Data preparation for NannyML
Monitoring Machine Learning in Python

Hakim Elakhrass
Co-founder and CEO of NannyML
Loading the data
dataset_name = "green_taxi_dataset.csv"
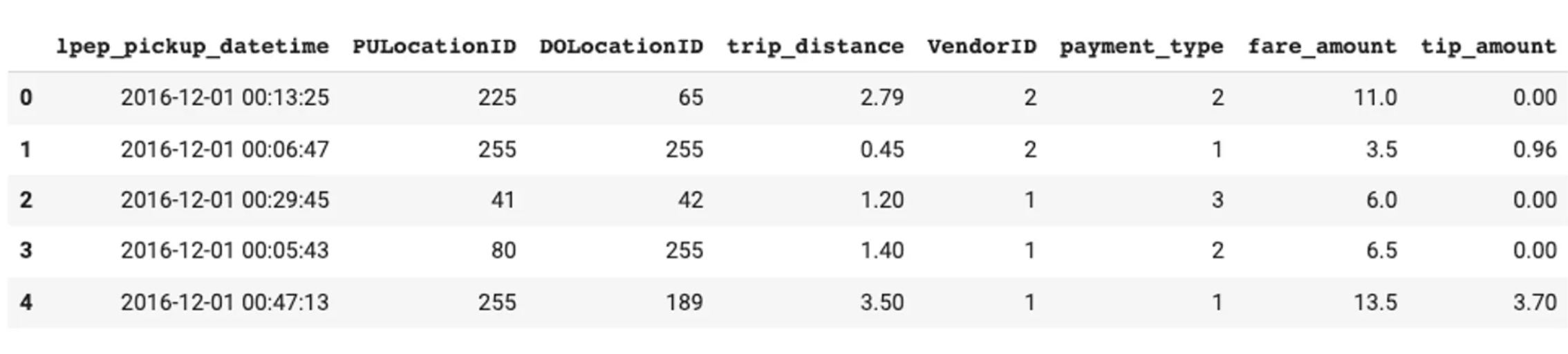
data = pd.read_csv(dataset_name)
data.head()
Processing the data
# Create data partition
data['partition'] = pd.cut(
data['lpep_pickup_datetime'],
bins= [pd.to_datetime('2016-12-01'),
pd.to_datetime('2016-12-08'),
pd.to_datetime('2016-12-16'),
pd.to_datetime('2017-01-01')],
right=False,
labels= ['train', 'test', 'prod']
)
Splitting the data
# Target column name
target = 'tip_amount'
# Features column name
features = ["PULocationID", "DOLocationID", "trip_distance", "VendorID", "pickup_time"]
# Train set
X_train = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'train', features]
y_train = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'train', target]
# Test set (later reference set)
X_test = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'test', features]
y_test = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'test', target]
# Production set (later analysis set)
X_prod = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'prod', features]
y_prod = data.loc[data['partition'] == 'prod', target]
Building the model
- Train
LGBMRegressorusinglightgbmlibrary - Evaluate the model on a test set
- Deploy the model
# Training the model
model = LGBMRegressor(random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Making predictions
y_pred_train = model.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = model.predict(X_test)
# Evaluating the model on train and test set
mae_train = MAE(y_train, y_pred_train)
mae_test = MAE(y_test, y_pred_test)
# Deploying the model to production
y_pred_prod = model.predict(X_prod)
Creating reference and analysis sets
Reference period
Uses a test set
Requires ground truth
Set the baseline performance
Analysis period
Latest production data
Ground truth is optional
NannyML analyzes the data drift and the performance
# Creating reference set
reference = X_test.copy() # Test set features
reference['y_pred'] = y_pred_test # Predictions
reference['tip_amount'] = y_test # Labels
reference = reference.join(
data['lpep_pickup_datetime']) # Timestamp
# Creating analysis set
analysis = X_prod.copy() # Production features
analysis['y_pred'] = y_pred_prod # Predictions
analysis = analysis.join(
data['lpep_pickup_datetime']) # Timestamp
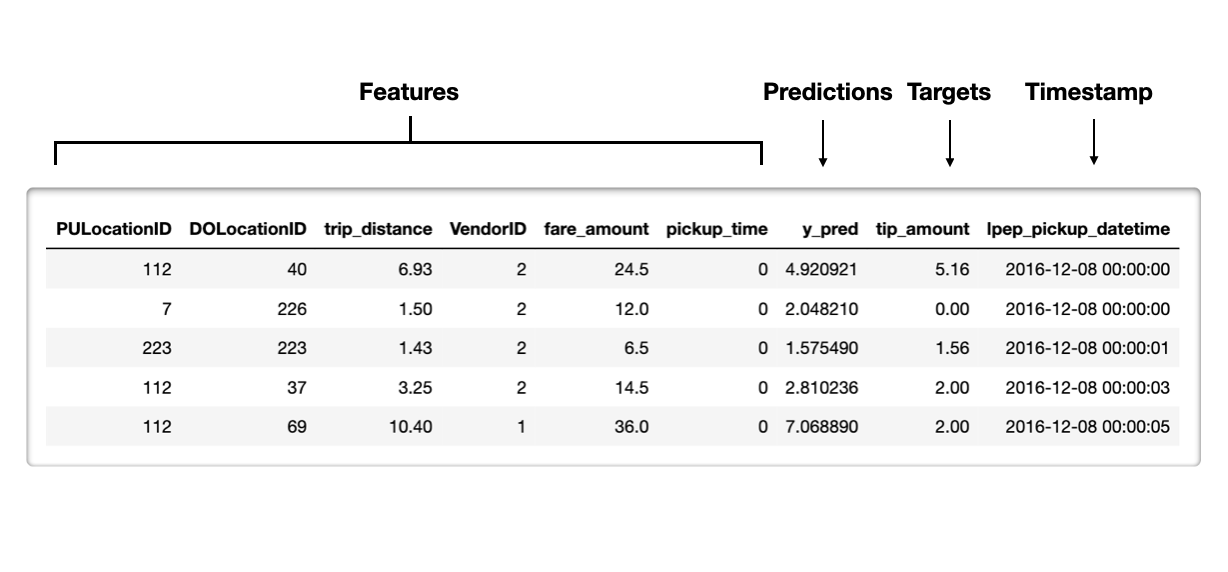
Reference set example
- Timestamp - the time when observation occurred (optional)
- Features - features fed to our model
- Model outputs
- Predictions - prediction score outputted by the model
- Prediction class labels - thresholded probability scores
- Target - contains ground truth
Let's practice!
Monitoring Machine Learning in Python

