Choosing the Right Approach
Introduction to Data Modeling in Snowflake

Nuno Rocha
Director of Engineering
Use cases for each modeling technique
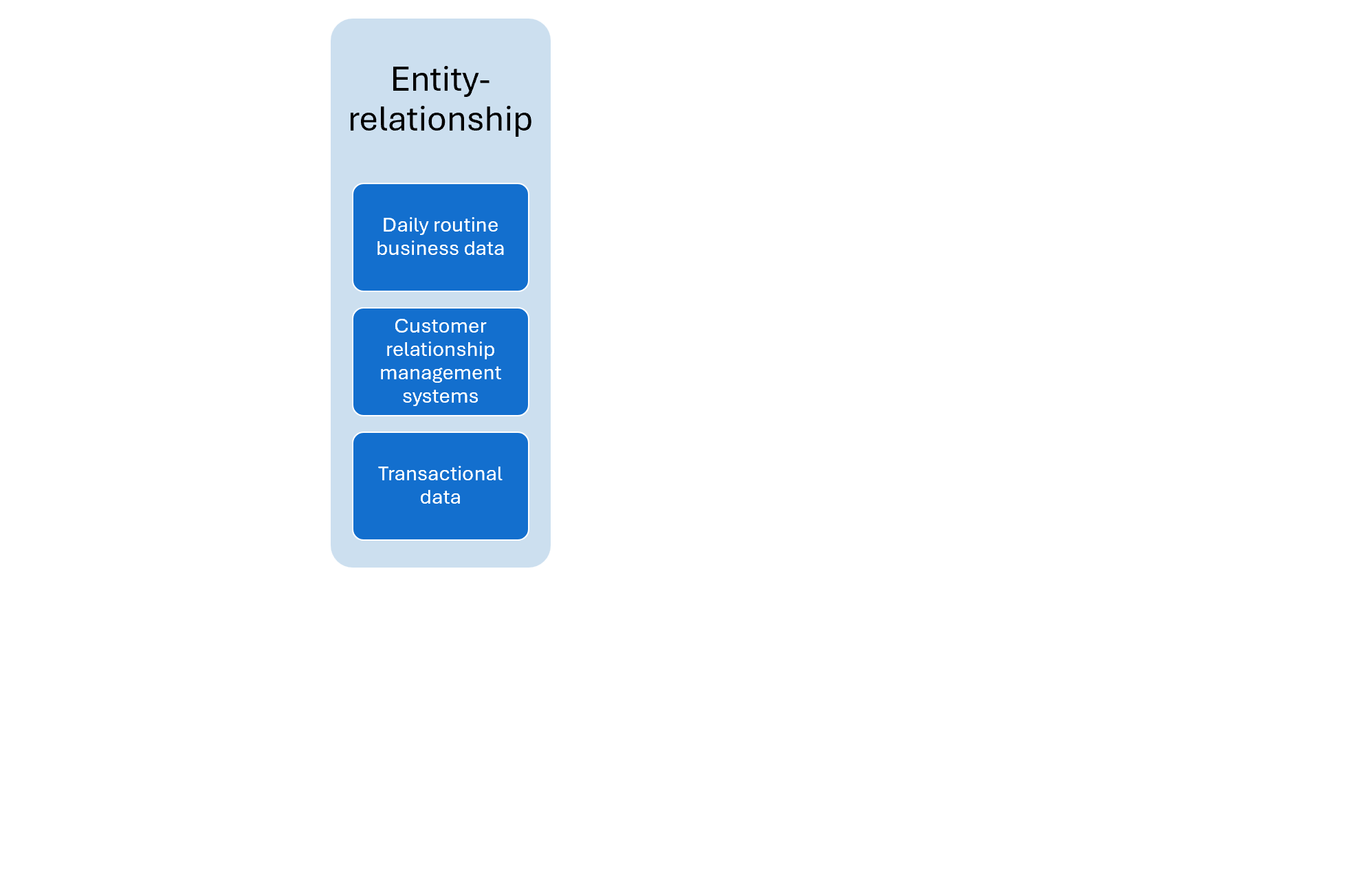
Use cases for each modeling technique (1)
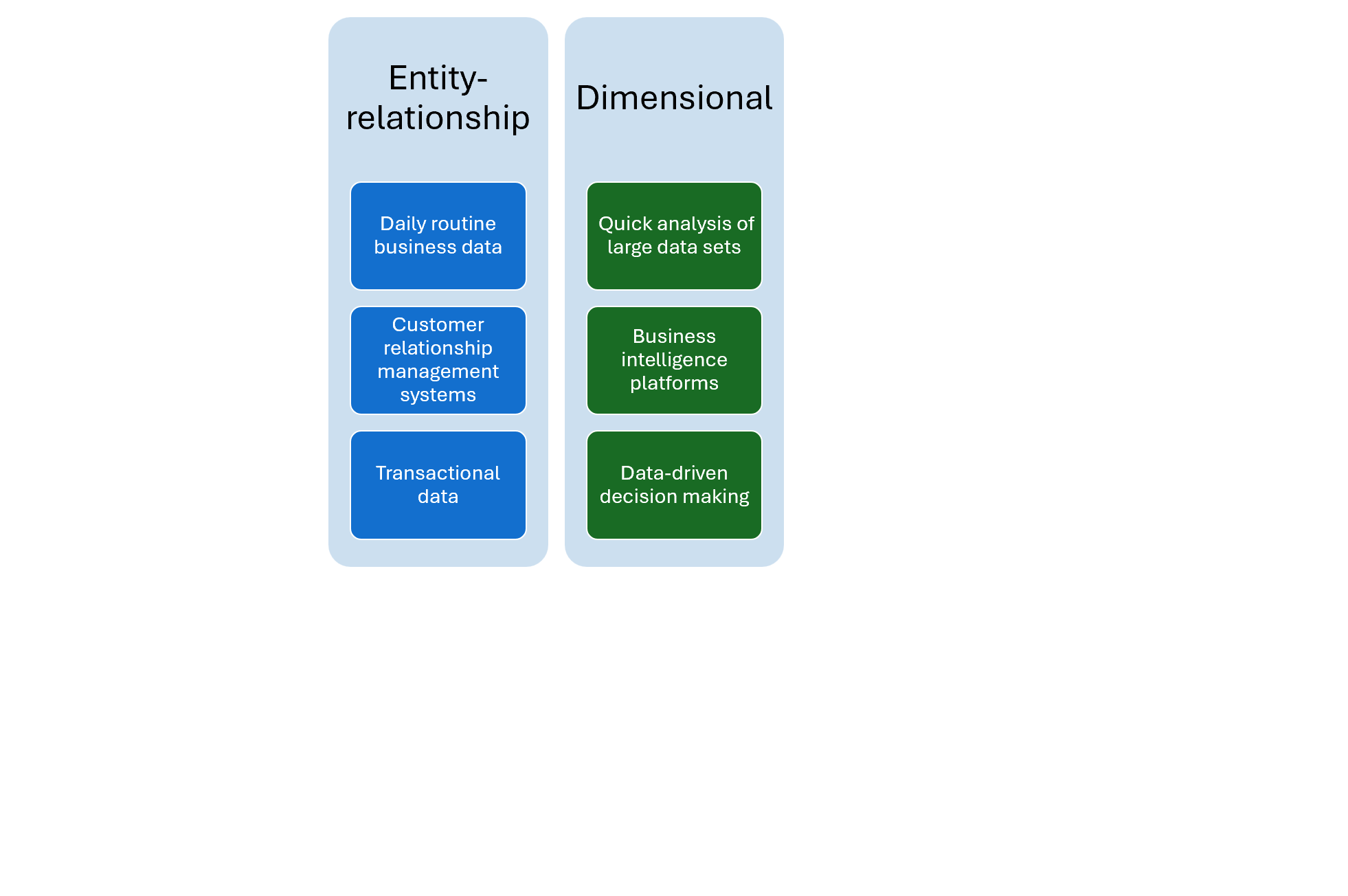
Use cases for each modeling technique (2)
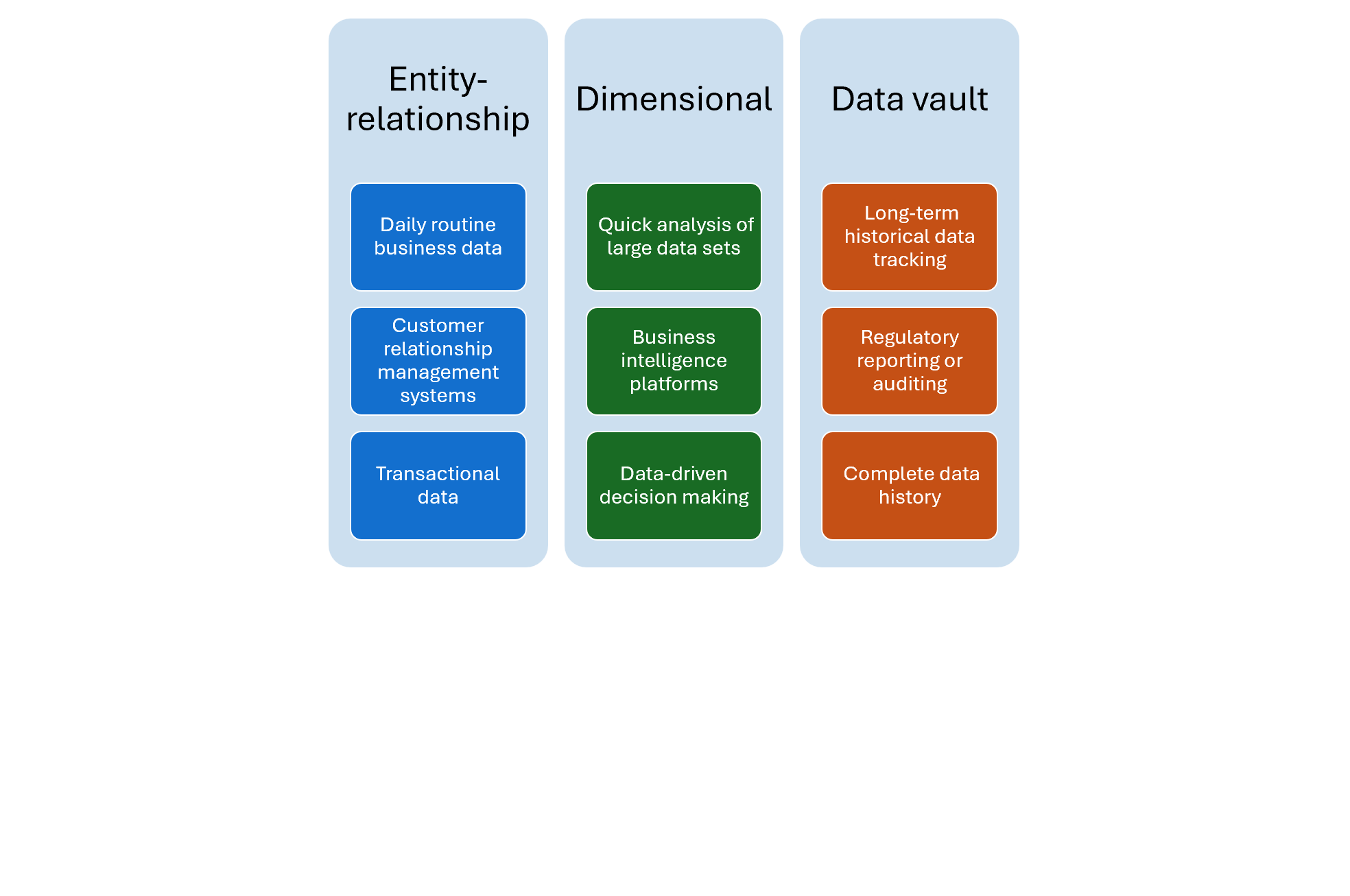
Technical considerations
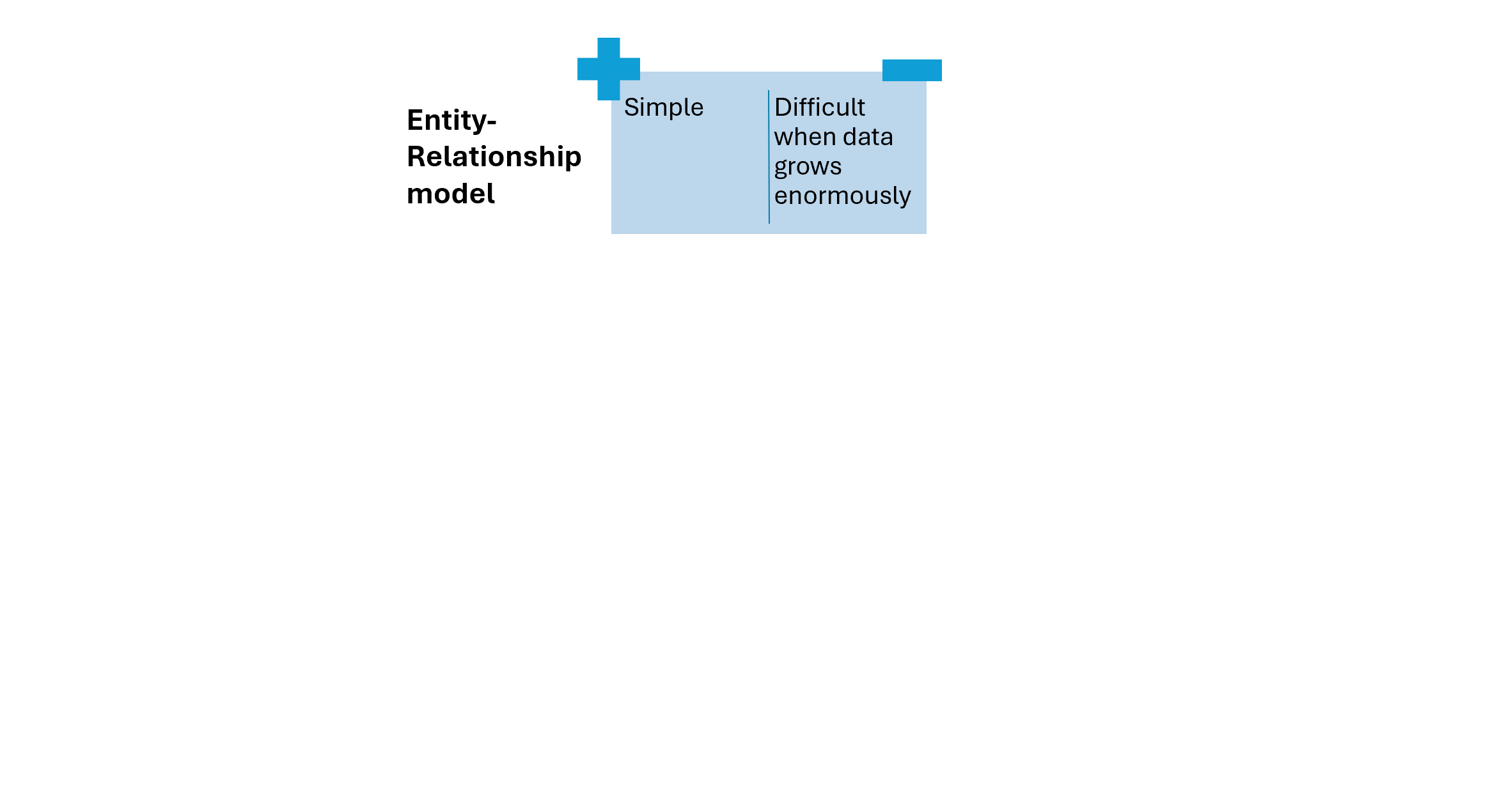
Technical considerations (1)
