Cloud deployment models
Understanding Cloud Computing

Lis Sulmont
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Cloud deployment models
- Important decision in cloud adoption
- How much control do you need over your cloud environment?
- Three main types: private, public, and hybrid
$$
$$

Private cloud
Cloud infrastructure is designated for exclusive use by its tenants.
Private clouds are accessed by a network link.
Pros: Direct control of resources and data
Cons: More upfront investment
Unlike on-premise, private cloud uses virtualization for on-demand compute resources and can be off-premises.

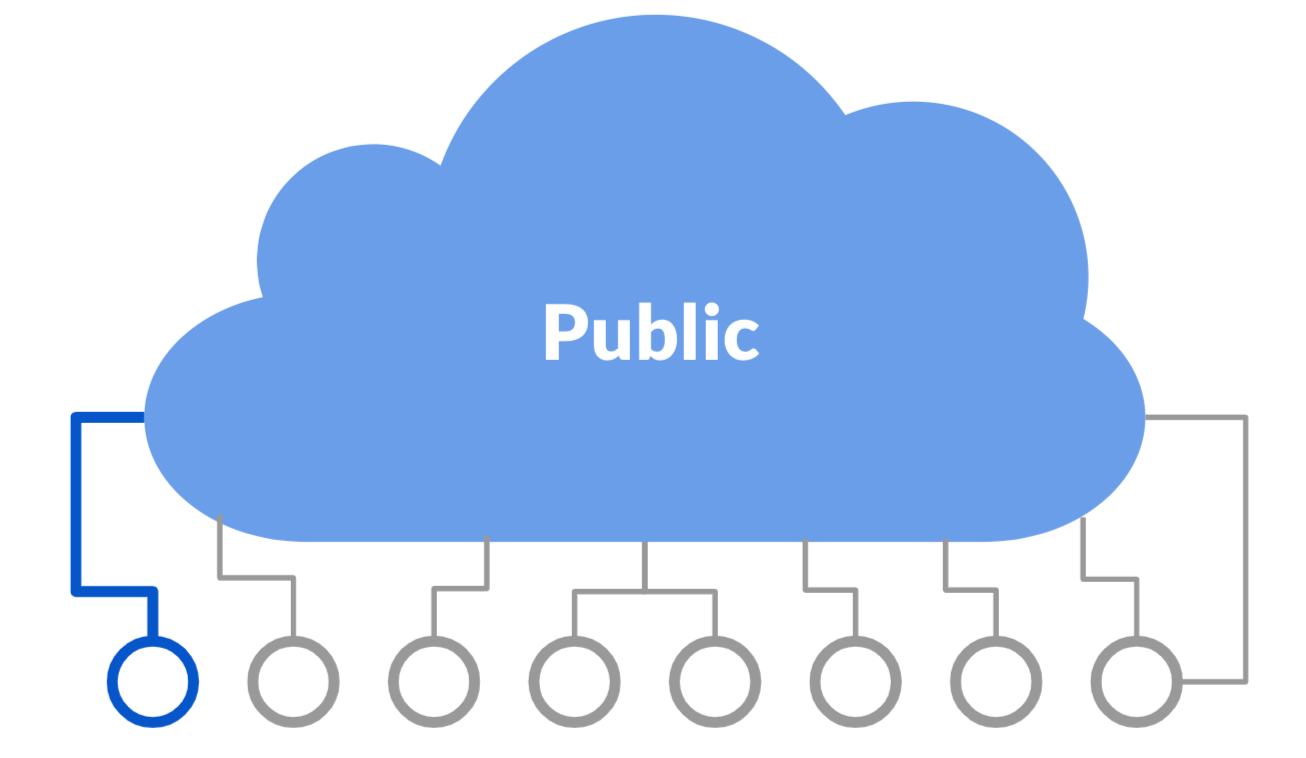
Public cloud
Cloud infrastructure is shared and open for use by the general public. It's owned and managed by a cloud service provider.
Public clouds are Internet accessible.
