Conditional probability
Introdução à estatística

George Boorman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Multiple meetings
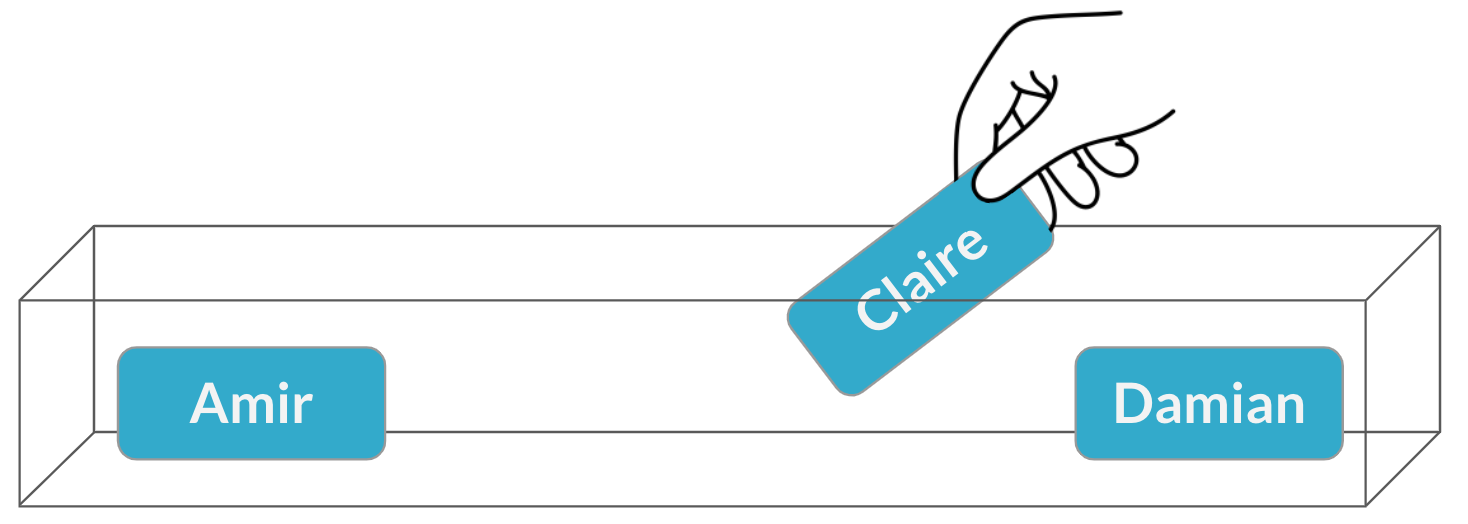
Sampling without replacement

Multiple meetings
Sampling without replacement
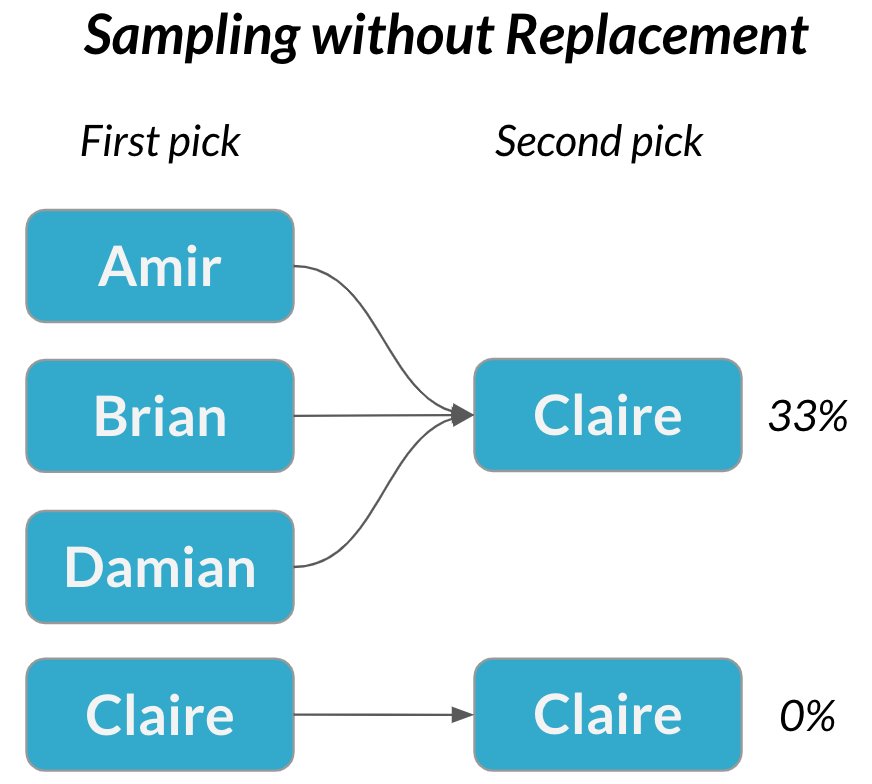
$$P(\text{Claire}) = \frac{1}{3} = 33\%$$
