Working with a forecast object
Designing Forecasting Pipelines for Production

Rami Krispin
Senior Manager, Data Science and Engineering
Work with a forecast object
- Data preparation
- Train and test multiple forecasting models
- Evaluate the models' performance
- The
statsforecastpackagemlforecastin the exercises
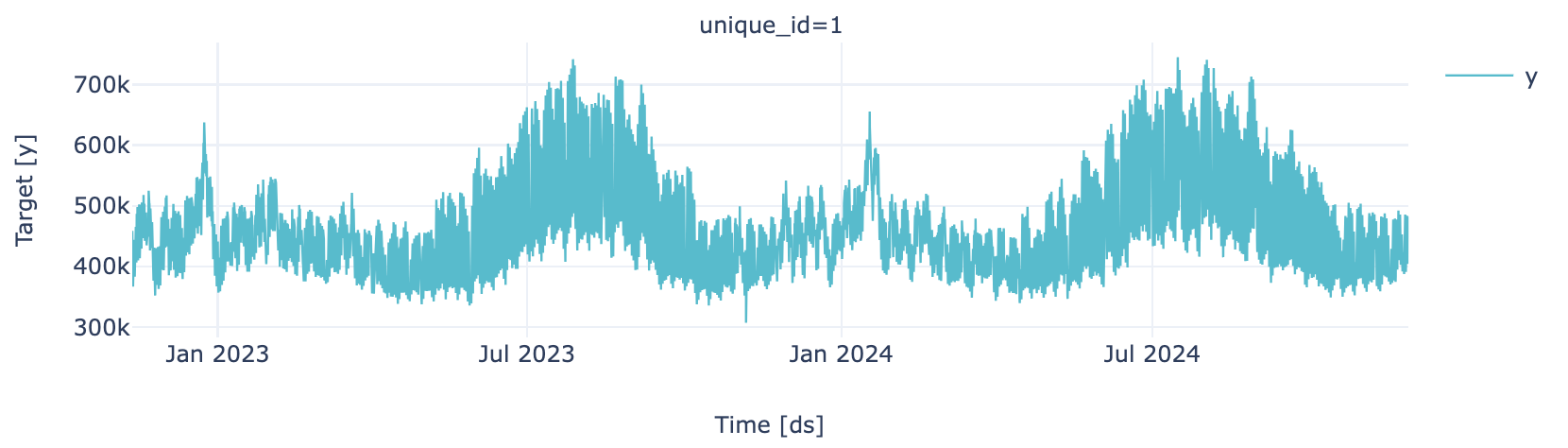
Training Partition
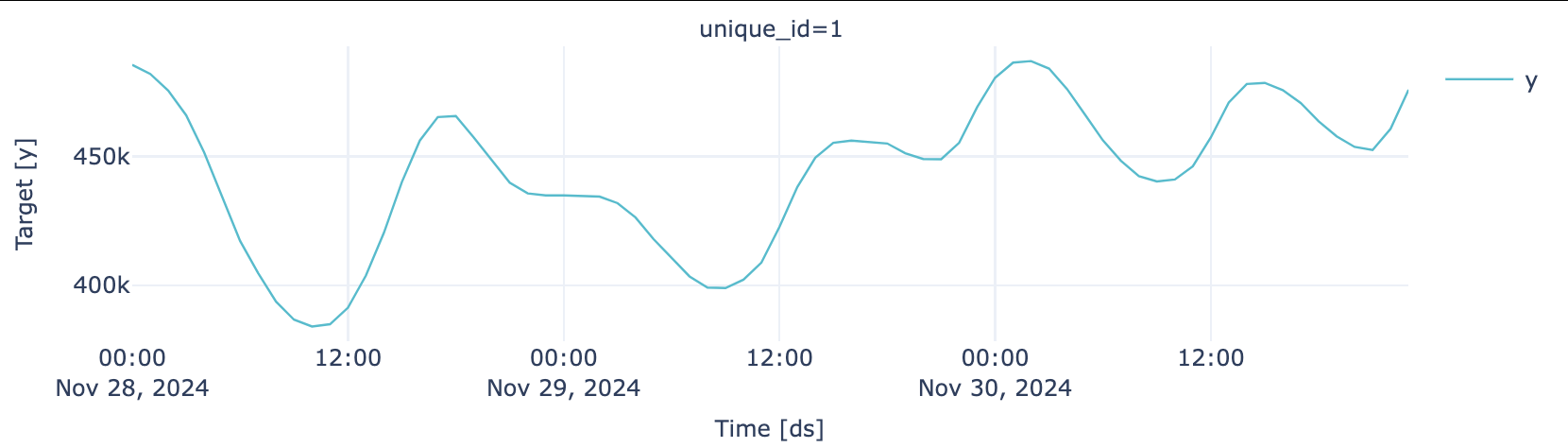
Testing Partition
Required libraries
import pandas as pd
import datetime
Required libraries
from statsforecast import StatsForecast
from statsforecast.models import (
DynamicOptimizedTheta,
SeasonalNaive,
AutoARIMA,
HoltWinters,
MSTL
)
from utilsforecast.plotting import plot_series
The statsforecast data format
Data input format:
unique_id- the series IDds- the series timestampy- the series values
Data preparation - data load
ts = pd.read_csv("data/data.csv")
ts["ds"] = pd.to_datetime(ts["ds"])
ts = ts.sort_values("ds")
ts = ts[["unique_id", "ds", "y"]]
os.environ['NIXTLA_ID_AS_COL'] = '1'
unique_id ds y
0 1 2022-11-11 23:00:00 456403
1 1 2022-11-12 00:00:00 458842
2 1 2022-11-12 01:00:00 455111
3 1 2022-11-12 02:00:00 448035
4 1 2022-11-12 03:00:00 438165
Data preparation - train/test split
- Split the time series into training and testing partitions
- using
datetime.timedelta - leave last 72 hours as test data
- using
test_length = 72
train_end = end - datetime.timedelta(hours = test_length)
train = ts[ts["ds"] <= train_end]