Pros:
- Get started quickly with minimal investment
- Easier to scale
Cons: No access to data center and hardware
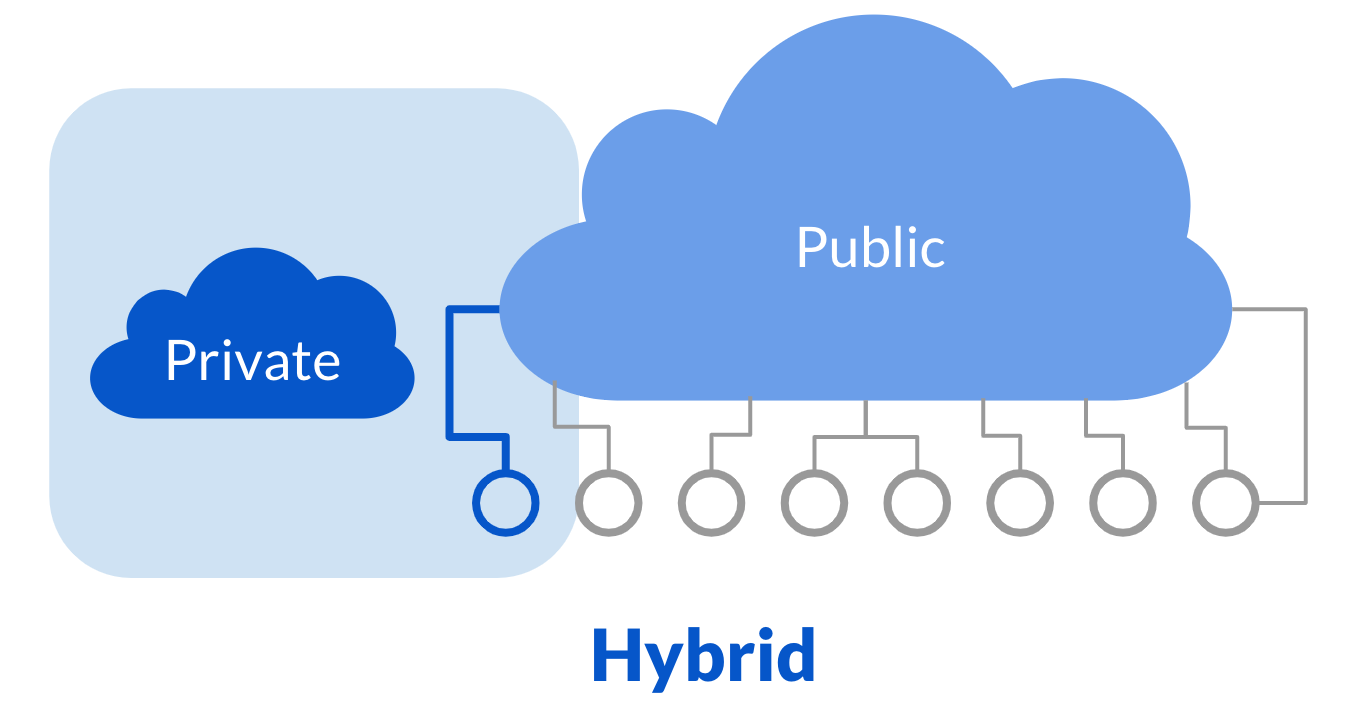
Hybrid cloud
Organization uses a combination of two or more distinct models.
Use cases:
- Store sensitive data on the private cloud and use application on public cloud for analytics
- Cloud bursting: when private cloud hits capacity, temporarily move overflow to the public cloud to avoid disruption of service
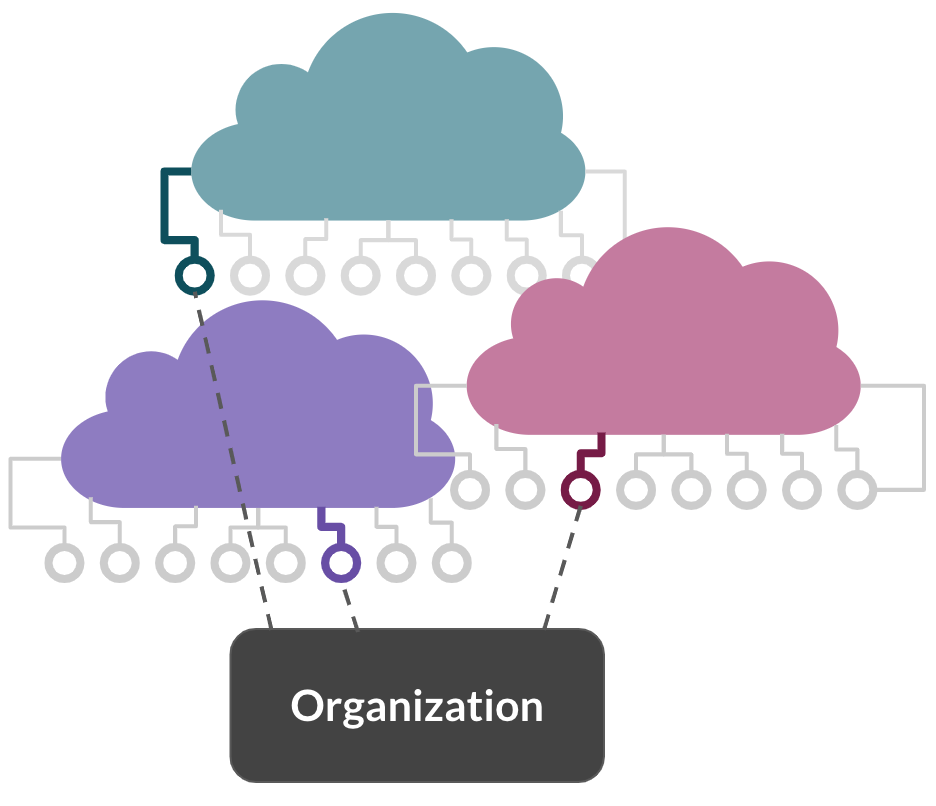
