Introduction to arrays
Introduction to Java

Jim White
Java Developer
Array is ...

Array is ... a row of lockers!
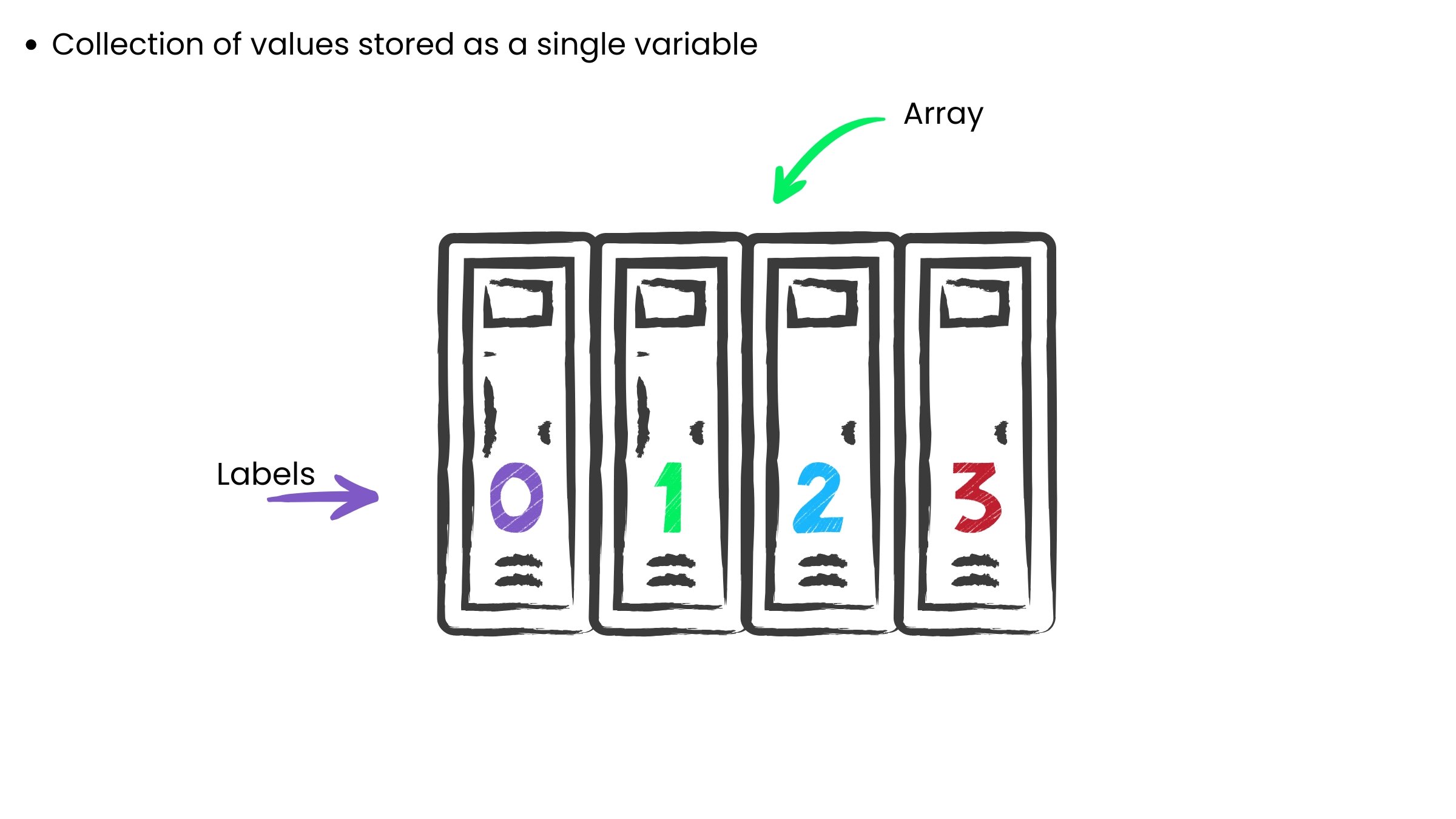
Declaring and filling arrays
- Using square brackets
[]
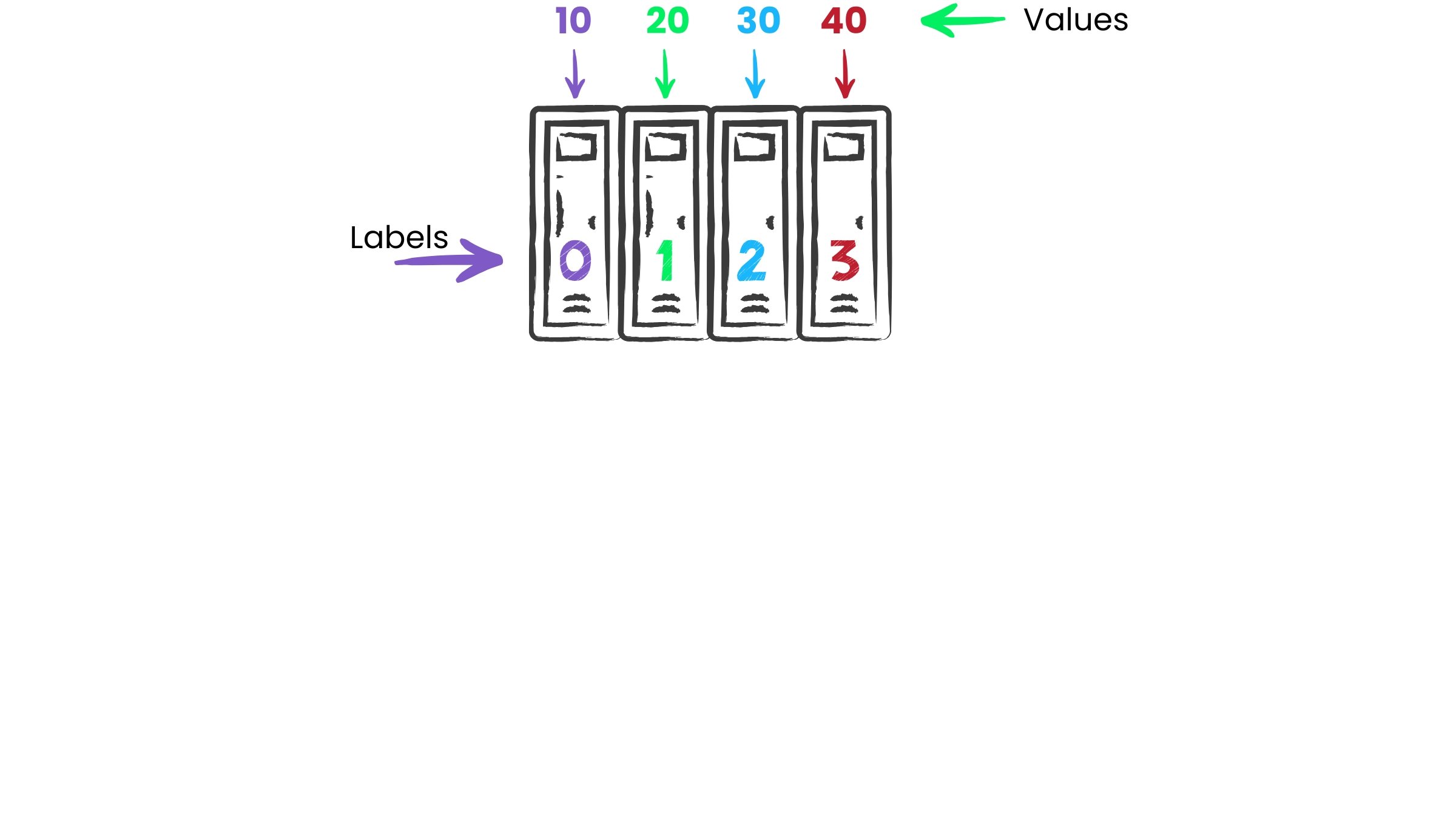
// Declare array variable int[] prices;// Assign value prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
Accessing elements
- Using
[]:
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// Accessing first element
int firstElement = prices[0]; // Value is 10
// Accessing second element
int secondElement = prices[1]; // Value is 20

