Algorithm Efficiency in Running Time and Space Complexity
Concepts in Computer Science

Pritesh Patel
Computer Scientist & Data Scientist for over 20 years
Introduction to Big-O Notation
- Measures time and space growth as input grows
- Examples: $O(n)$, $O(n^2)$, $O(log\, n)$
- 'O' stands for the 'order' of growth, e.g., O(n) = linear
Time complexity - using office analogy
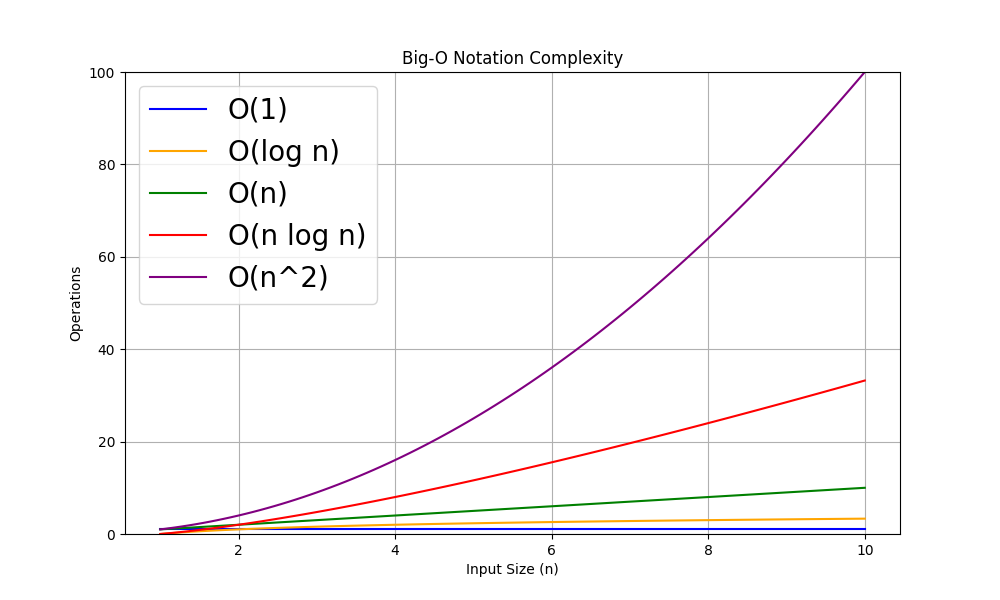
- $O(1)$ - constant time - "Quick glance" - "constant"
- $O(log\,n)$ - slow increase in time - "Stack dividing" - "logarithmic"
- $O(n)$ - linear increase - "Document reading" - "linear"
- $O(n\,log\,n)$ - faster increase in time - "Pile sorting" - "linearithmic"
- $O(n^2)$ - quadratic time increase - "Document comparison" - "quadratic"
Space complexity - using office analogy

- $O(1)$ - constant space - "Desk space" - "constant"
- $O(log\,n)$ - slower increase in space - "minimal notes" - "logarithmic"
- $O(n)$ - linear increase - "sticky notes" - "linear"
- $O(n\,log\,n)$ - faster increase in space - "Temp piles" - "linearithmic"
- $O(n^2)$ - quadratic space increase - "comparison grid" - "quadratic"
Let's practice!
Concepts in Computer Science

