History of programming
Concepts in Computer Science

Pritesh Patel
Computer Scientist & Data Scientist for over 20 years
Introduction of Programming Languages

- Purpose: Communicate instructions to a computer.
- Overall
- High-level languages: Easy for humans to read and write.
- Low-level languages: Close to machine code, harder for humans to read but easier to control lower level details
High Level
Low Level
Functional, procedural, and low-level programming
- Functional Programming
- Mathematical functions (pure function - ex: tidy up desk)
- Immutability (no side effects - ex: no changes in filing cabinet)
- Procedural Programming
- Sequence of commands (step by step instructions - ex: tidy up desk, move file to cabinet)
- Immutable data (side effects - ex: new files in cabinet or sign document)
- Low-level Programming
- Access inner workings (hardware manipulation - ex: change office thermostat)
- Immutable (side effects - ex: thermostat, spacing in file cabinet)
- Examples
- Functional: (
Lisp, Scheme) - Procedural: (
Python, Java) - Low-Level: (
C, Assembly)
- Functional: (
The evolution of programming languages
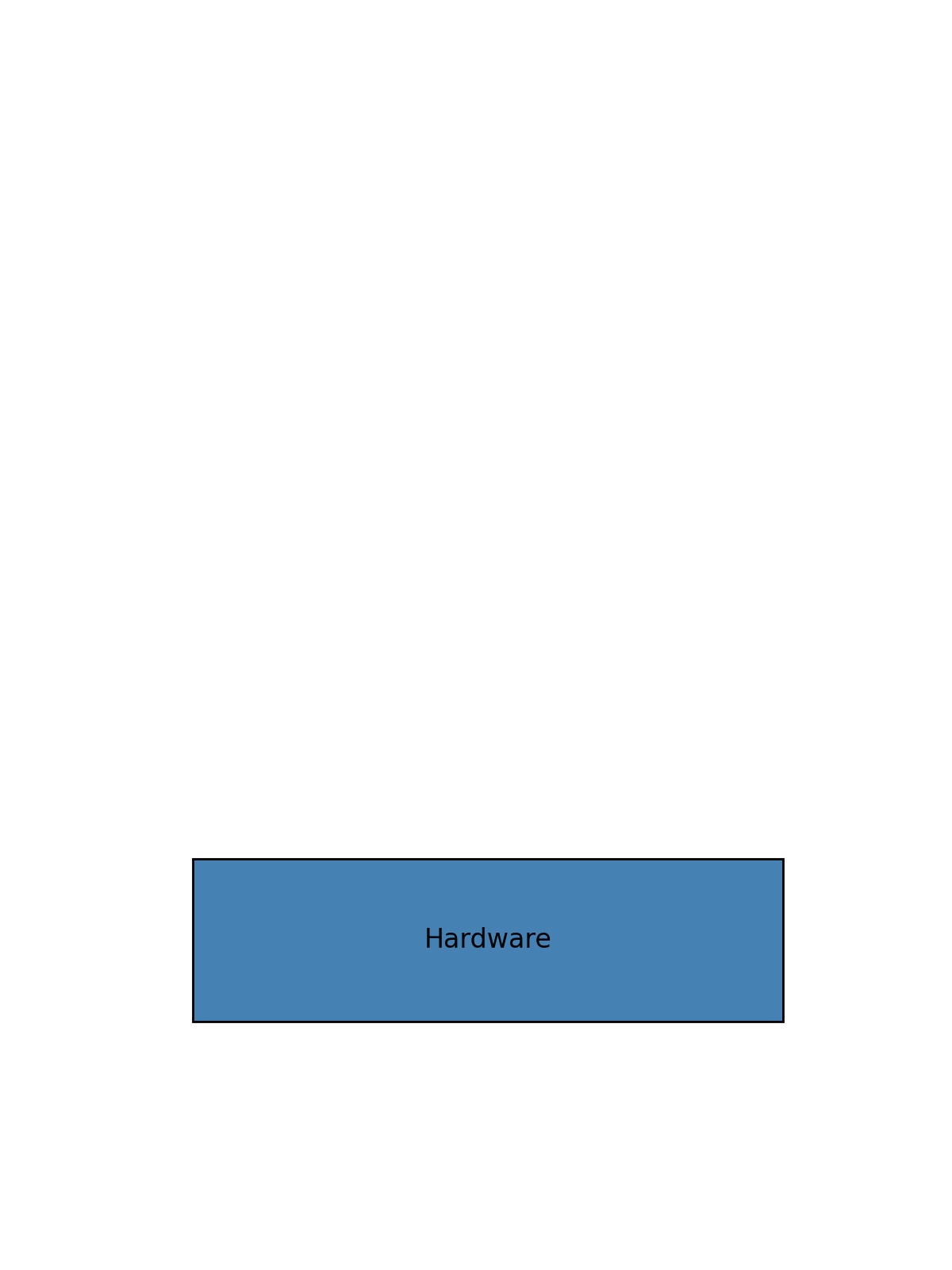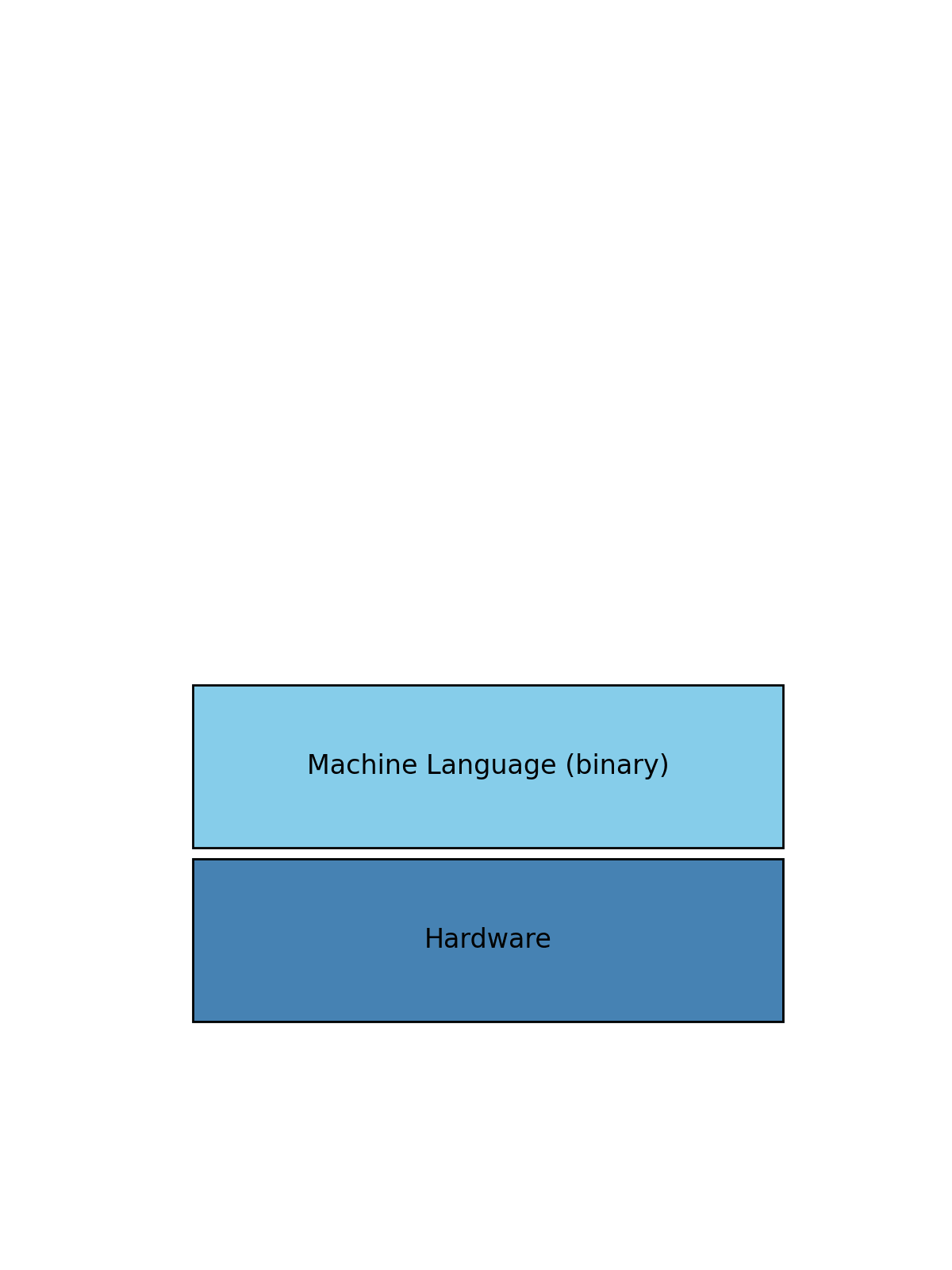