Selection bias
Conquering Data Bias

Konstantinos Kattidis
Data Analytics Lead
What is selection bias?
It's the bias introduced when the data for analysis is selected in a way that systematically favors certain individuals, groups, or characteristics
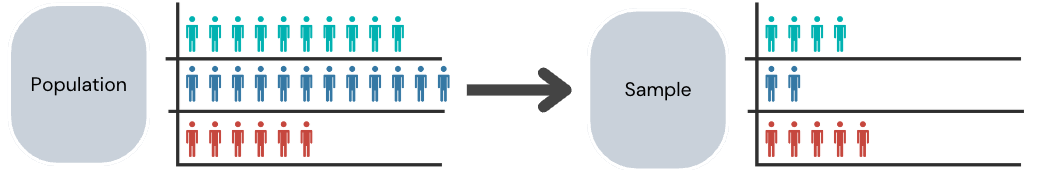
Hence, the sample obtained is not representative of the population intended to be analyzed
Let's delve into the five common types of selection bias
1. Sampling bias
- Sampling bias occurs when the sampling method is not fair or random
- It originates from the approach we choose to obtain our sample which can make it hard or impossible to apply the findings to the whole population
- For example:
- An e-commerce platform analyzes customer satisfaction using convenience sampling
- The findings may not reflect the sentiments of the entire customer base
2. Undercoverage bias
- Consider a market research study targeting online consumers, excluding individuals without internet access
- Undercoverage bias highlights the inadequate representation of certain groups within the chosen sample
- It is distinguished from sampling bias by its focus on the representation of specific groups rather than the randomness or fairness of the sampling method itself

3. Non-response bias
Non-response bias arises when individuals who choose not to participate in a survey or study differ systematically from those who do participate

- In a survey assessing employee satisfaction dissatisfied employees are less likely to participate
- This leads to to an overly optimistic view of employee morale
4. Self-selection bias

- Self-selection bias occurs when individuals choose to participate in a study or provide feedback
- For example:
- Customers self-select to participate in a satisfaction survey
- When their views do not represent the broader customer base
- This skews the overall perception
5. Survivorship bias
It occurs when only successful entities are included in the analysis
For example:
- Analyzing successful product launches without considering the ones that failed
- This would lead to biased insights, overlooking critical factors that contribute to failure
Creating a cohesive understanding
- It's not uncommon for multiple biases to interact, complicating analyses
- For example, a customer satisfaction survey may exhibit both self-selection bias and non-response bias
Let's practice!
Conquering Data Bias

