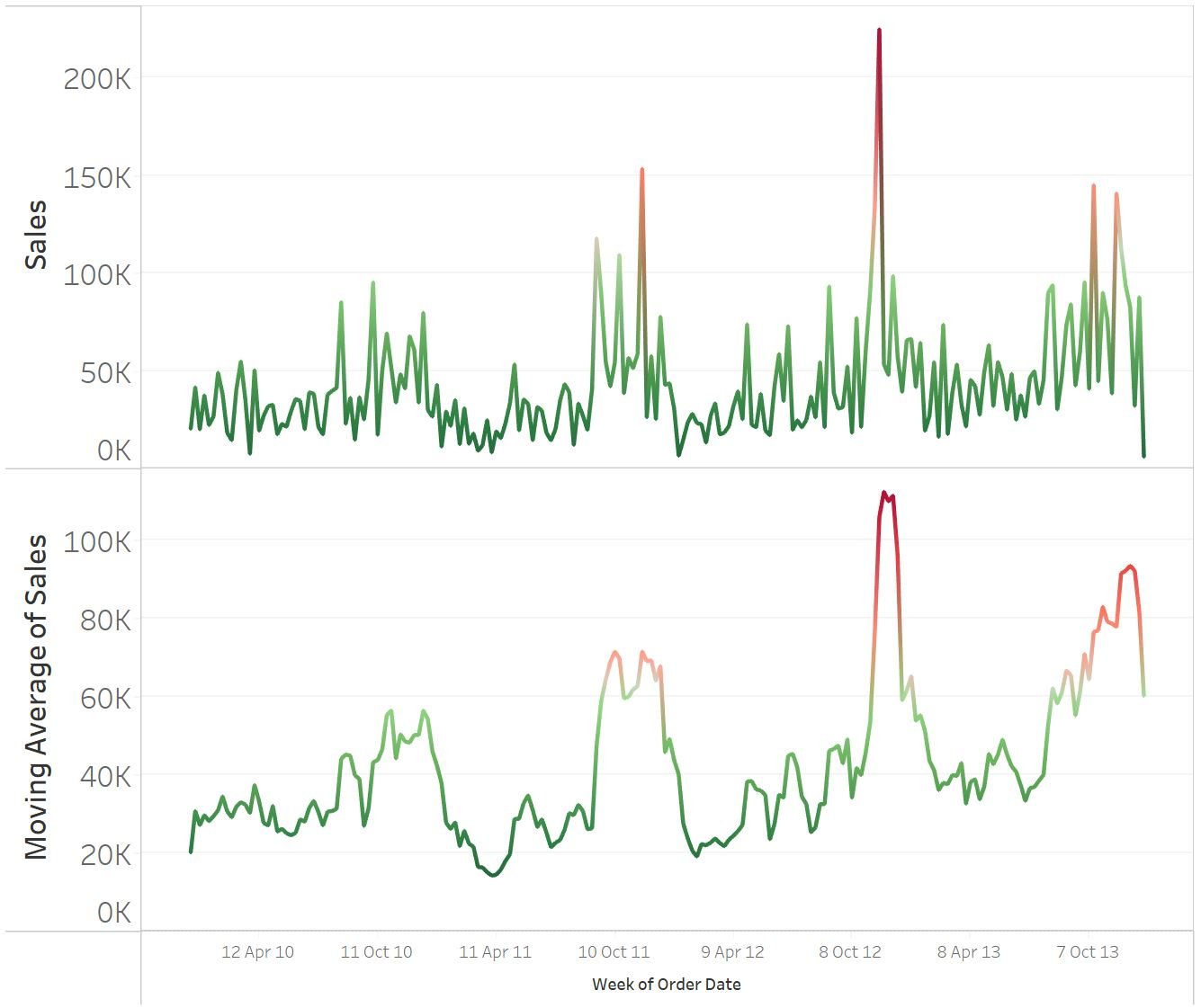
Treating seasonality with moving averages
Common methods to treat seasonality:
- Moving averages
- Technique to smooth out short term fluctuations (peaks/troughs) in the data over a specific time window
- Used to filter out noise while preserving the underlying signal
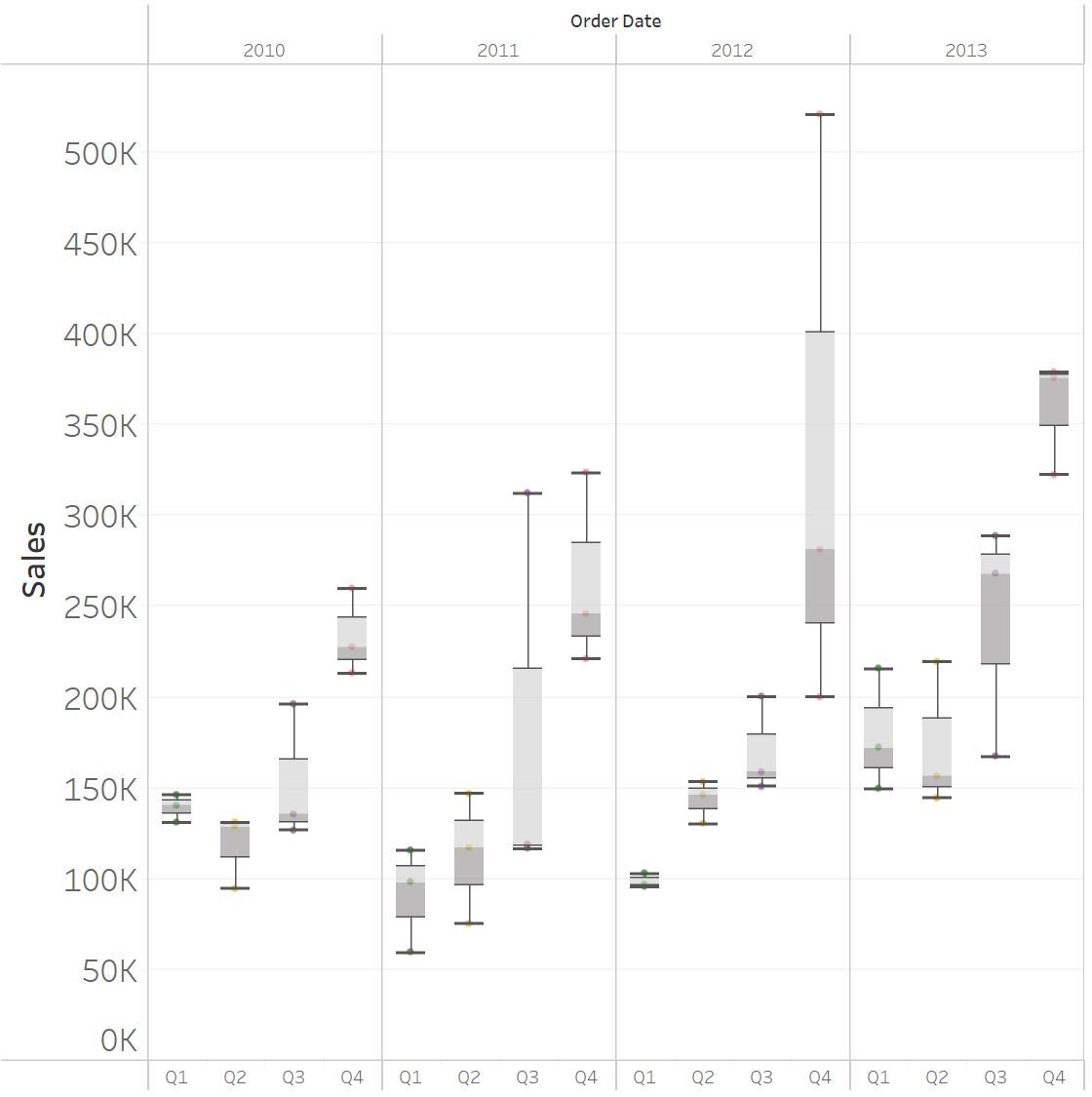
Identifying seasonality with seasonal boxplots
Common methods to identify seasonality:
