Managing and formatting data
Introduction to Excel

Jess Ahmet
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Ways to manage data
- Data stored and managed in tabular layout
- Columns and rows in all sheets
- Create named ranges
- Create Subtotals
- Data validation
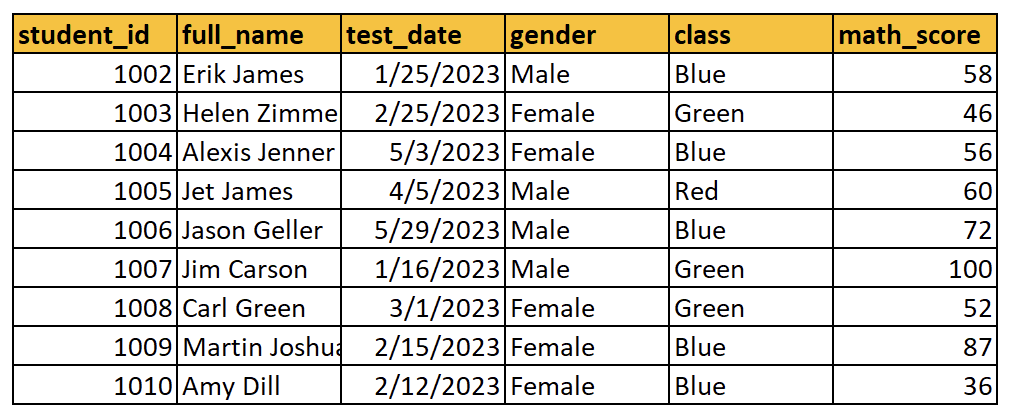
Named ranges
- Name a range of columns or rows
- Benefits include:
- Easier to reference range in formulas
- Less time searching sheets for important ranges of data
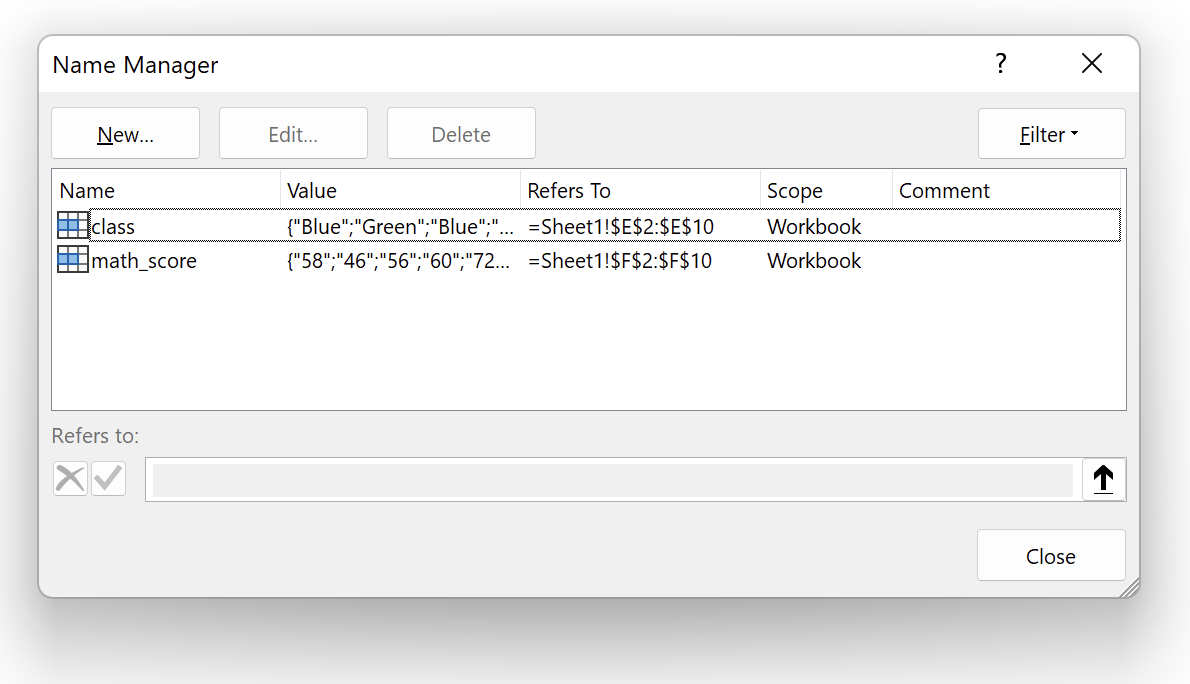
- The Name Manager feature allows you to:
- Edit named ranges
- Create news named ranges
- Deleted named ranges
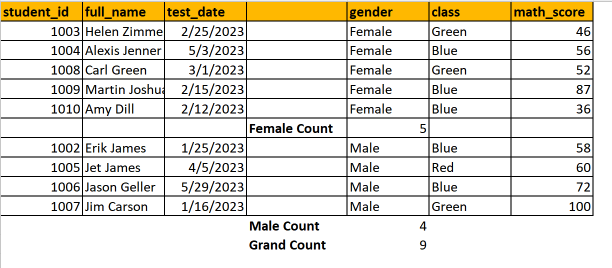
Subtotals
- Sense check numerical data through calculations
- Can help spot large anomalies early on
- Subtotal creates aggregation within the dataset
- Sum
- Count
- Average
- Can also add a grand total of the column
Validating data
- Useful when sharing workbooks
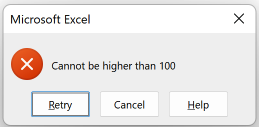