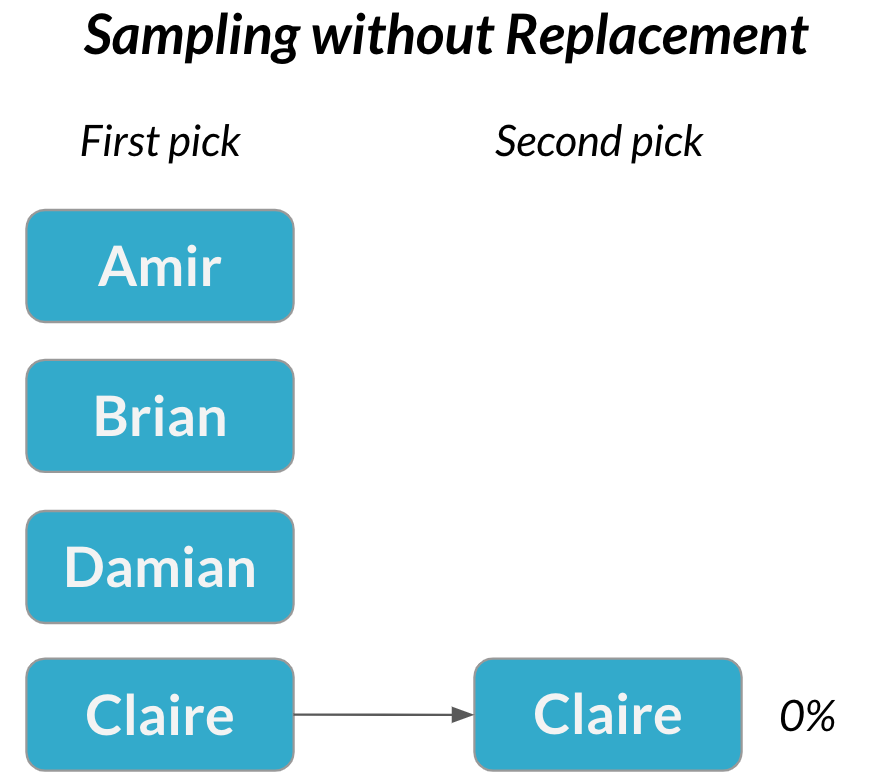
Dependent events
Probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event
Dependent events
Probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event
Dependent events
Probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event
