Histogramas
Introducción a la visualización de datos con ggplot2

Rick Scavetta
Founder, Scavetta Academy
Tipos de gráficos comunes
| Tipo de gráfico | Geomas posibles |
|---|---|
| Diagramas de dispersión | points, jitter, abline, smooth, count |
| Gráficos de barras | histogram, bar, col, errorbar |
| Gráficos lineales | line, path |
Histogramas
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_histogram()
- Un gráfico de valores agrupados en contenedores
- es decir, una función estadística
`stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`.
Pick better value with `binwidth`.
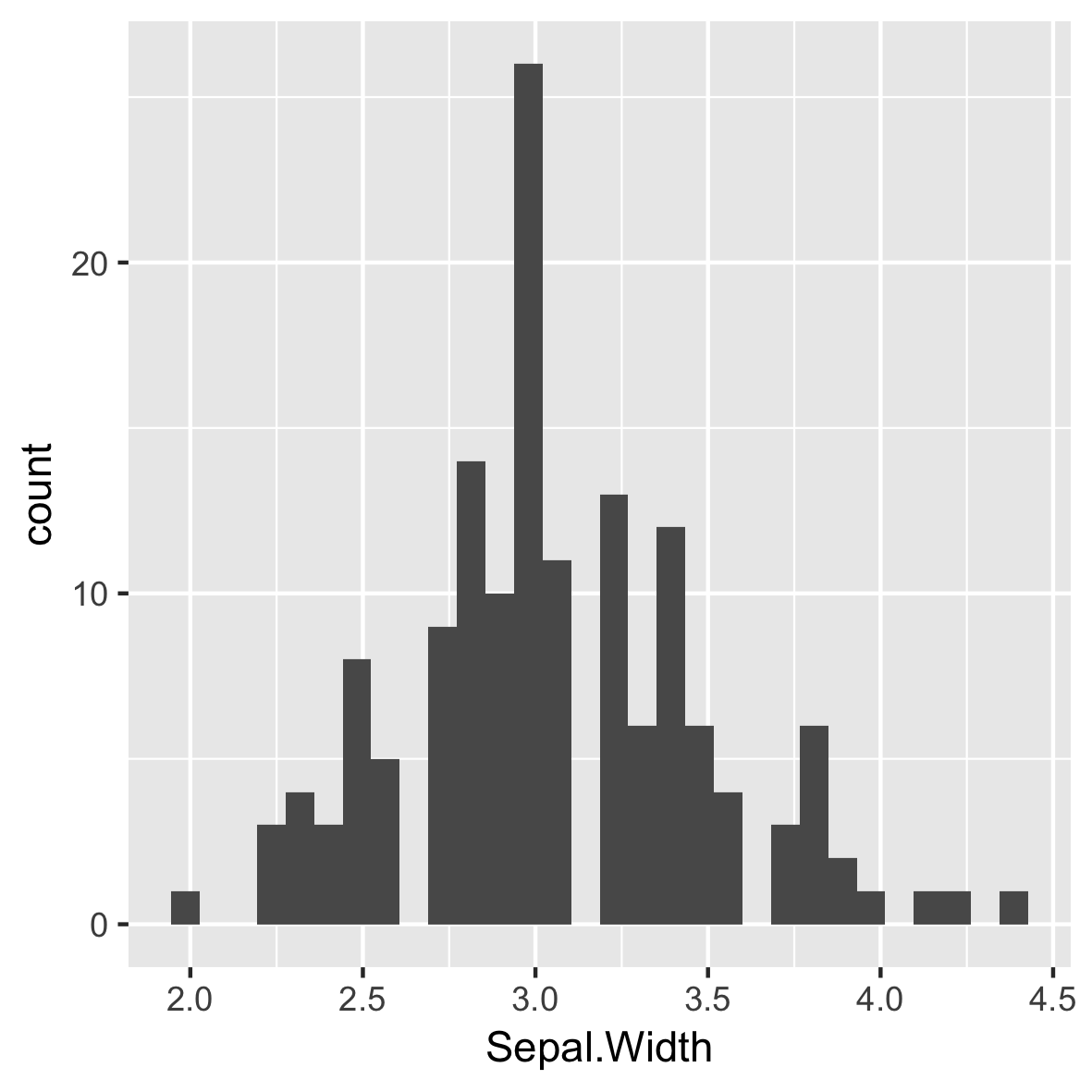
Predeterminado de 30 ubicaciones pares
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_histogram()
- Un gráfico de valores agrupados en contenedores
- es decir, una función estadística
# Default bin width:
diff(range(iris$Sepal.Width))/30
[1] 0.08

Anchos de contenedor intuitivos y significativos
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 0.1)
Establece siempre una anchura de recipiente significativa para tus datos.