test = ts[ts["ds"] > train_end]
Data preparation
plot_series(train, engine = "plotly")

plot_series(test, engine = "plotly")

Forecasting with StatsModels
# Instantiate models with hourly seasonality auto_arima = AutoARIMA() s_naive = SeasonalNaive(season_length=24) theta = DynamicOptimizedTheta(season_length=24)# Instantiate models with hourly and weekly seasonality mstl1 = MSTL(season_length=[24, 24 * 7], trend_forecaster=AutoARIMA(), alias="MSTL_ARIMA_trend") mstl2 = MSTL(season_length=[24, 24 * 7], trend_forecaster=HoltWinters(), alias="MSTL_Holt_trend")
Forecasting with StatsModels
# Combine models into a list stats_models = [auto_arima, s_naive, theta, mstl1, mstl2]# Instantiate the model object sf = StatsForecast( models=stats_models, freq="h", fallback_model = AutoARIMA(), n_jobs= -1)
Forecasting with StatsModels
# Combine models into a list stats_models = [auto_arima, s_naive, theta, mstl1, mstl2]# Instantiate the model object sf = StatsForecast( models=stats_models, freq="h", fallback_model = AutoARIMA(), n_jobs= -1)# Create the forecast forecast_stats = sf.forecast(df=train, h=72, level=[95])
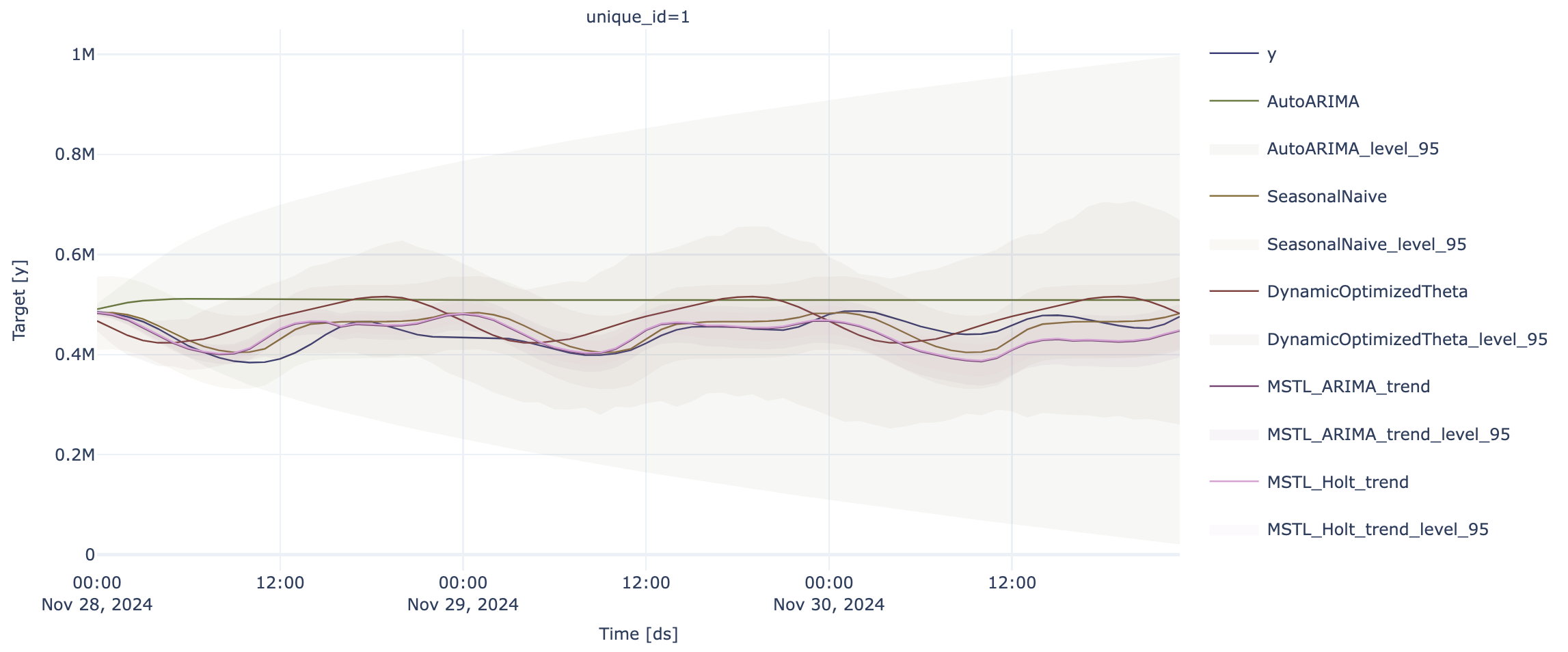
Forecast Forecasting with StatsModels StatsModels
p = sf.plot(test, forecast_stats, engine = "plotly", level=[95])
p.update_layout(height=400)
Model evaluation
def mape(y, yhat):
mape = mean(abs(y - yhat)/ y)
return mape
def rmse(y, yhat):
rmse = (mean((y - yhat) ** 2 )) ** 0.5
return rmse