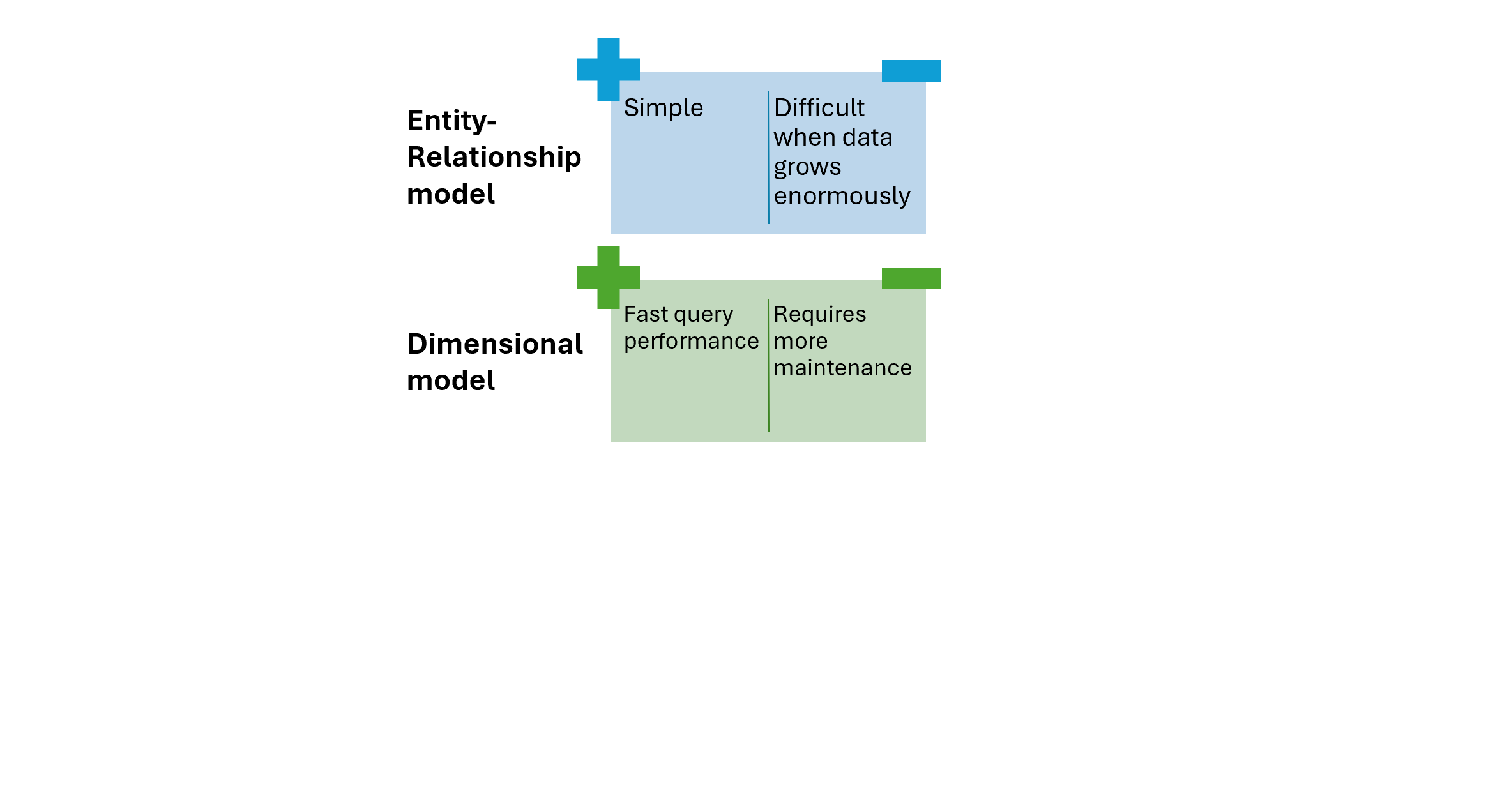
Technical considerations (2)
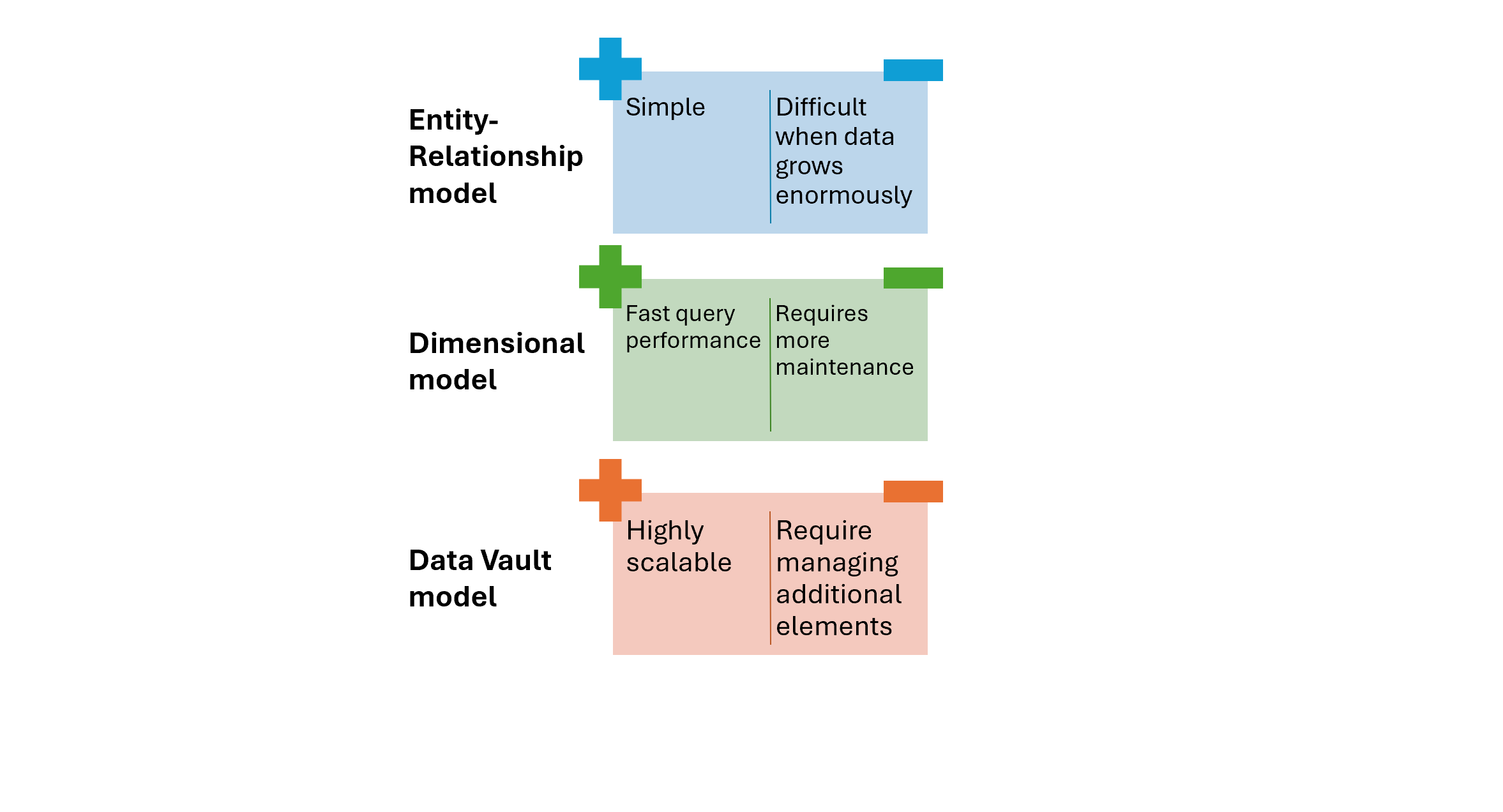
Data models in action
Data models in action (1)
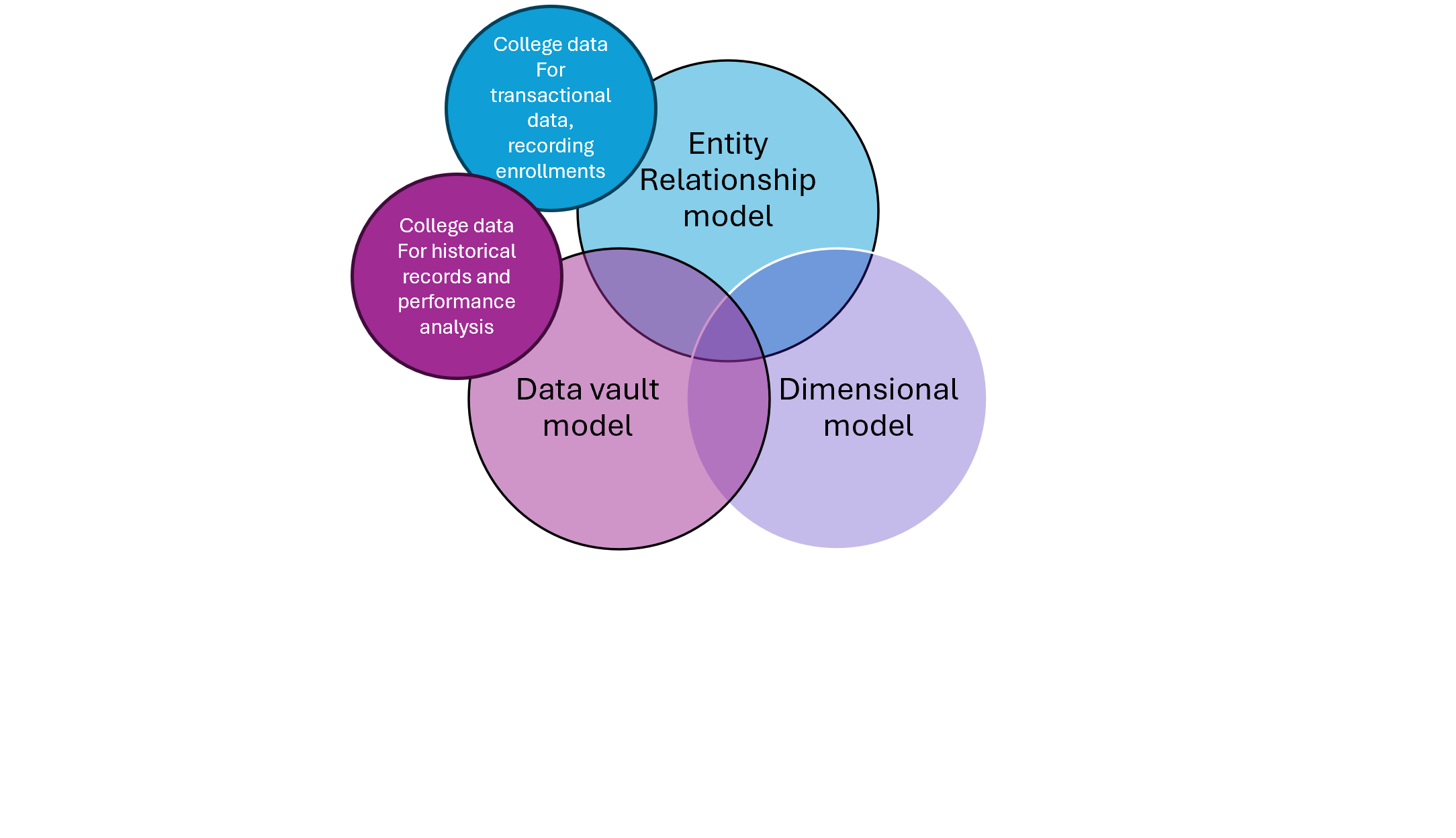
Retrieving data from the models
- Retrieve detailed data from students by referencing the hub entity and its satellite:
SELECT
hs.student_key,
ss.student_name
FROM hub_students AS hs
JOIN sat_student AS ss ON hs.student_key = ss.student_key;
Retrieving data from the models (1)