Sin espacios entre barras.
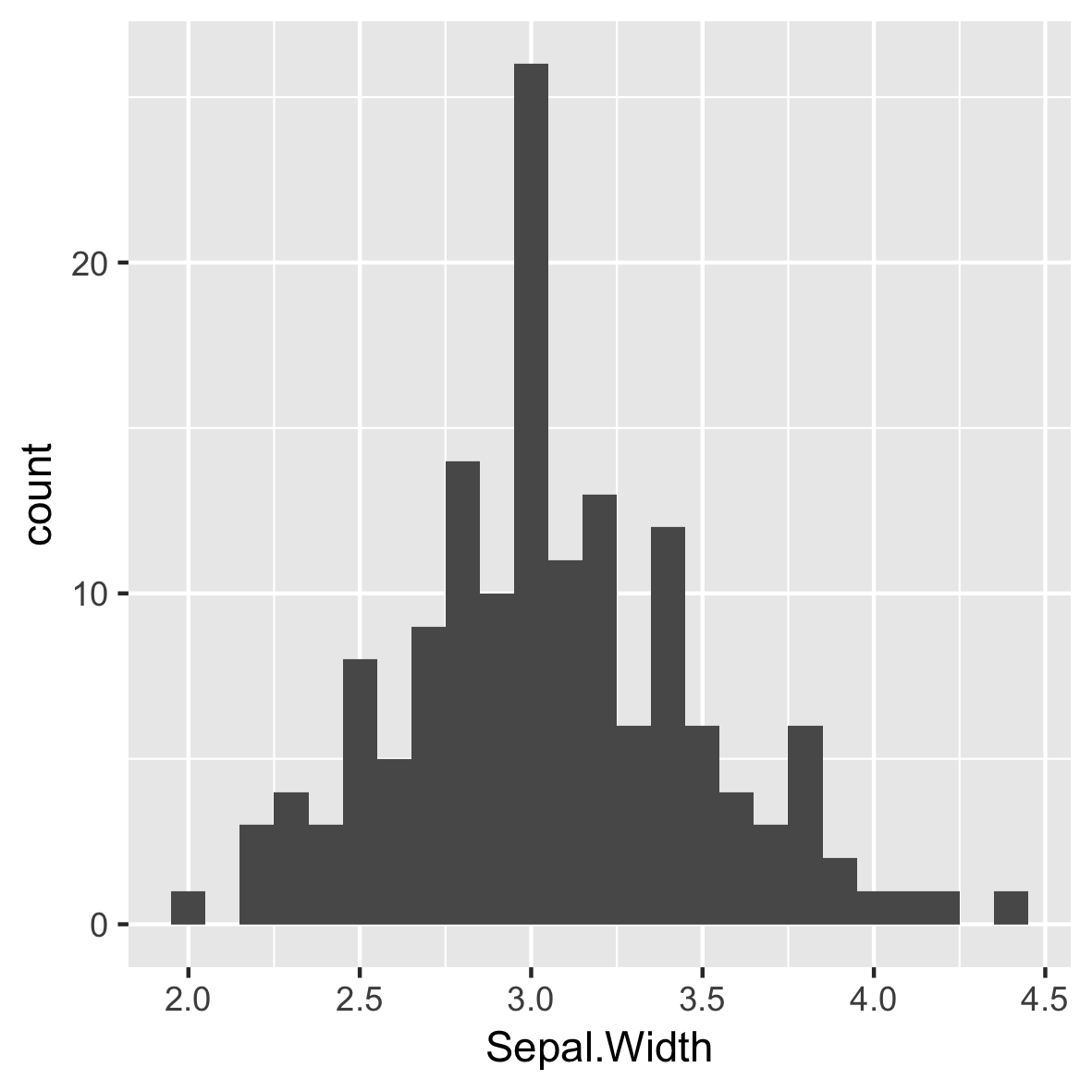
Reposicionar marcas de graduación
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 0.1,
center = 0.05)
Establece siempre una anchura de recipiente significativa para tus datos.