Changing value of an element
- Change value by assigning new value to specific index
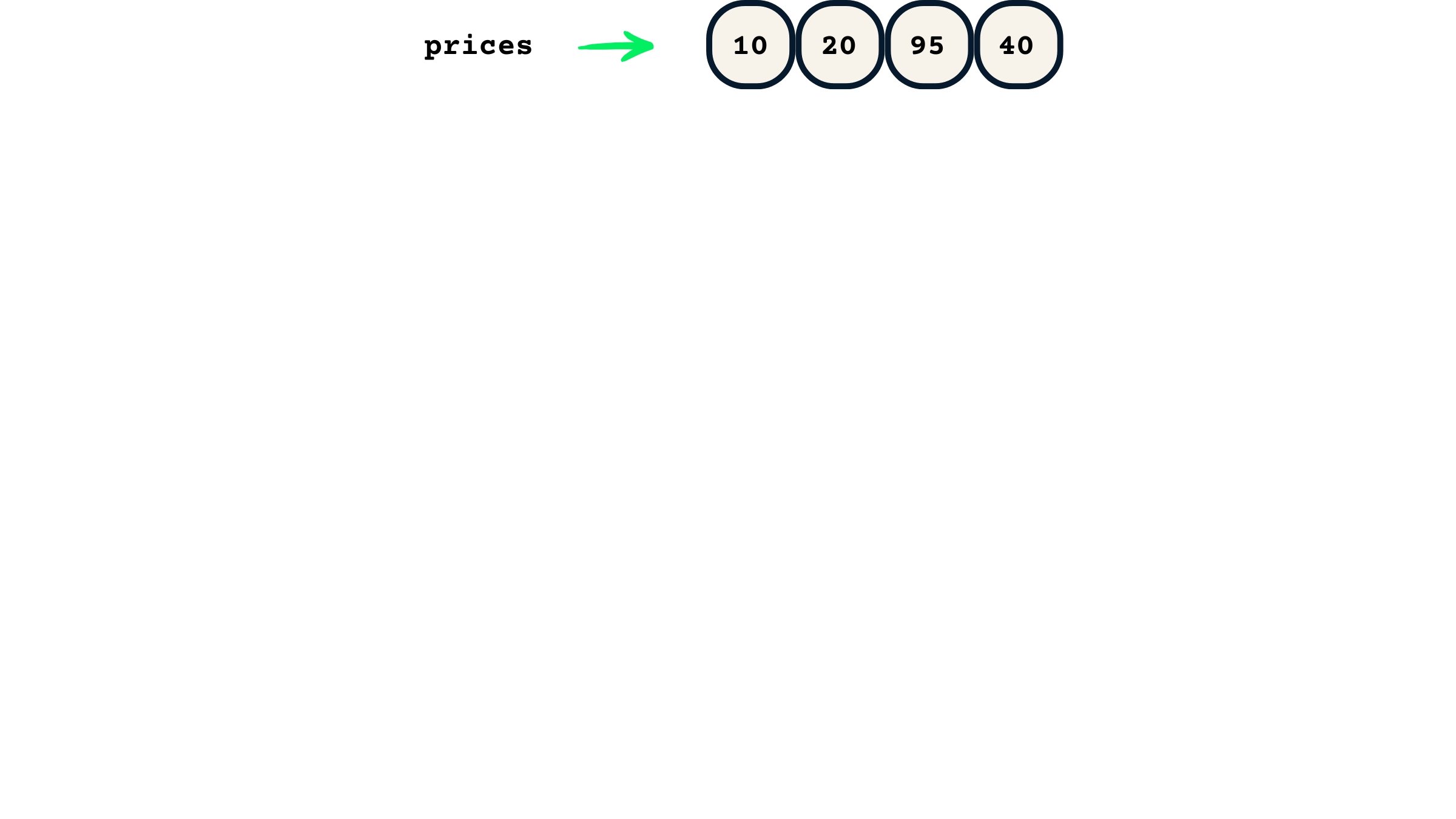
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};// Change value of third element to 95 prices[2] = 95;
Array length is fixed
- Array's length is fixed on creation
int[] itemIDs = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Accessing sixth element that isn't there
itemIDs[5] = 60; // <- This will cause an error
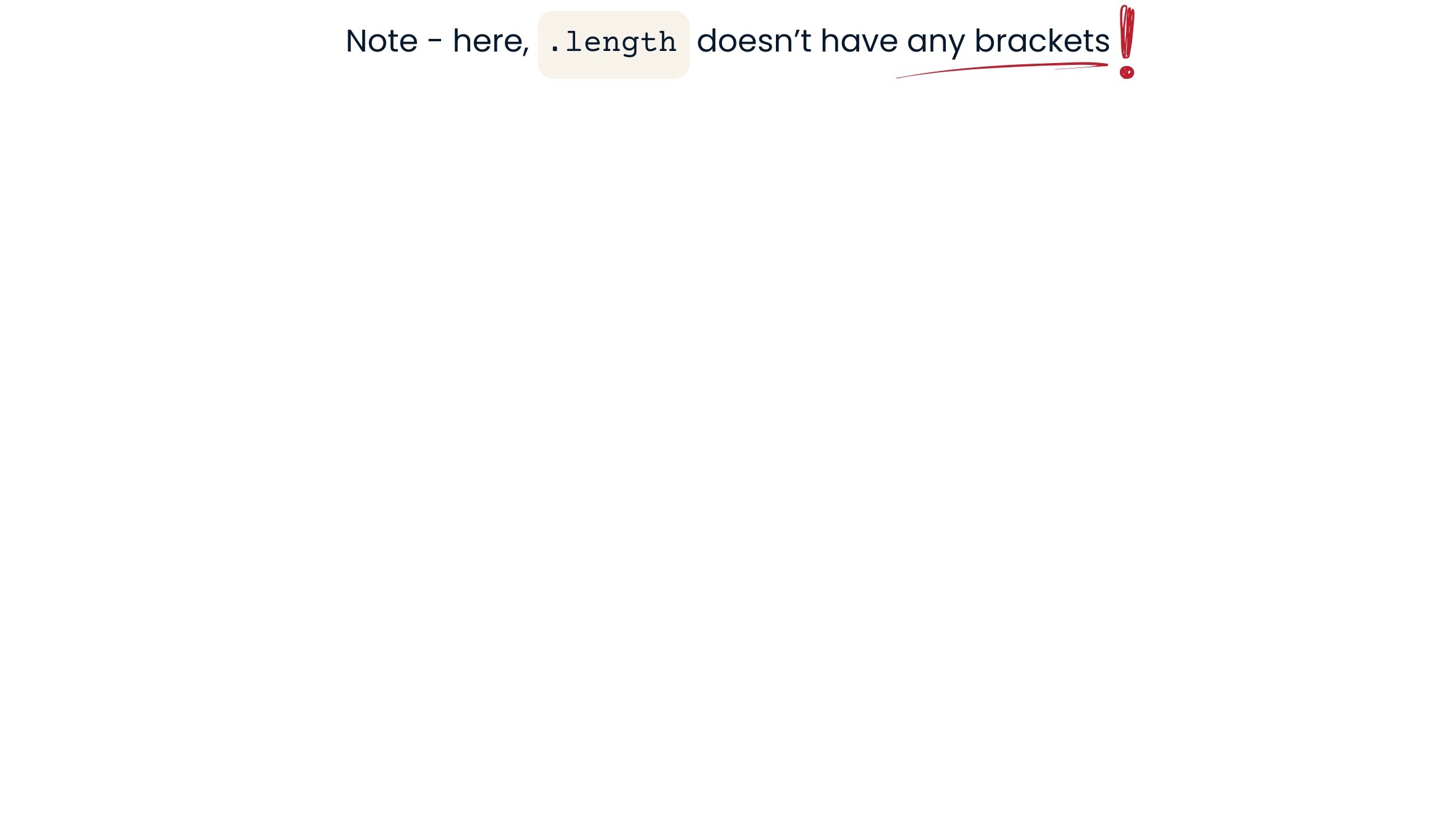
- Check array's length using
.lengthproperty
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
int pricesLength = prices.length; // Value is 4
Printing out values
We can print out individual values:
class ArrayElementPrinting {
public static void main (String[] args){
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// Printing element by element
System.out.println(prices[0]);
System.out.println(prices[1]);
}
}
10
20
Trying to print an entire array
Printing whole array returns representation:
class ArrayPrinting {
public static void main (String[] args){
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// Printing whole thing
System.out.println(prices);
}
}
[I@d041cf
Arrays of other things
// Array of Strings
String[] productNames = {"Organic Honey",
"Cold Brew Coffee",
"Dark Chocolate Bar"};
Values in an array
- Not limited to just numbers or
Strings

Recap
- Arrays are useful of storing multiple values of the same type
- Arrays are indexed from 0
- Arrays have fixed length
// Declare and assign
int[] prices = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// Retrieve
int secondElement = prices[1];
// Update
prices[1] = 25;
// Length
// Value is 4
int pricesLength = prices.length;
Let's practice!
Introduction to Java