Sampling without replacement = each pick is dependent
Conditional probability
Conditional probability is used to calculate the probability of dependent events
- The probability of one event is conditional on the outcome of another

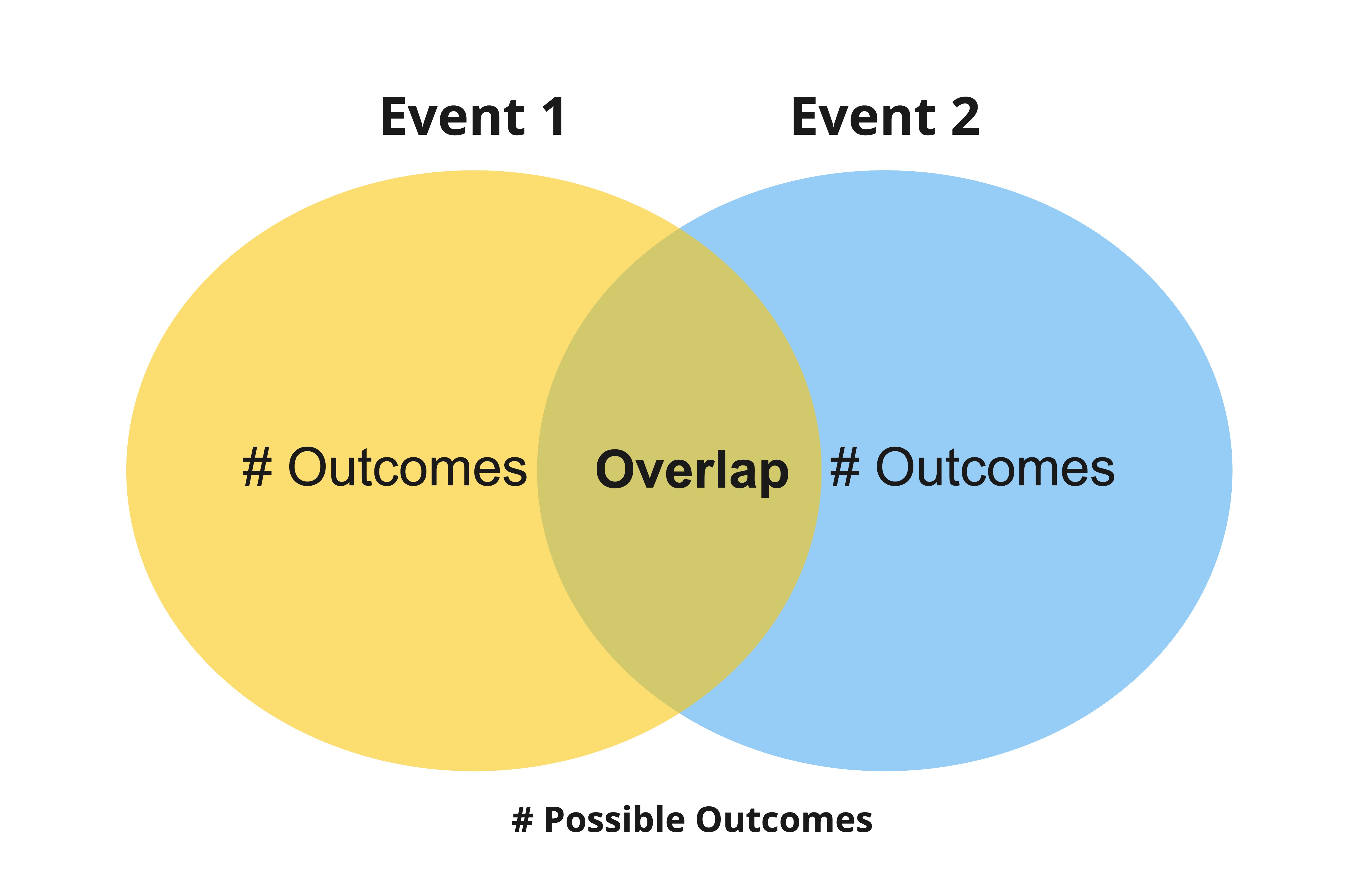
Venn diagrams
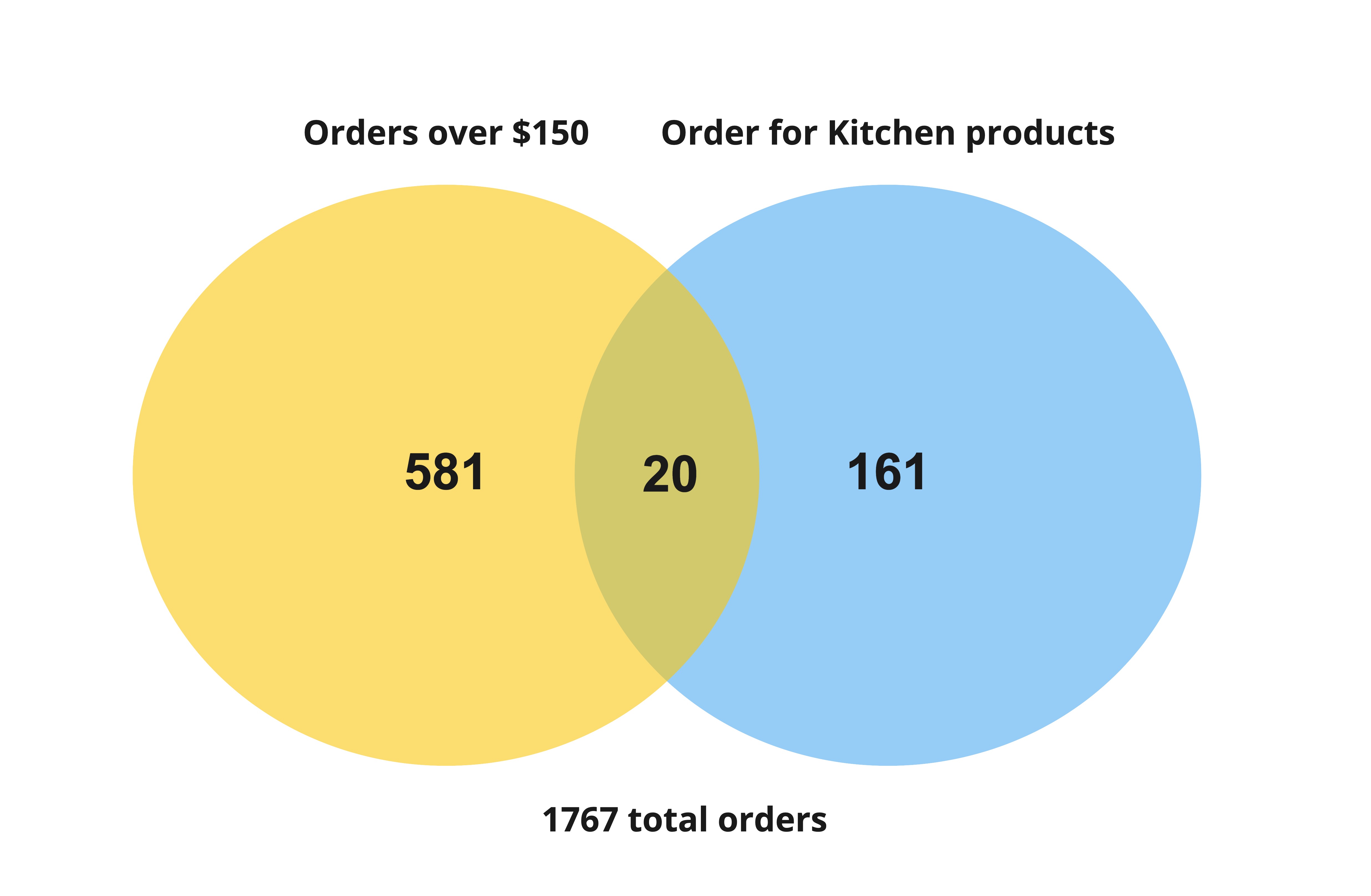