Sin espacios entre barras.
Las etiquetas del eje X están entre las barras.
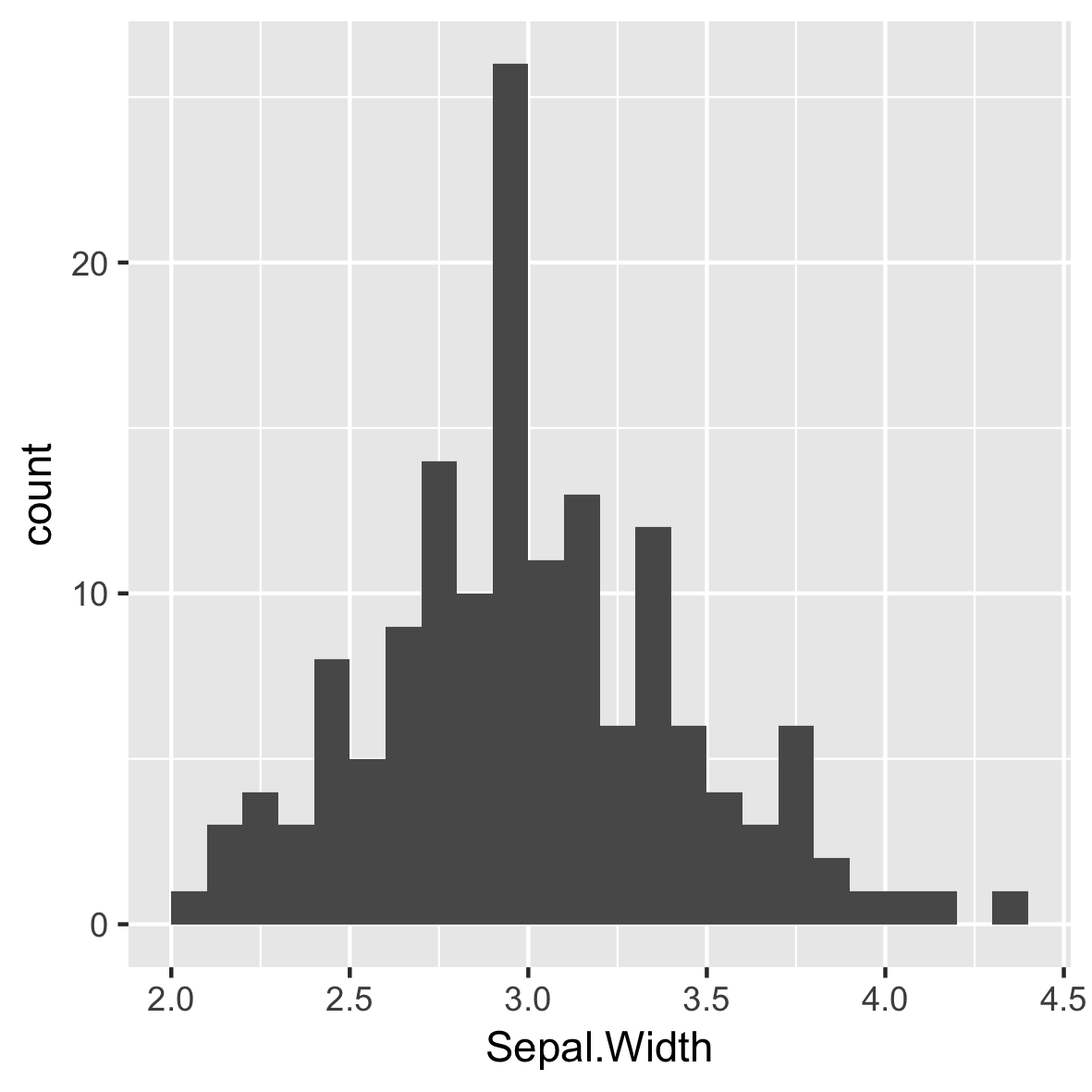
Especies diferentes
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width,
fill = Species)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .1,
