Executar uma passagem direta
Introdução ao Aprendizado Profundo com o PyTorch

Jasmin Ludolf
Senior Data Science Content Developer, DataCamp
O que é passagem direta?
$$
- Dados de entrada fluem pelas camadas
- Cálculos realizados em cada camada
- A camada final gera resultados
$$
- Resultados com base em pesos e vieses
- Usado para treinar e fazer previsões
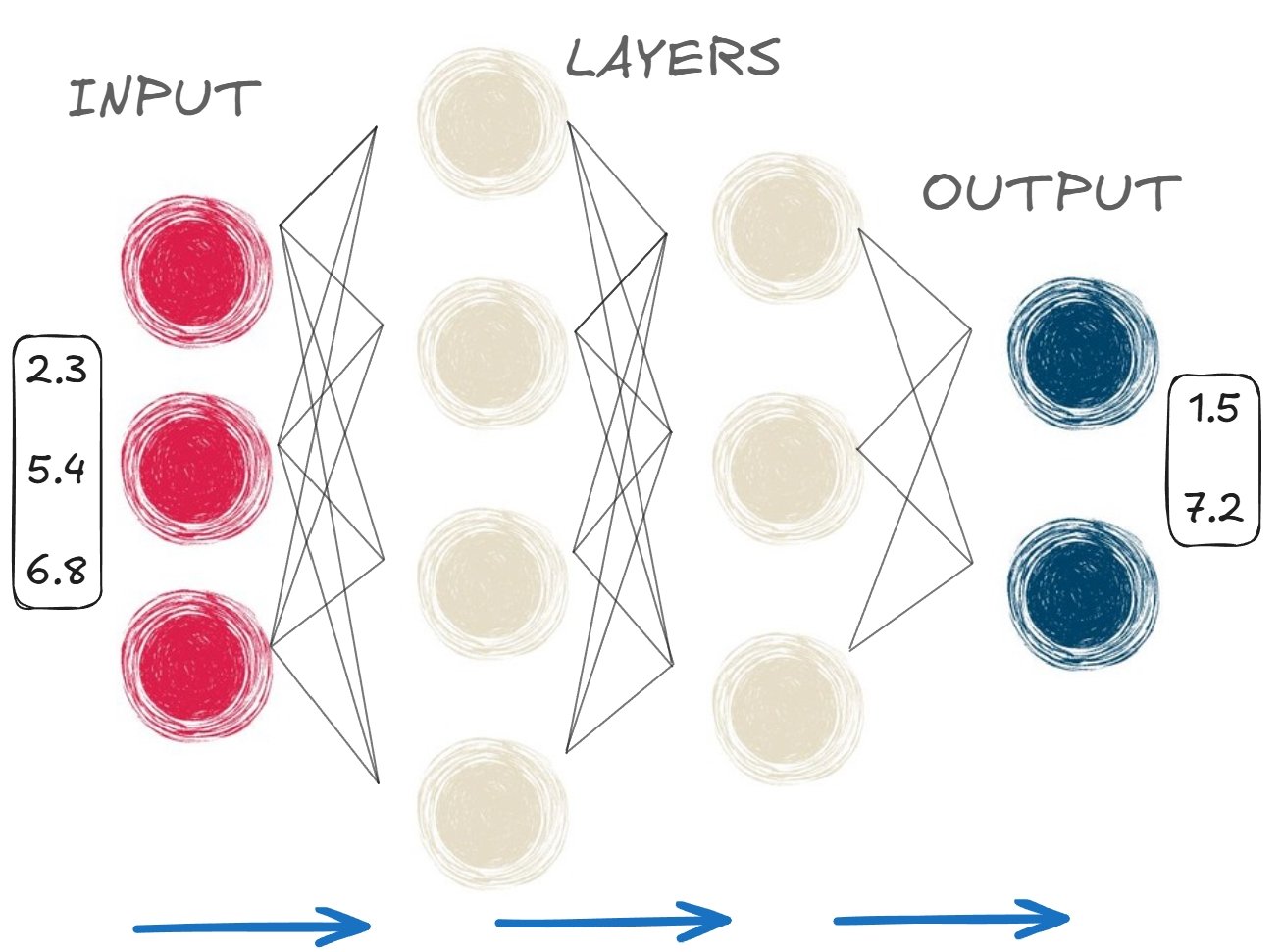
O que é passagem direta?
$$
Possíveis saídas:
- Classificação binária
- Classificação multiclasse
- Regressões
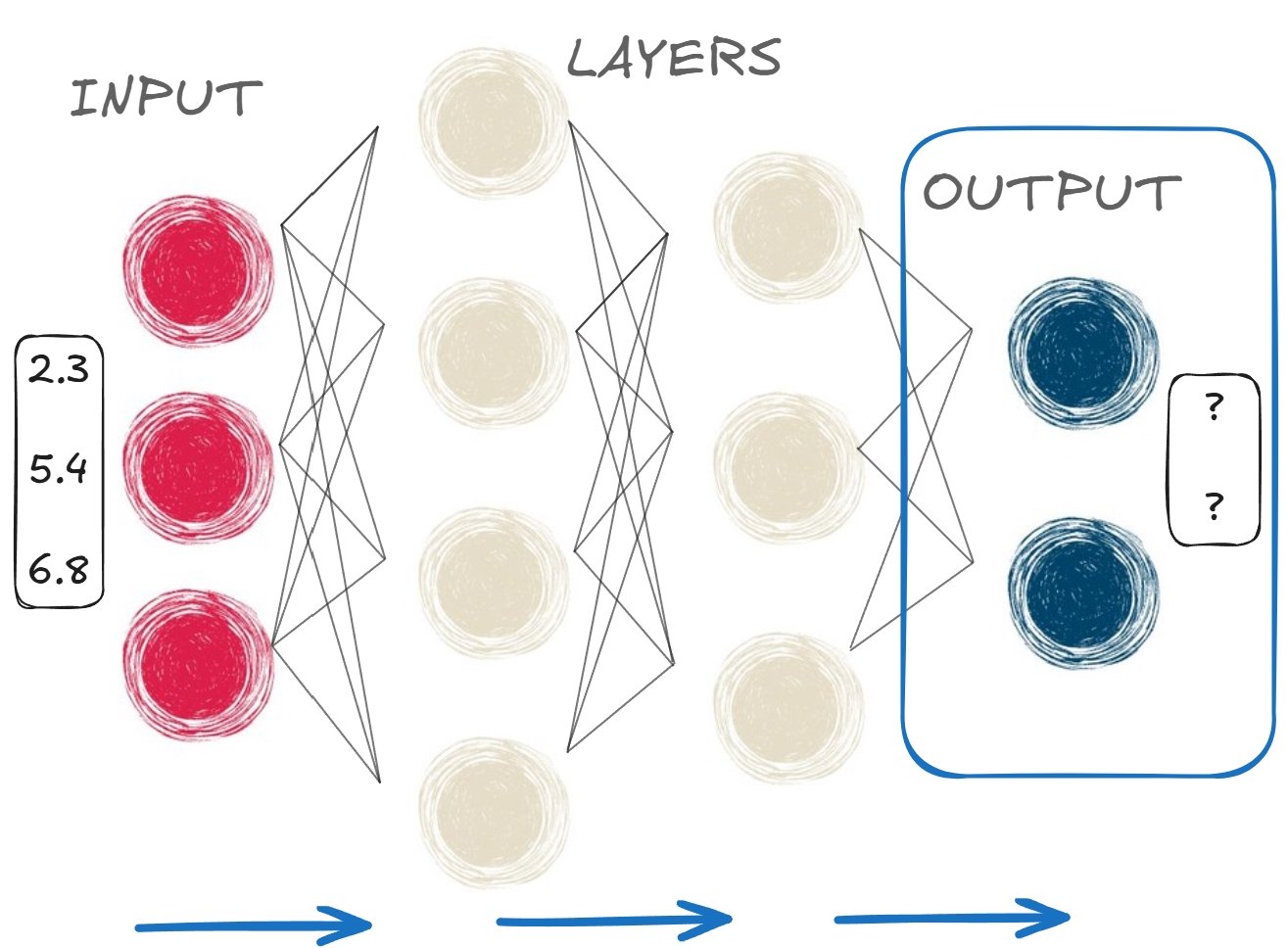
Classificação binária: passagem direta

