Hyperparameter optimization with Optuna
Deep Reinforcement Learning in Python

Timothée Carayol
Principal Machine Learning Engineer, Komment
What are hyperparameters
- Large number of hyperparameters in DRL algorithms
- Can have large effect on performance
- Search complexity grows with number of hyperparameters
| Examples |
|---|
| Discount rate |
| PPO: clipping epsilon, entropy bonus |
| Experience replay: buffer size, batch size |
| Decayed epsilon greediness schedule |
| Fixed Q-targets: $\tau$ |
| Learning rate |
| Number of layers, nodes per layer... |
How to choose hyperparameter values
Objective: average cumulative rewards
Hyperparameter search techniques:
- Trial and error by hand
- Grid search
- Random search
- Dedicated algorithms

Optuna workflow:
- Define an objective function
- Instantiate an Optuna
study - Let Optuna iterate over trials
import optunadef objective(trial): ...study = optuna.create_study()study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100)
study.best_params
{'learning_rate': 0.001292481, 'batch_size': 8}
Specifying the objective function
In the objective function:
- Define the hyperparameters of interest
- Define the metric(s) to optimize
Offers full flexibility on hyperparameter specification:
- float
- integer
- categorical
def objective(trial: optuna.trial.Trial):# Hyperparameters x and y between -10 and 10x = trial.suggest_float('x', -10, 10) y = trial.suggest_float('y', -10, 10)# Return the metric to minimize return (x - 2) ** 2 + 1.2 * (y + 3) ** 2
The optuna study
- Use sqlite to save the study
- Sample
n_trialswith default sampler (TPE)- Picks hyperparameters at random at first
- Then focus more on promising regions
- If
n_trialsomitted: run trials until interrupted - Can load study from database later
import sqlite study = optuna.create_study( storage="sqlite:///DRL.db", study_name="my_study")study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100)
loaded_study = optuna.load_study(
study_name="my_study",
storage="sqlite:///DRL.db")
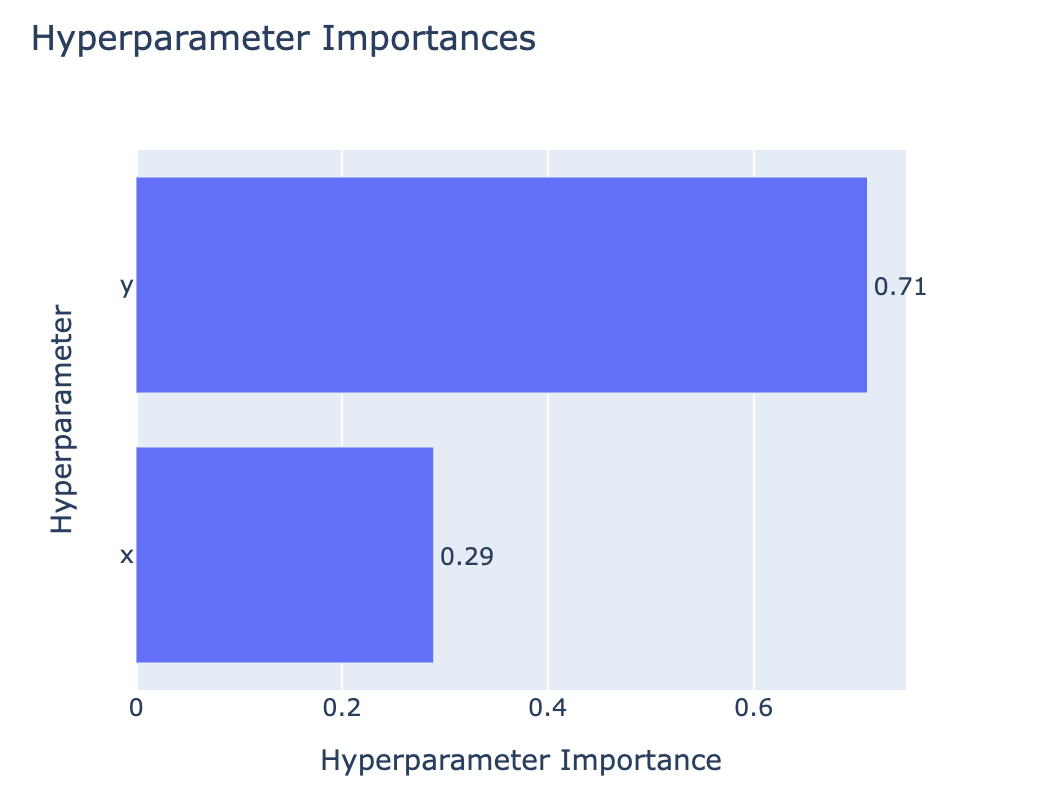
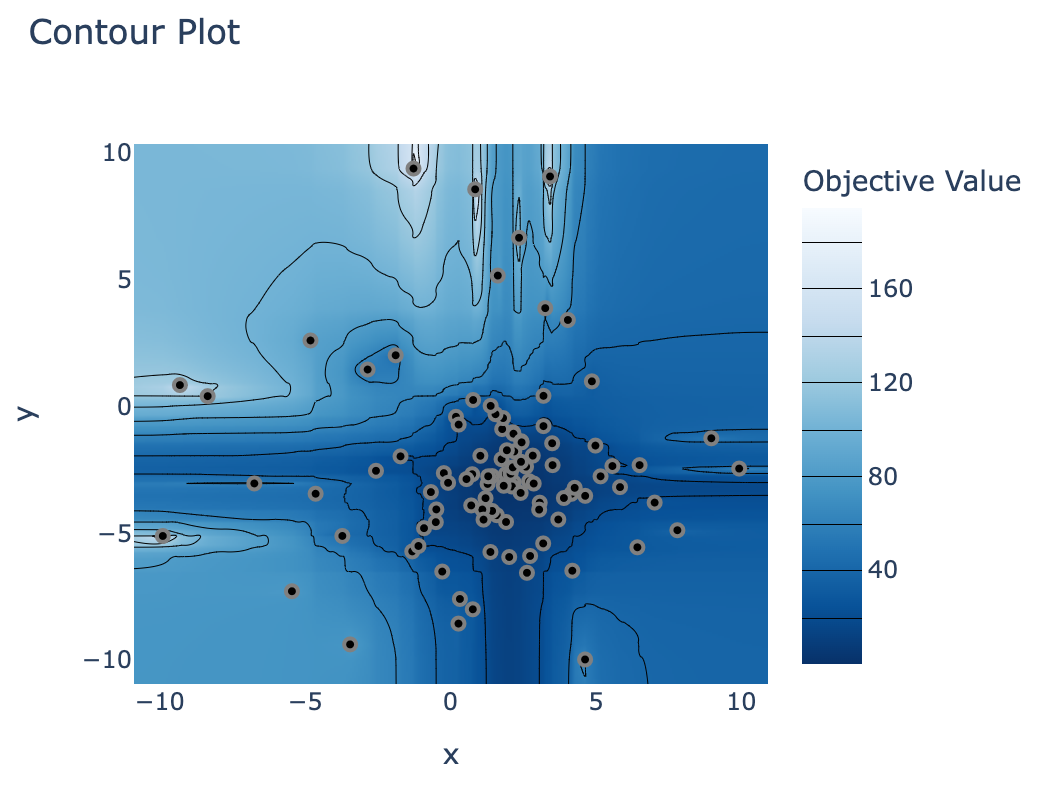
Exploring the study results
optuna.visualization.plot_param_importances(study)
optuna.visualization.plot_contour(study)
Let's practice!
Deep Reinforcement Learning in Python

