Primitive number data types
Introduction to Java

Jim White
Java Developer
Primitive types
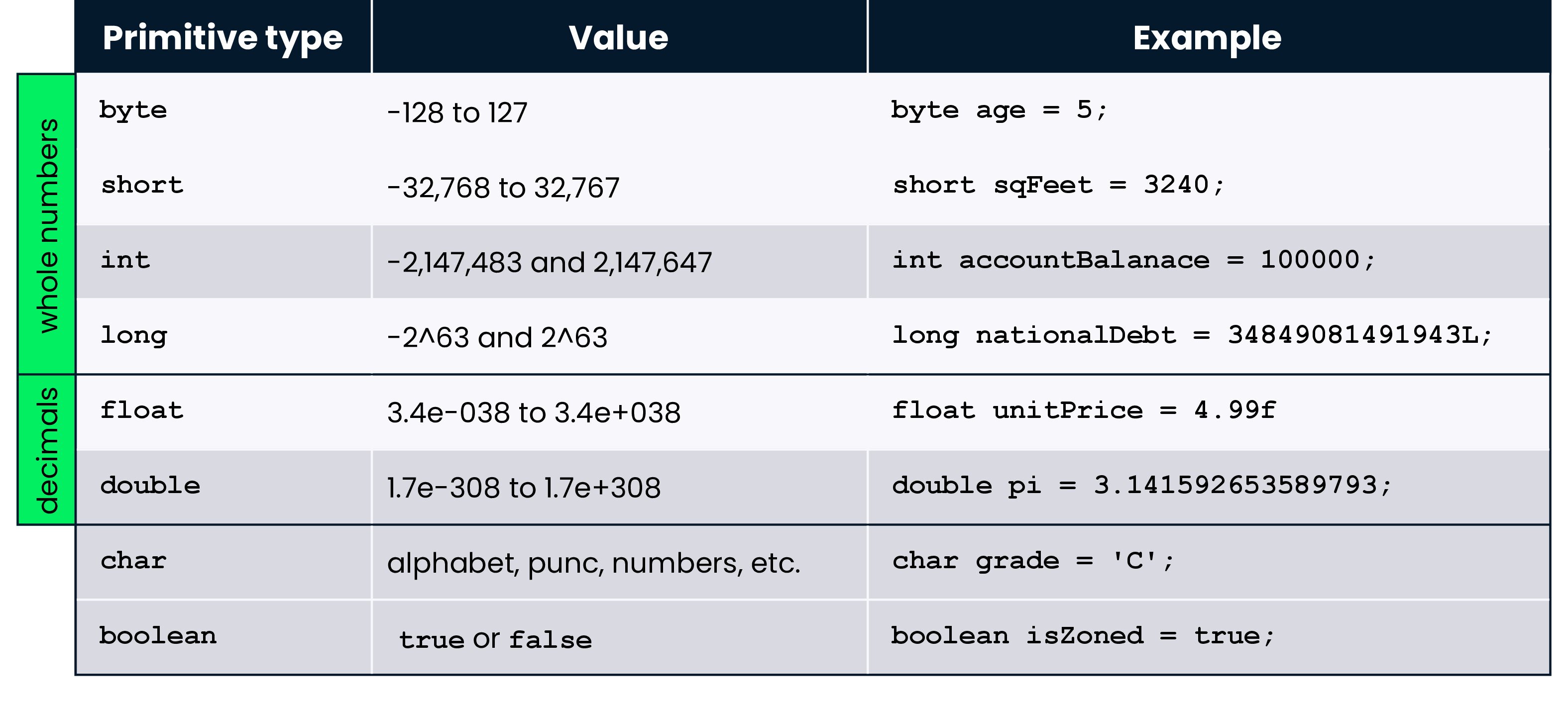
Numerical primitive types
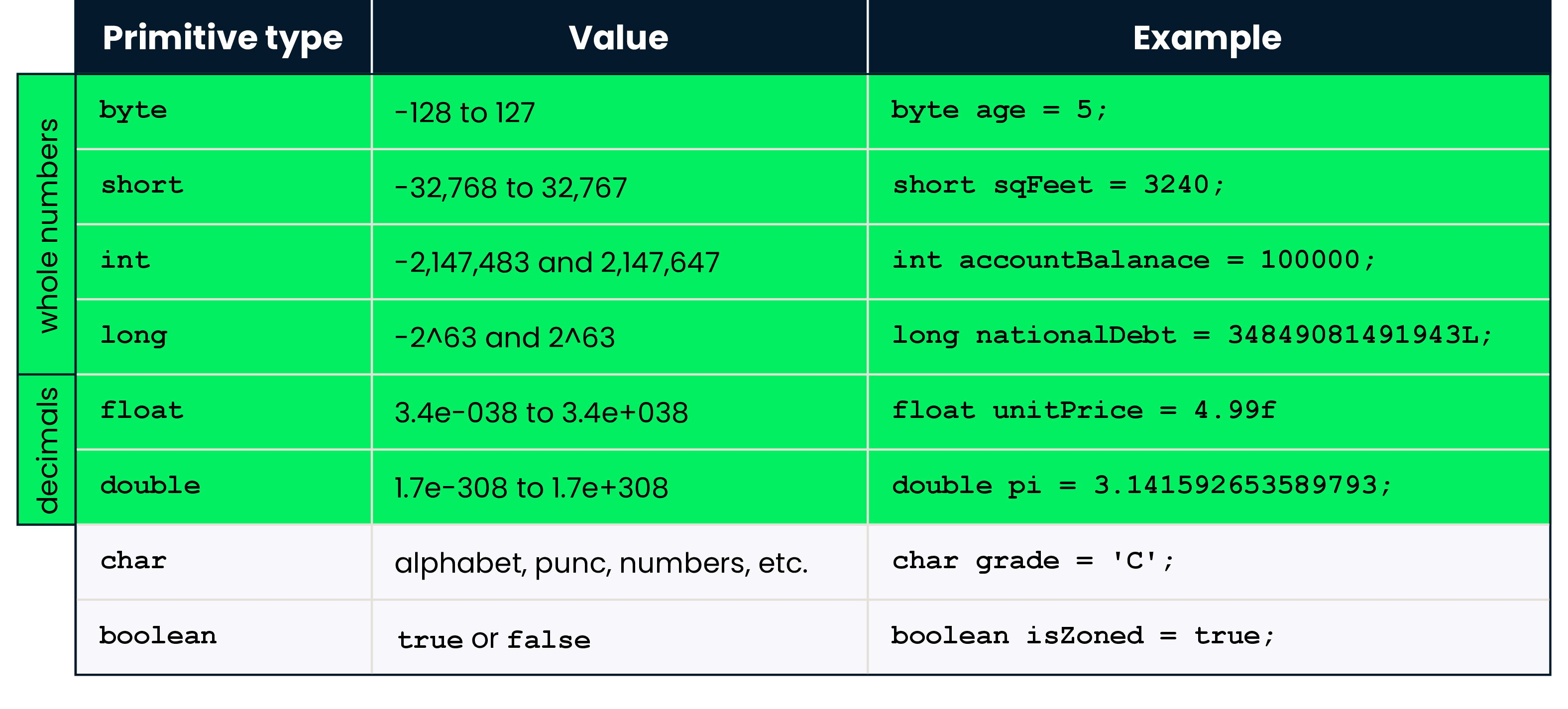
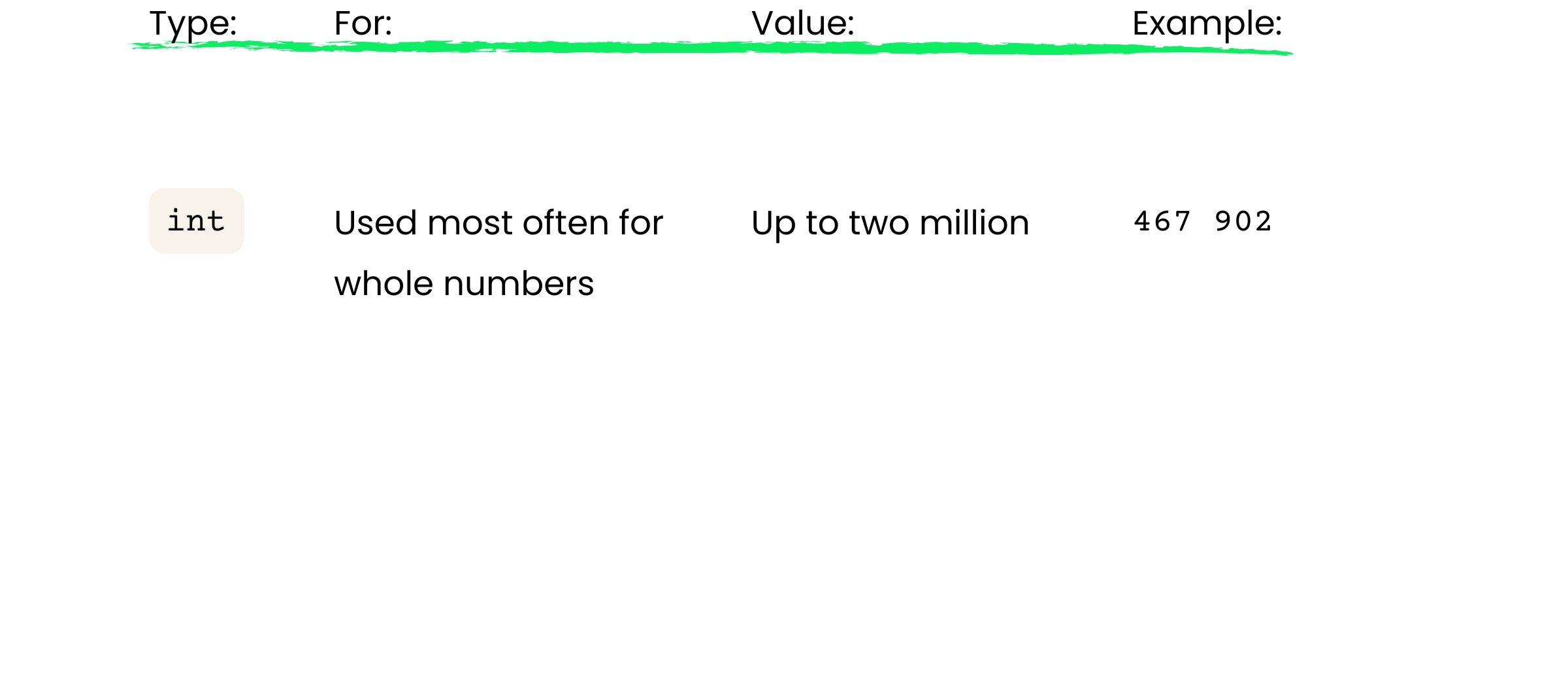
Primitives for whole numbers - int
long, short, and byte

int is the primitive of choice

double

float

double is the primitive for decimal numbers

Declaring primitives - int

Declaring primitives - int, double, short, byte

Declaring primitives - float and long

Numerical primitives in action
class PrintlnAsCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 60000;
byte y = 1;
short z = 300;
long w = 20000000L;
System.out.println(x + y + z + w);
}
}
20060301
class PrintlnAsCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double pi = 3.1415926535;
float half = 0.5F;
System.out.println(pi + half);
}
}
$$
3.6415926535
Let's practice!
Introduction to Java

