Filtering and counting with DAX
DAX Functions in Power BI

Maarten Van den Broeck
Content Developer at DataCamp
Filter functions
- Filters are applied on the filter context
- Filters take precedence over any visual
Total Sales = SUM(Orders[Sales])
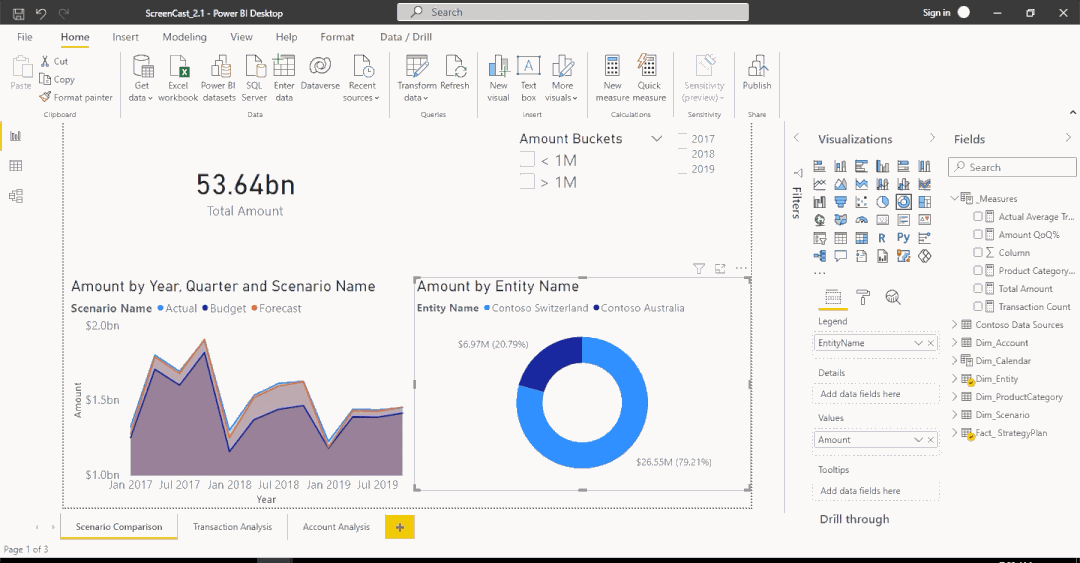