- Data Validation allows user to control the values entered into a cell
- Including the data type
- Can add input messages to inform user of data validation settings
- Customize error message if user enters invalid data

Formatting data
- In Excel, you can format whole sheets, individual cells, or specific values
- Examples:
- Font size
- Sheets with borders around all cells
- Values matching their data type (i.e., currencies)
- Conditional formatting
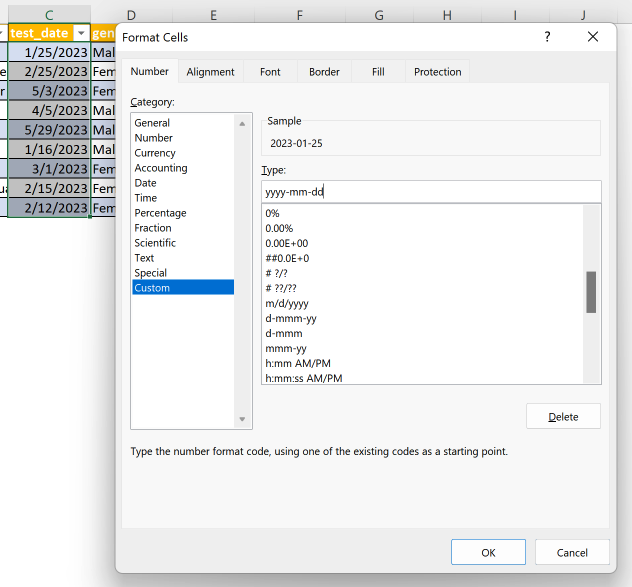
Custom formats
- Many available formats for different data types
- Custom section also available
Conditional formatting
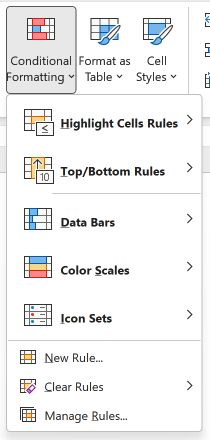
- Conditional Formatting allows users to set conditions for highlighting cells within the data.
- Helps identify patterns or trends
- Formatting options include:
- Icons
- Data bars
- Highlighting cells using color scales
- Can create, edit, and delete rules through the Manage Rules window.
Let's practice!
Introduction to Excel

