Introducing arrays
Introduction to NumPy

Izzy Weber
Core Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
NumPy and the Python ecosystem
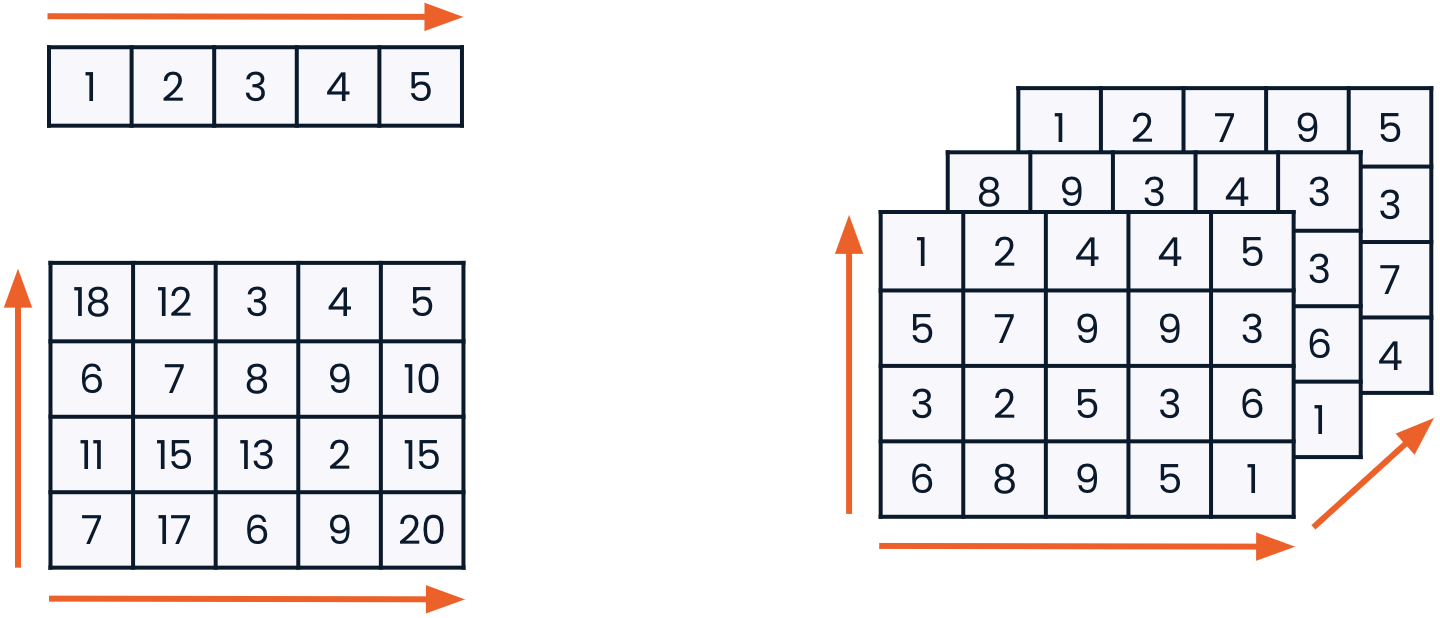
NumPy arrays
Importing NumPy
import numpy as np
Creating 1D arrays from lists
python_list = [3, 2, 5, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6, 1]
array = np.array(python_list)
array
array([3, 2, 5, 8, 4, 9, 7, 6, 1])
type(array)
numpy.ndarray
Creating 2D arrays from lists
python_list_of_lists = [[3, 2, 5],
[9, 7, 1],
[4, 3, 6]]
np.array(python_list_of_lists)
array([[3, 2, 5],
[9, 7, 1],
[4, 3, 6]])
Python lists
- Can contain many different data types
python_list = ["beep", False, 56, .945, [3, 2, 5]]
NumPy arrays
- Can contain only a single data type
- Use less space in memory
numpy_boolean_array = [[True, False], [True, True], [False, True]]
numpy_float_array = [1.9, 5.4, 8.8, 3.6, 3.2]
Creating arrays from scratch
There are many NumPy functions used to create arrays from scratch, including:
np.zeros()np.random.random()np.arange()
Creating arrays: np.zeros()
np.zeros((5, 3))
array([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
Creating arrays: np.random.random()
np.random.random((2, 4))
array([[0.88524516, 0.85641352, 0.33463107, 0.53337117],
[0.69933362, 0.09295327, 0.93616428, 0.03601592]])
Creating arrays with np.arange()
np.arange(-3, 4)
array([-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3])
np.arange(4)
array([0, 1, 2, 3])
np.arange(-3, 4, 3)
array([-3, 0, 3])
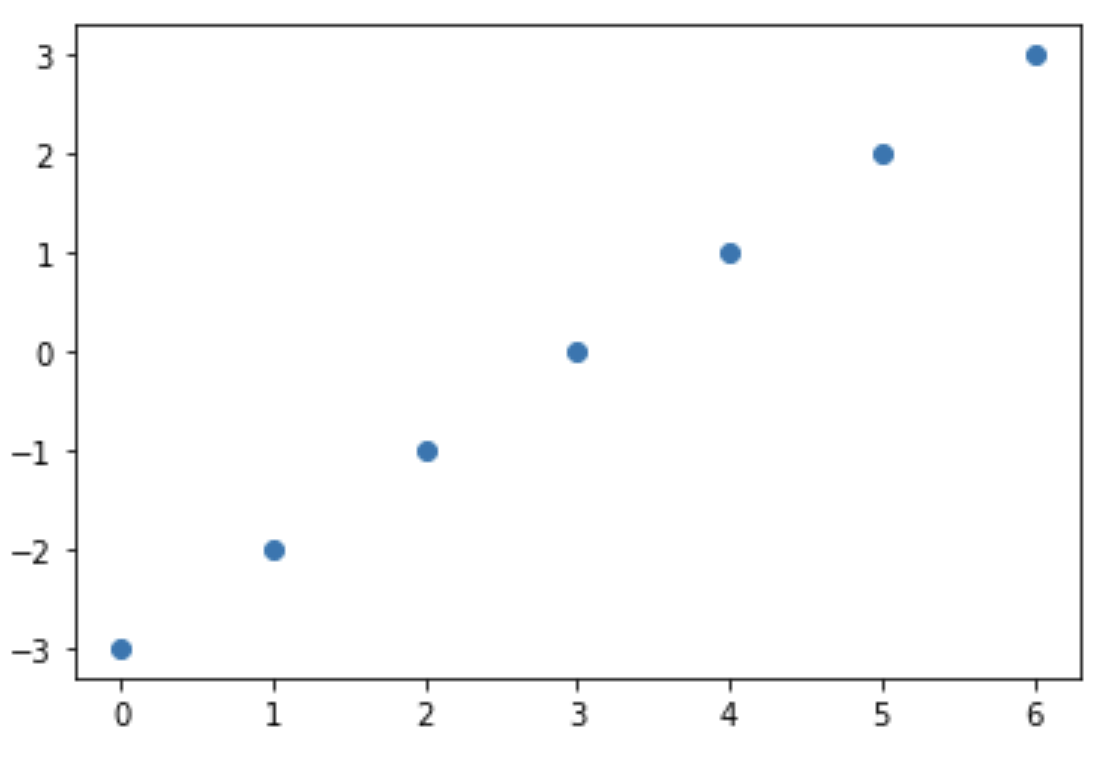
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.scatter(np.arange(0, 7),
np.arange(-3, 4))
plt.show()
Let's practice!
Introduction to NumPy