center = 0.05)
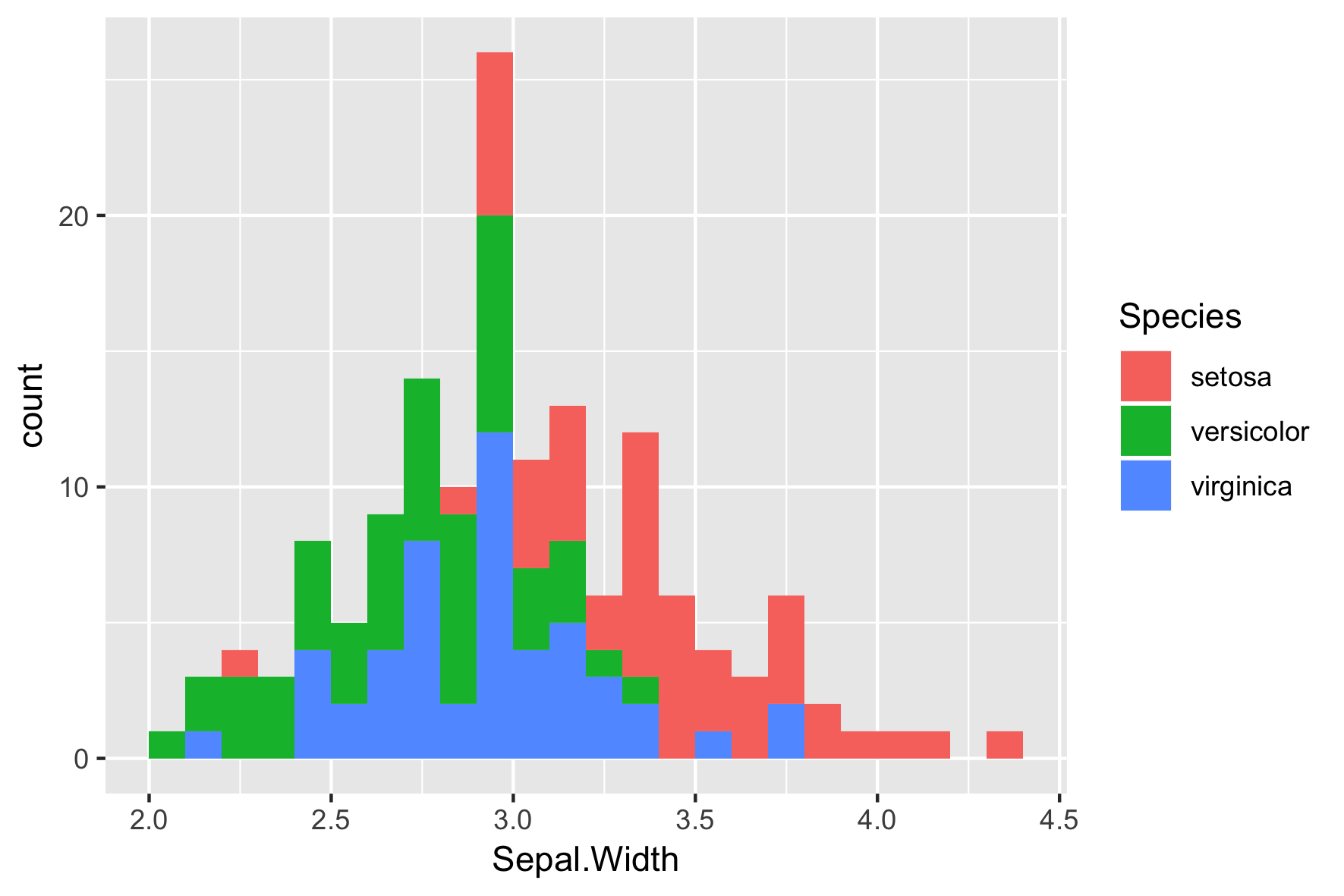
La posición por defecto es "stack"
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width,
fill = Species)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .1,
center = 0.05,
position = "stack")