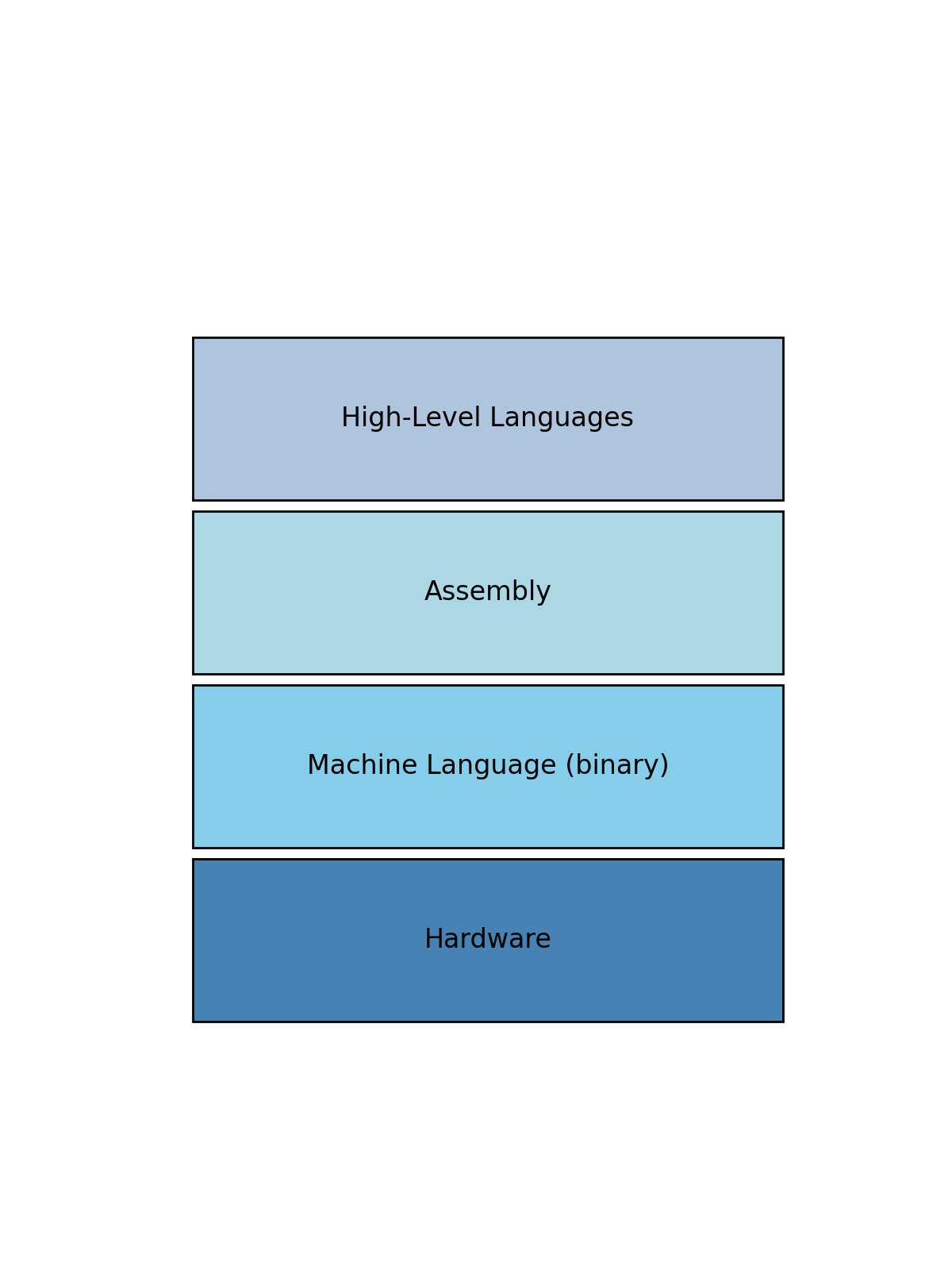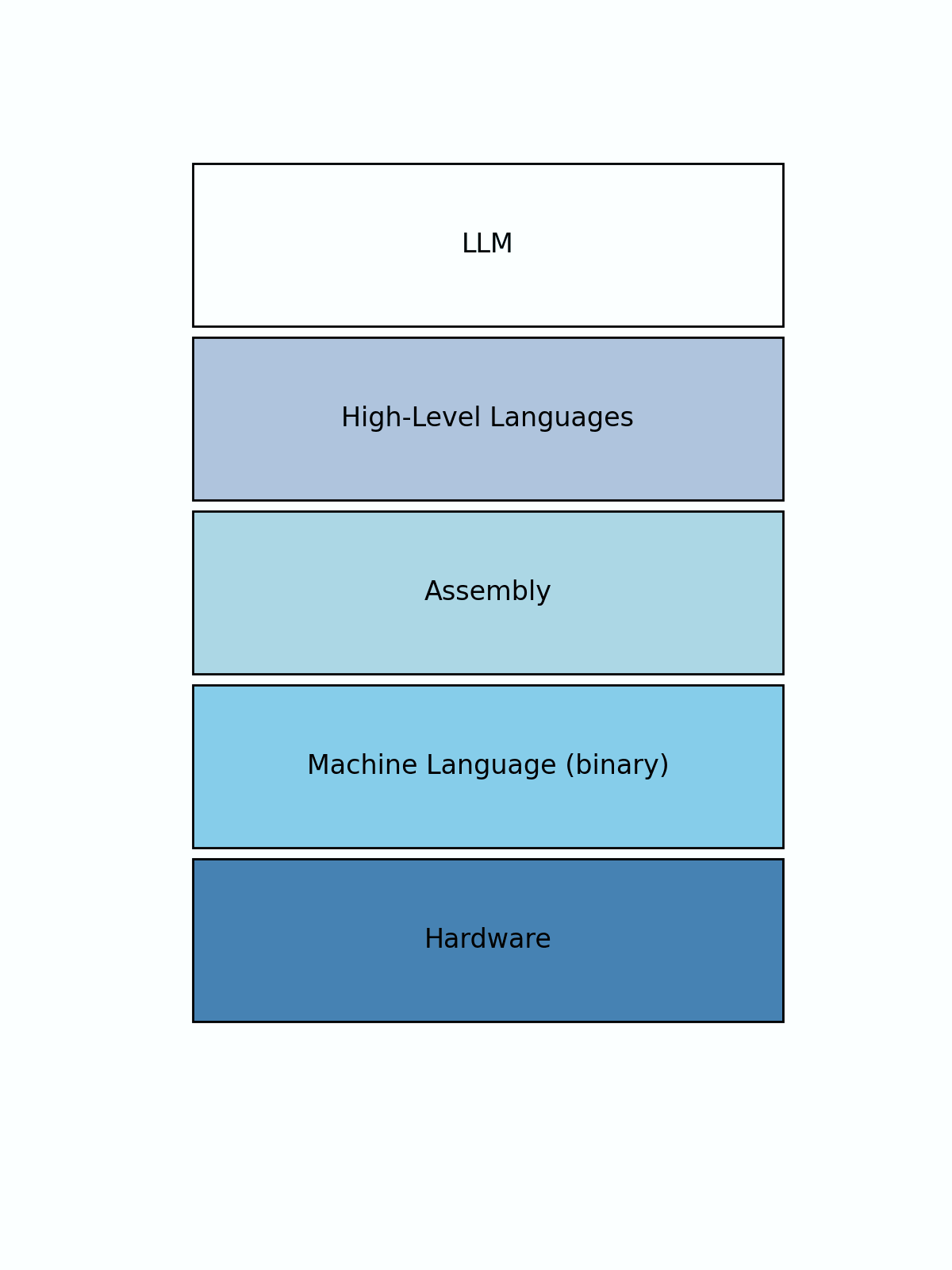
Examples:
- LLM's (Large Language Models):
GPT-4, Claude-3, Google Gemini - High-Level Languages:
Python, Java, Cobol, Javascript - Assembly Languages:
x86, ARM - Machine Language:
binary - Hardware: No programming this is the core hardware that does the work
Refer to programming paradigms
Let's practice!
Concepts in Computer Science