Kitchen sales over $150
Kitchen sales over $150

$$P(Order > 150 | Kitchen) = \frac{\frac{20}{1767}}{\frac{181}{1767}}$$
$$P(Order > 150 | Kitchen) = \frac{20}{181} $$
The order of events matters
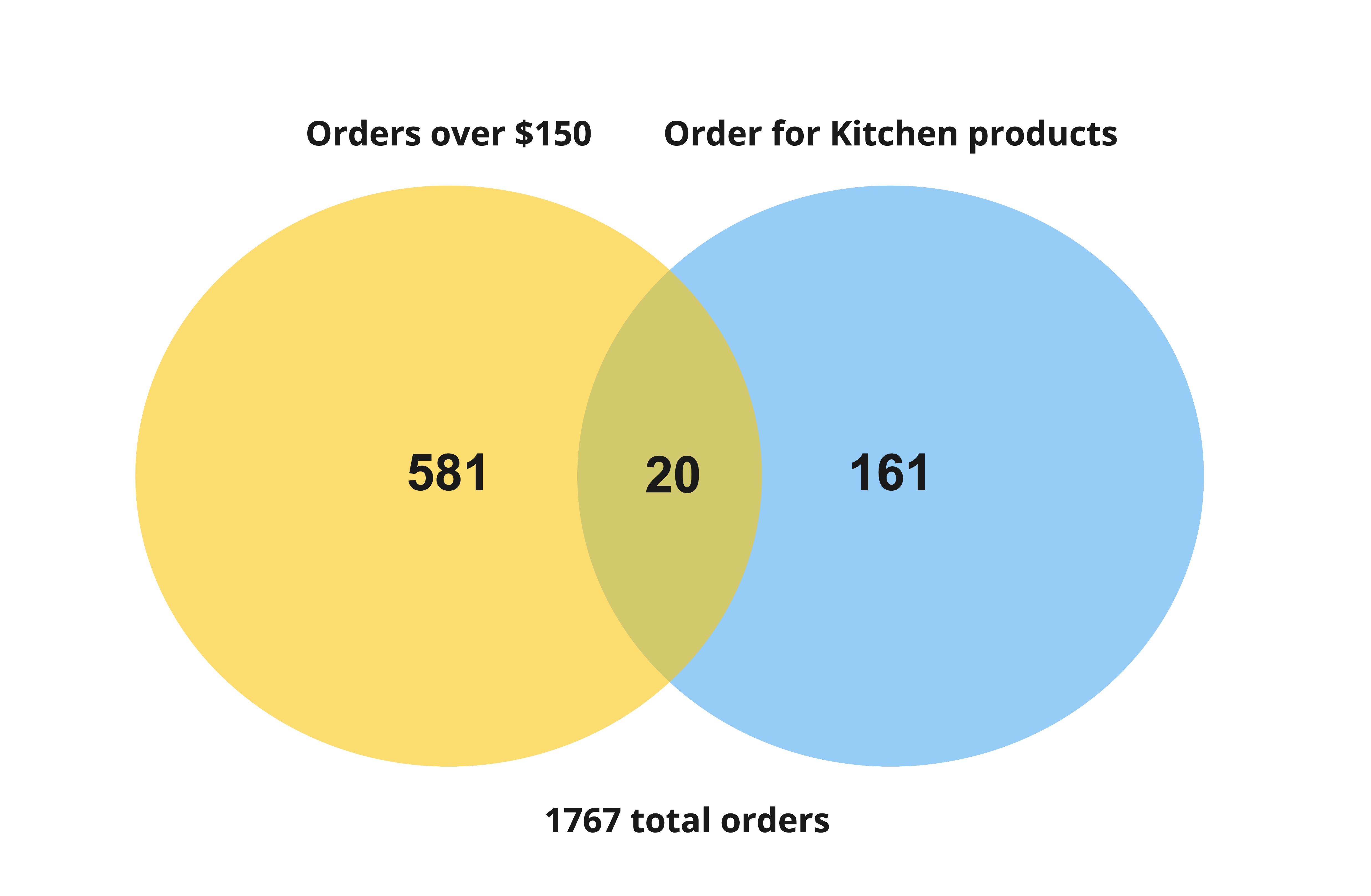
$$P(Kitchen | Order > 150) = \frac{\frac{20}{1767}}{\frac{601}{1767}}$$
$$P(Kitchen | Order > 150) = \frac{20}{601} $$
Conditional probability formula
$$P(A | B) = \frac{{P(A \ \cap \ B)}}{{P(B)}}$$
$P(A | B)$ → Probability of event A, given event B
$P(A \ \cap \ B)$ → Probability of event A and event B
- Divided by the probability of event B → $P(B)$
Let's practice!
Introdução à estatística