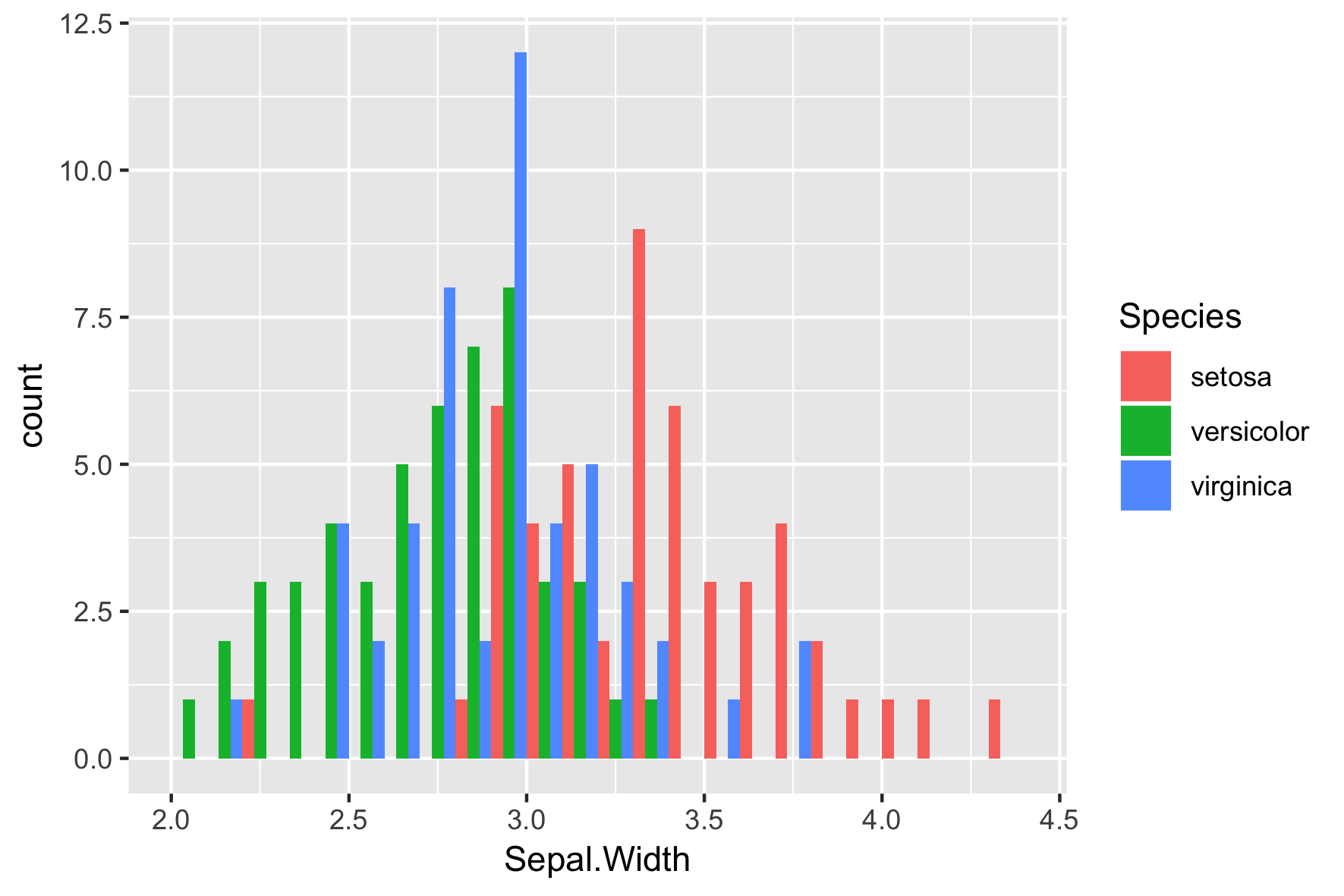
position = "dodge"
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width,
fill = Species)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .1,
center = 0.05,
position = "dodge")
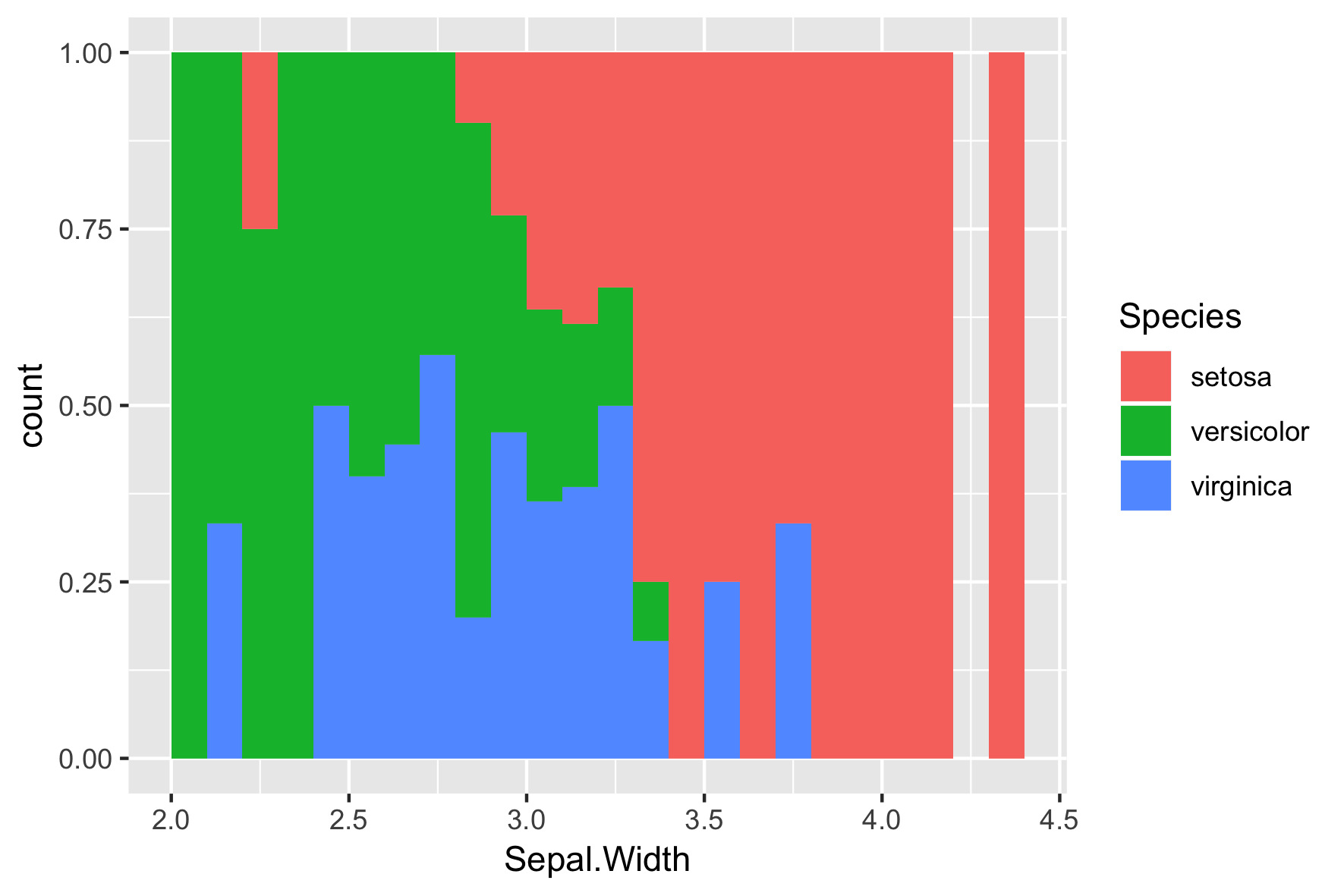
position = "fill"
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width,
fill = Species)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = .1,
center = 0.05,
position = "fill")
Diapositiva final
Introducción a la visualización de datos con ggplot2

