Data Pipelines
Understanding Data Science

Sara Billen
Curriculum Manager
$$
$$
$$
How do we scale?
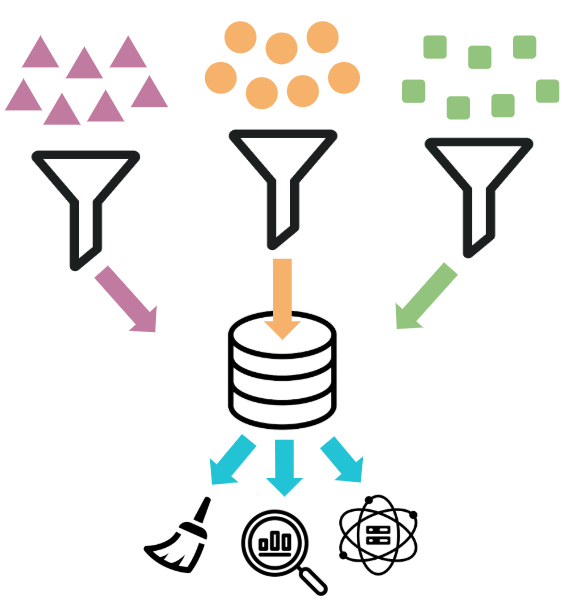
More than one data source:
- Public records
- APIs
- Databases
Different data types:
- Unstructured data
- Tabular data
- Real-time streaming data e.g., tweets
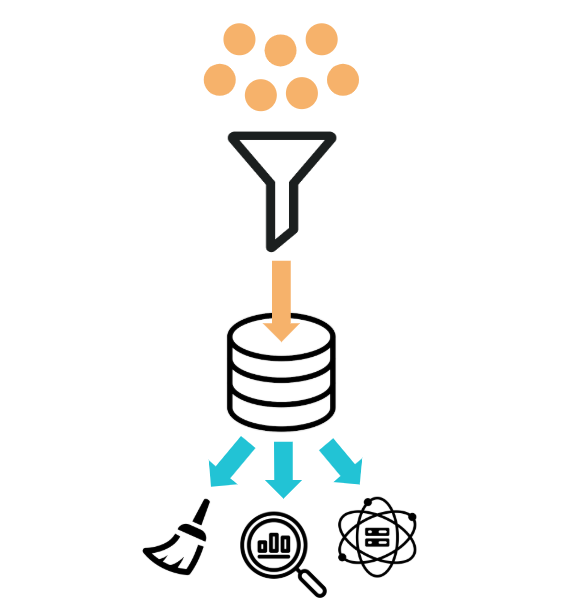
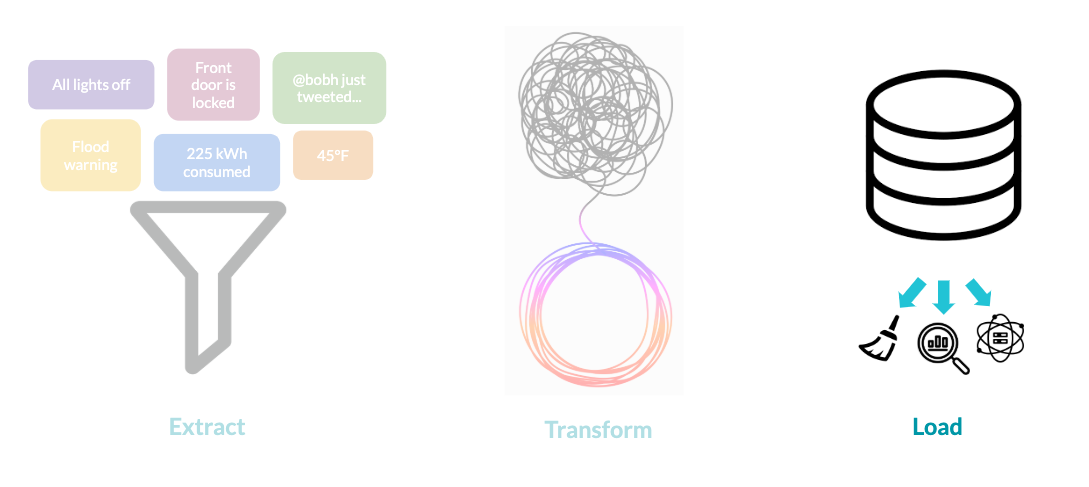
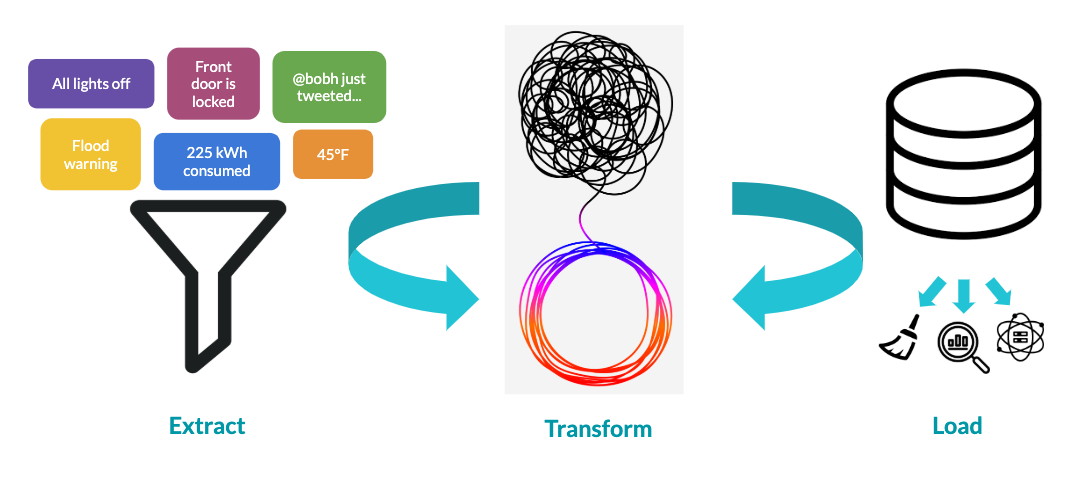
What is a data pipeline?