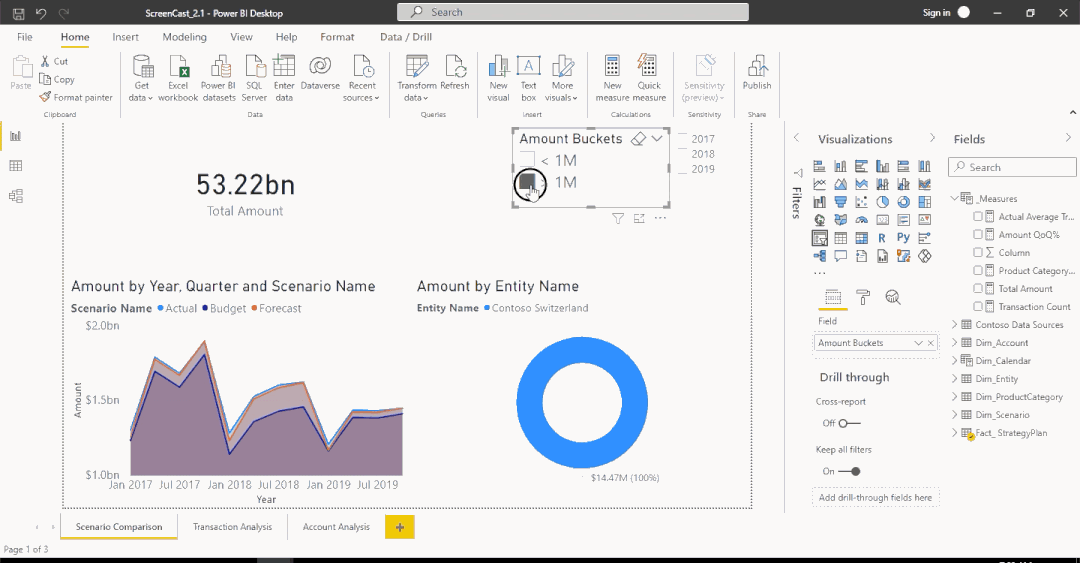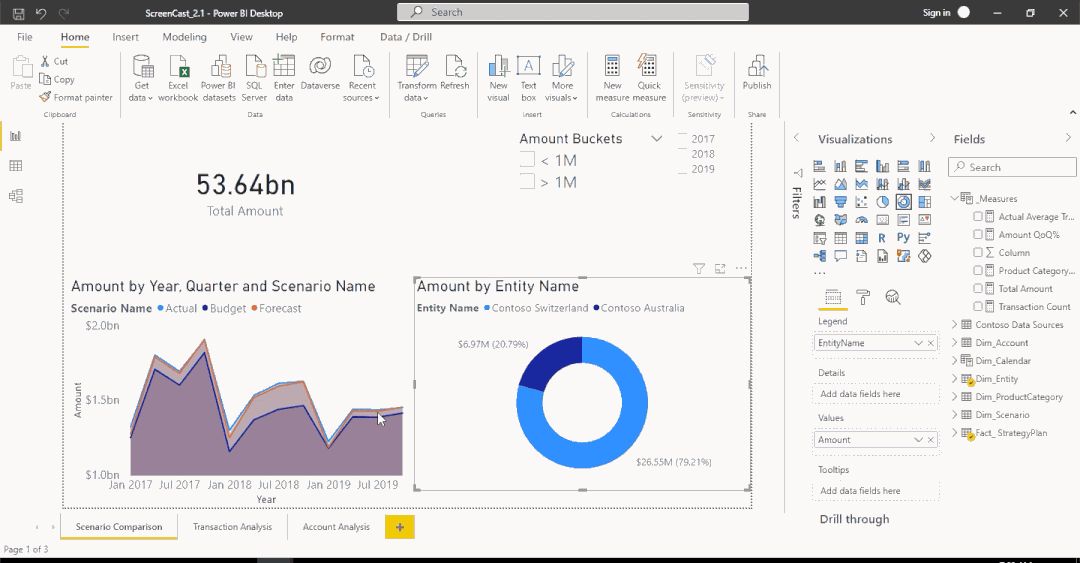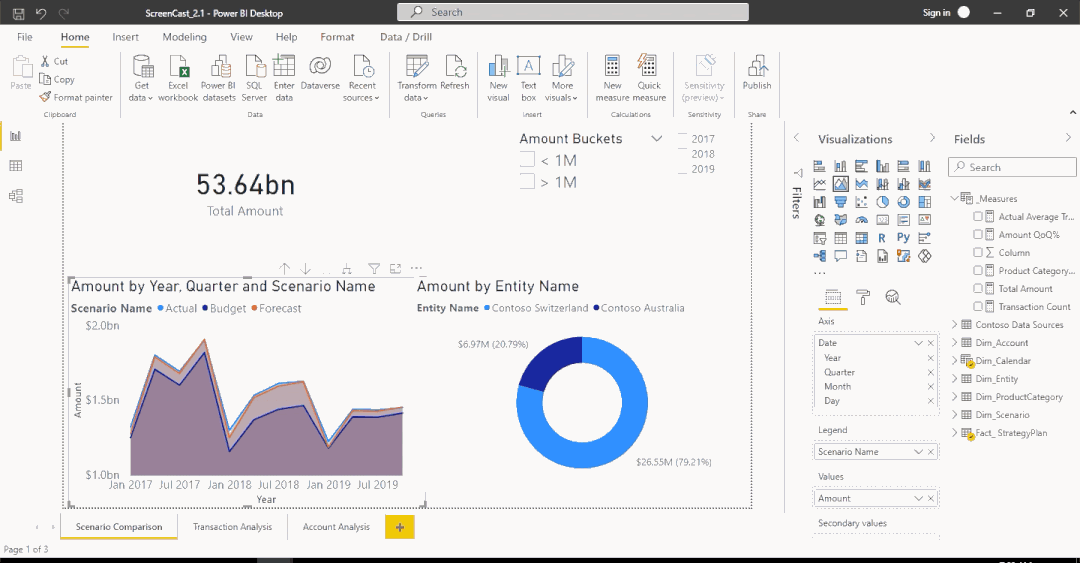
Filter functions
- Filters are applied on the filter context
- Filters take precedence over any visual
Total Sales = SUM(Orders[Sales])
CALCULATE(<expression>,
<filter1> , [<filter2> [, ...]])