- Seasonal boxplots (quarterly analysis)
- Segments the data quarterly to enable visualization of seasonal (quarterly) fluctuations
- Consistent volatility across quarters are an indicator of seasonal behavior
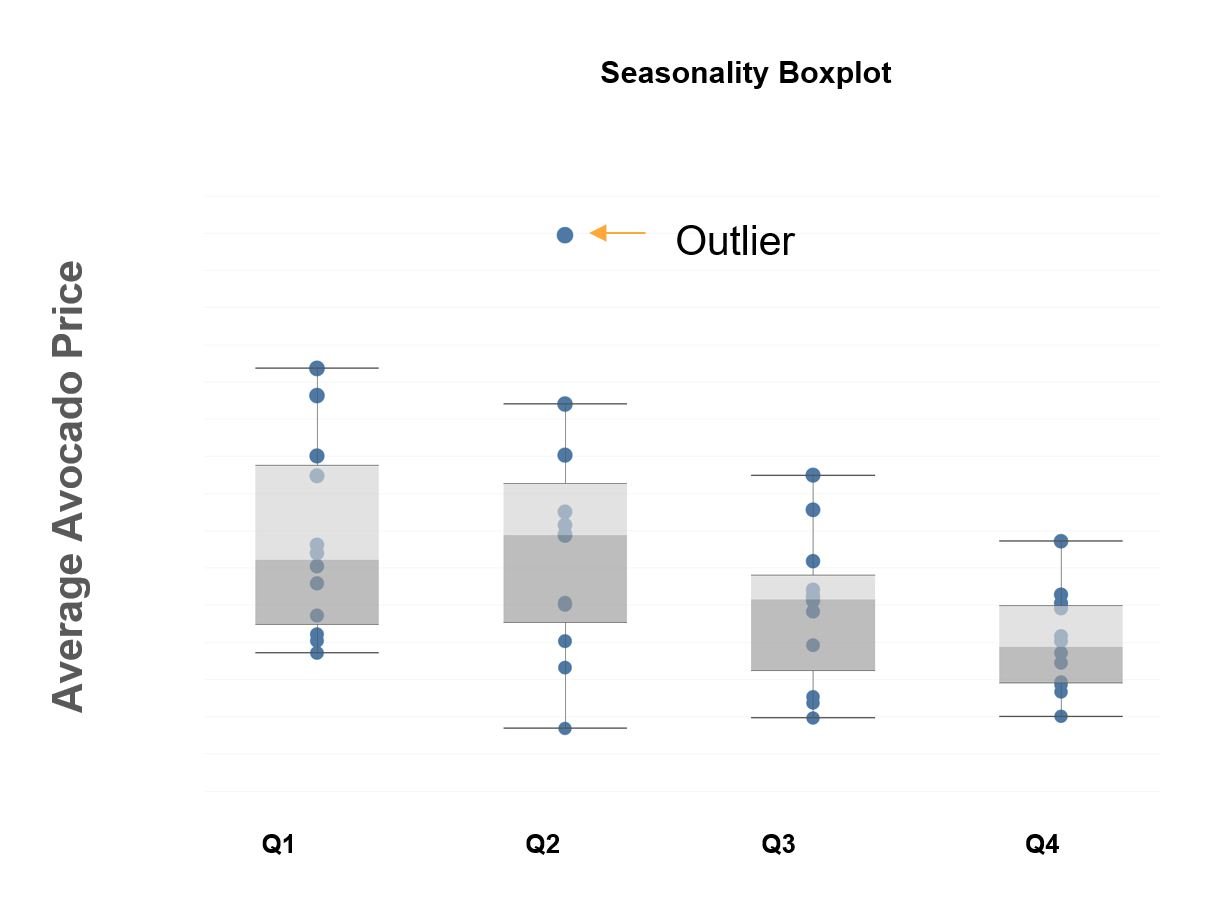
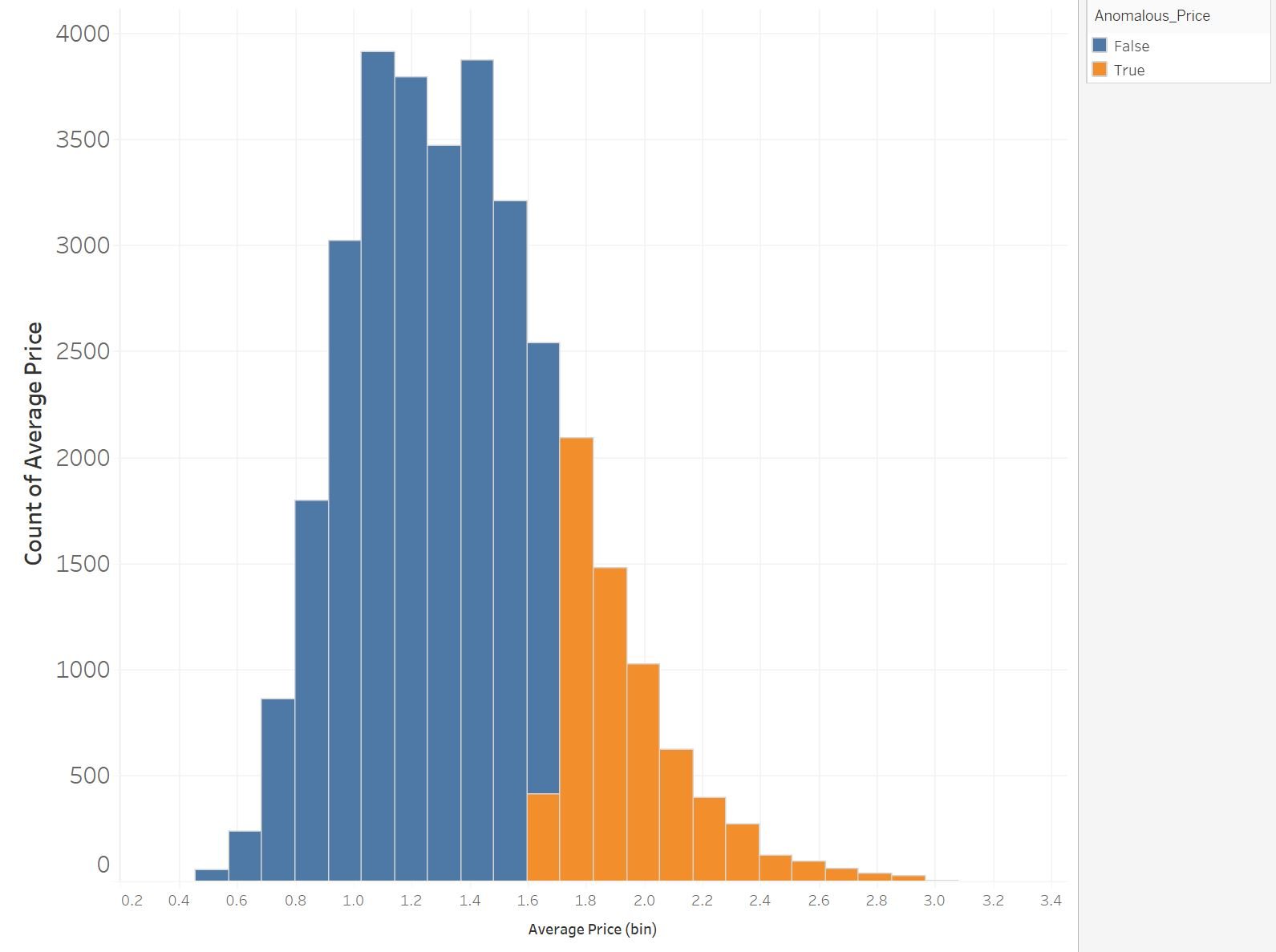
What's an anomaly?
Anomalous values (outliers), are values that deviate outside the normal distribution
Outliers can be considered to be:
- Any value outside +- 3 standard deviations away from the mean
- More than 1.5 x IQR below Q1 or more than 1.5 x IQR above Q3
(Standard deviation is a measure of how far any value is from the population mean)
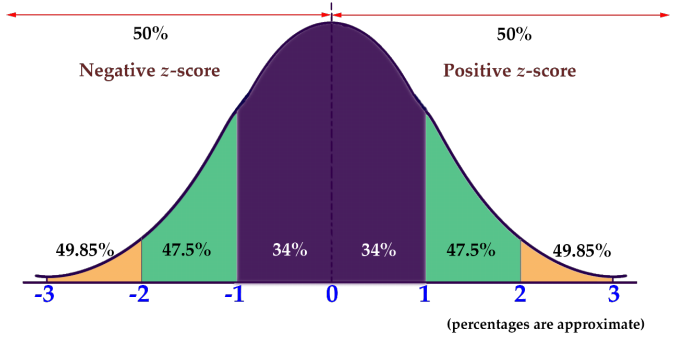
Z-score and the normal distribution
The Z-score is the number of standard deviations a given data point lies above or below mean
Z-scores within +-3 means ~99.7% of the population values lies within this range
Subsequently, any Z-score outside the +-3 range can be considered an outlier
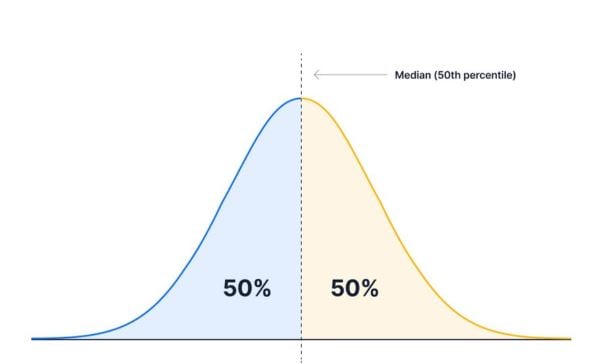
Unpacking percentiles in Tableau
- Percentiles determine where a value stands relative to other values
- Median (50th Percentile)
- Upper & Lower Quartiles (75th / 25th percentiles)
- Provides a flexible approach to outlier detection beyond the traditional Z-score methodology
Let's practice!
Time Series Analysis in Tableau