- Moves data into defined stages
- Automated collection and storage
- Scheduled hourly, daily, weekly, etc
- Triggered by an event
- Monitored with generated alerts
- Necessary for big data projects
- Data engineers work to customize solutions
- Extract Transform Load (ETL)

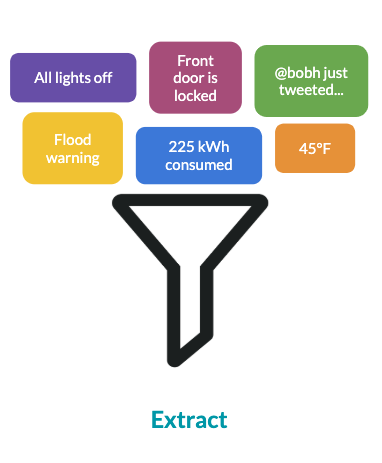
Case study: smart home
| Data | Source | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Weather conditions | National Weather Service API | Every 30 minutes |
| Tweets in your area | Twitter API | Real-time stream |
| Indoor temperature | Smart home thermostat | Every 5 minutes |
| Status of lights | Smart light bulbs | Every minute |
| Status of locks | Smart door locks | Every 15 seconds |
| Energy consumption | Smart meter | Weekly |
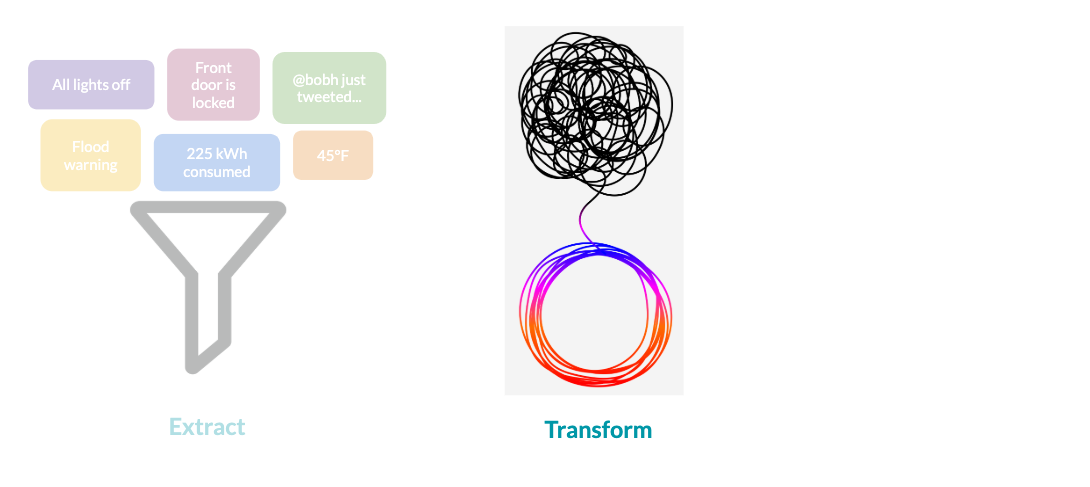
Extract
| Source | Frequency |
|---|---|
| National Weather API | Every 30 minutes |
| Twitter API | Real-time stream |
| Smart home thermostat | Every 5 minutes |
| Smart light bulbs | Every minute |
| Smart door locks | Every 15 seconds |
| Smart meter | Weekly |
Transform
Transform
With all the data coming in, how do we keep it organized and easy to use?
$$ Example transformations:
- Joining data sources into one data set
- Converting data structures to fit database schemas
- Removing irrelevant data
Data preparation and exploration does not occur at this stage
Load
Automation
Let's practice!
Understanding Data Science