- Used with intermediate functions
Total Sales ALL = CALCULATE(
[Total Sales],
ALL(Orders))
$$ $$ $$
| Region | Total Sales |
|---|---|
| Central | $501,239.89 |
| East | $678,781.24 |
| South | $391,721.91 |
| West | $725,457.82 |
| TOTAL | $2,297,200.86 |
Filter functions
- Filters are applied on the filter context
- Filters take precedence over any visual
Total Sales = SUM(Orders[Sales])
CALCULATE(<expression>,
<filter1> , [<filter2> [, ...]])
- Used with intermediate functions
Total Sales ALL = CALCULATE(
[Total Sales],
ALL(Orders))
$$ $$ $$
| Region | Total Sales | Total Sales ALL |
|---|---|---|
| Central | $501,239.89 | $2,297,200.86 |
| East | $678,781.24 | $2,297,200.86 |
| South | $391,721.91 | $2,297,200.86 |
| West | $725,457.82 | $2,297,200.86 |
| TOTAL | $2,297,200.86 | $2,297,200.86 |
More filter options
FILTER(<table>, <filter>)- Returns a filtered table
Total Sales Chuck =
CALCULATE(
[Total Sales],
FILTER(Fact_Orders,
RELATED(Dim_Sales[Salesperson]) = "Chuck"))
More filter options
FILTER(<table>, <filter>)- Returns a filtered table
Total Sales Chuck =
CALCULATE(
[Total Sales],
FILTER(Fact_Orders,
RELATED(Dim_Sales[Salesperson]) = "Chuck"))
| Total Sales | Total Sales Chuck |
|---|---|
| $2,297,200.86 | $235,856.05 |
$$
RELATED()is used to return values from another table
More filter options
CROSSFILTER(<col1>, <col2>, <direction>)- Specifies the cross-filtering direction between two columns
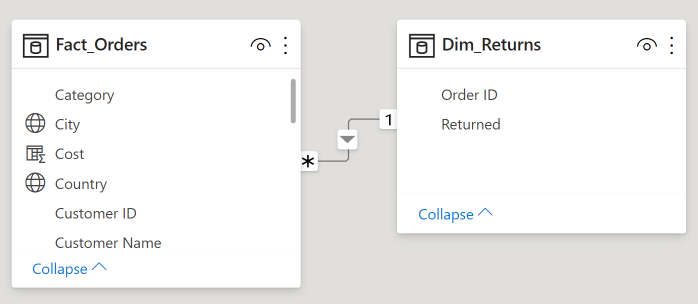
CROSSFILTER(Dim_Returns[Order ID],
Fact_Orders[Order ID],
Both)
- Overrides relationship direction of data model
The benefits of filtering in DAX
- Improves performance
- Filter out unnecessary data
- Define specific relationships between tables
- Reusability
- Refer to other calculated measures
- More complex computations
- Concise syntax
Counting
COUNT(<column>)- Returns the amount of rows with numbers, dates, or strings in a column
COUNTA(<column>)- Returns the amount of rows with numbers, dates, strings, or booleans in a column
COUNTBLANKS(<column>)- Returns the amount of blank rows
DISTINCTCOUNT(<column>)- Returns the amount of distinct values in a column
COUNTROWS(<table>)- Returns the amount of rows with numbers, dates, and strings in a table
Let's practice!
DAX Functions in Power BI