# Create binary classification model
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(6, 4), # First linear layer
nn.Linear(4, 1), # Second linear layer
nn.Sigmoid() # Sigmoid activation function
)
Classificação binária: passagem direta
# Pass input data through model
output = model(input_data)
print(output)
tensor([[0.5188], [0.3761], [0.5015], [0.3718], [0.4663]],
grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward0>)
Saída: cinco probabilidades entre 0 e 1, uma para cada animal
Classificação (limite de 0.5):
- Classe = 1 (mamífero) para valores ≥ 0.5 (
0.5188,0.5015) - Classe = 0 (não mamífero) para valores < 0.5 (
0.3761,0.3718,0.4633)
- Classe = 1 (mamífero) para valores ≥ 0.5 (
Classificação multiclasse: passagem direta
- Classe 1: mamífero, classe 2: ave, classe 3: réptil
n_classes = 3# Create multi-class classification model model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(6, 4), # First linear layer nn.Linear(4, n_classes), # Second linear layernn.Softmax(dim=-1) # Softmax activation )# Pass input data through model output = model(input_data) print(output.shape)
torch.Size([5, 3])
Classificação multiclasse: passagem direta

- Cada linha soma um
- Rótulo previsto = classe com a maior probabilidade
- Linha 1 = classe 1 (mamífero), linha 2 = classe 1 (mamífero), linha 3 = classe 3 (réptil)
Regressão: passagem direta
# Create regression model
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(6, 4), # First linear layer
nn.Linear(4, 1) # Second linear layer
)
# Pass input data through model
output = model(input_data)
# Return output
print(output)
tensor([[0.3818],
[0.0712],
[0.3376],
[0.0231],
[0.0757]],
grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>)
Vamos praticar!
Introdução ao Aprendizado Profundo com o PyTorch