LEFT JOIN ON: SQL clause that combines all rows from the left entity with the matching rows from the right table, basedONa key
SELECT
hs.student_key,
ss.student_name
FROM hub_students AS hs
JOIN sat_student AS ss ON hs.student_key = ss.student_key
LEFT JOIN link_enrollment AS le ON hs.student_key = le.student_key
Retrieving data from the models (2)
COUNT: SQL aggregate function that returns the number of items in a group.GROUP BY: SQL clause to aggregate data that have the same values.
SELECT
hs.student_key,
ss.student_name,
COUNT(le.class_key) AS NumberOfEnrollments
FROM hub_students AS hs
JOIN sat_student AS ss ON hs.student_key = ss.student_key
LEFT JOIN link_enrollment AS le ON hs.student_key = le.student_key
GROUP BY hs.student_key,
ss.student_name
Retrieving data from the models (3)
MAX: SQL aggregate function that finds the highest value in a set of values for an attribute.
SELECT
hs.student_key,
ss.student_name,
COUNT(le.class_key) AS NumberOfEnrollments
MAX(sc.load_date) AS MostRecentEnrollmentDate
FROM hub_students hs
JOIN sat_student ss ON hs.student_key = ss.student_key
LEFT JOIN link_enrollment le ON hs.student_key = le.student_key
LEFT JOIN sat_class sc ON le.class_key = sc.class_key
GROUP BY hs.student_key,
ss.student_name;
Functions overview
SELECT FROM: SQL command to fetch columns from an entityJOIN ON: SQL clause combining rows from entities based ON a related attributeLEFT JOIN ON: SQL clause that combines all rows from the left entity with the matching rows from the right table, basedONa key. If there's no match, the result will still show the left entity rows with empty values for the right attributesCOUNT: SQL aggregate function that returns the number of items in a groupMAX: SQL aggregate function that finds the highest value in a set of values for an attributeGROUP BY: SQL clause to aggregate data that have the same values
Functions overview
SELECT column_name,
COUNT(another_column) AS alias_name,
MAX(other_column) AS alias_name
FROM table_name table_alias
-- Merge entities based on their keys
JOIN other_table AS other_alias
ON table_alias.FK = other_alias.PK
LEFT JOIN another_table AS another_alias
ON table_alias.FK = other_alias.PK
-- Aggregate data by specific columns
GROUP BY column_name;
Let's practice!
Introduction to Data Modeling in Snowflake