def coverage(y, lower, upper):
coverage = sum((y <= upper) & (y >= lower)) / len(y)
return coverage
Model evaluation
fc = forecast_stats.merge(test, how="left", on="ds") fc_performance = None for i in [str(m) for m in stats_models]: m = mape(y = fc["y"], yhat = fc[i]) r = rmse(y = fc["y"], yhat = fc[i]) c = coverage(y = fc["y"], lower = fc[i + "-lo-95"], upper = fc[i + "-hi-95"])perf = {"model": i, "mape": m, "rmse": r, "coverage": c} if fc_performance is None: fc_performance = pd.DataFrame([perf]) else: fc_performance = pd.concat([fc_performance, pd.DataFrame([perf])]) fc_performance.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
Model evaluation
print(fc_performance.sort_values("rmse"))
model mape rmse coverage
1 SeasonalNaive 0.041340 22410.483959 1.000000
4 MSTL_Holt_trend 0.053939 30201.299395 0.513889
3 MSTL_ARIMA_trend 0.053771 30428.240235 0.666667
2 DynamicOptimizedTheta 0.090566 45189.869437 0.916667
0 AutoARIMA 0.149790 70483.617198 1.000000
Model evaluation
print(fc_performance.sort_values("rmse"))
model mape rmse coverage
1 SeasonalNaive 0.041340 22410.483959 1.000000
4 MSTL_Holt_trend 0.053939 30201.299395 0.513889
3 MSTL_ARIMA_trend 0.053771 30428.240235 0.666667
2 DynamicOptimizedTheta 0.090566 45189.869437 0.916667
0 AutoARIMA 0.149790 70483.617198 1.000000
Can we improve the results?
- Different settings for better accuracy
- Experiments come in handy
Let's practice!
Designing Forecasting Pipelines for Production