Other deployment models
- Multicloud
- Combination of different cloud provider services
- Flexibility on pricing plans and service offerings
- No reliance on one vendor
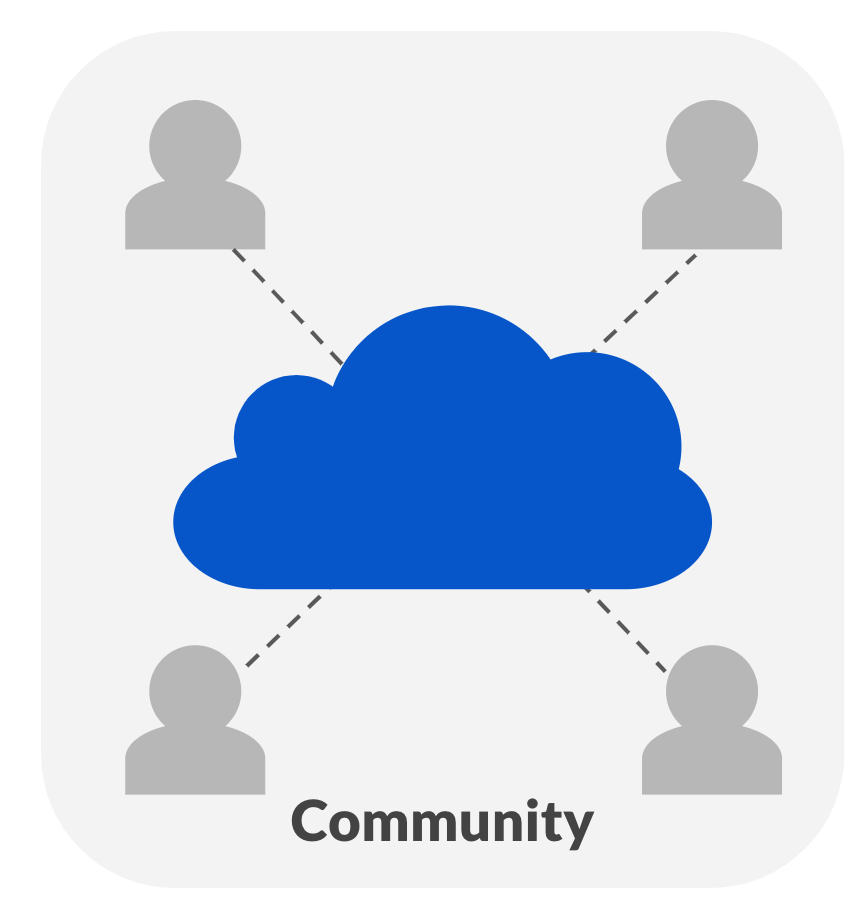
Other deployment models
- Community
- Infrastructure shared by a specific community for exclusive use
- Common interest or concern, e.g., security, jurisdiction, mission
- Can be managed and hosted internally or externally
Let's practice!
Understanding Cloud Computing

