Diskrete Verteilungen
Einführung in die Statistik

George Boorman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Würfeln
Auswahl von Vertrieblern
Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilung
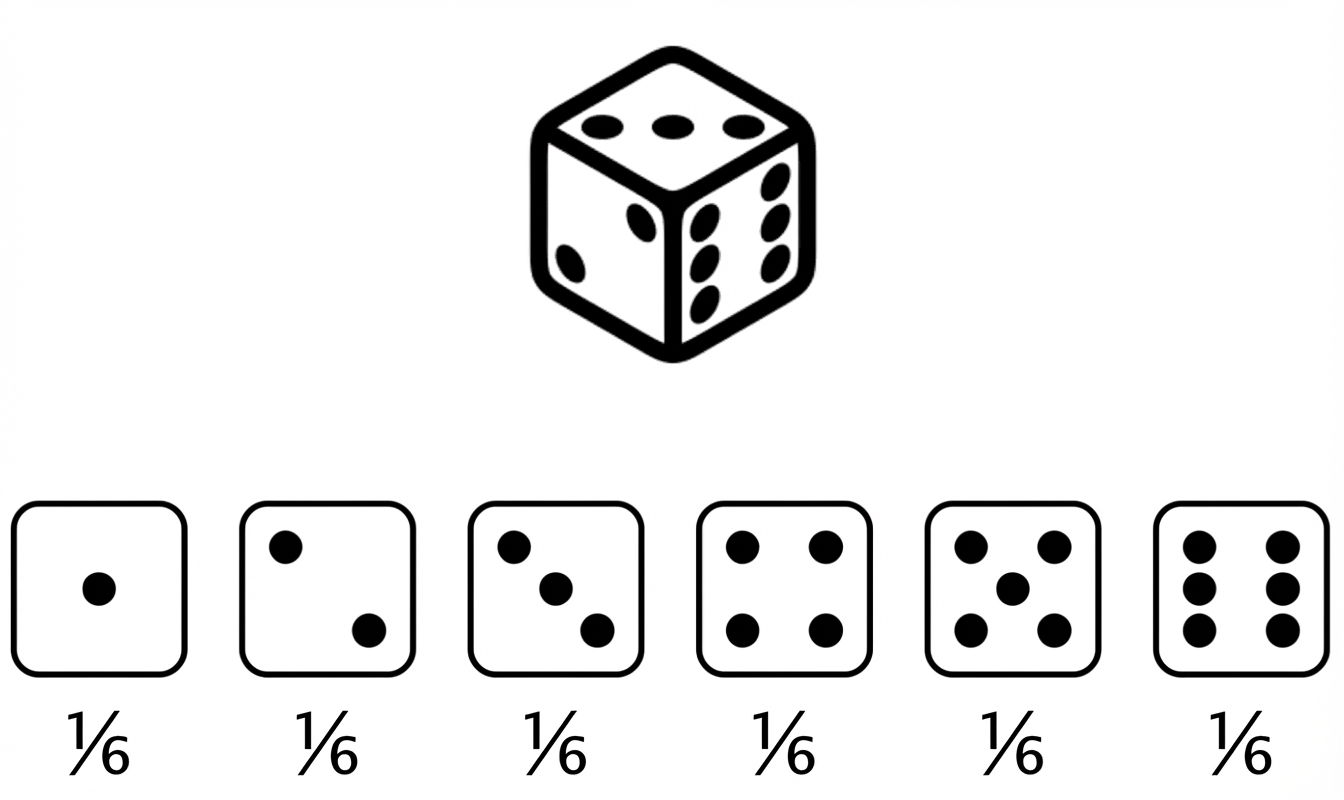
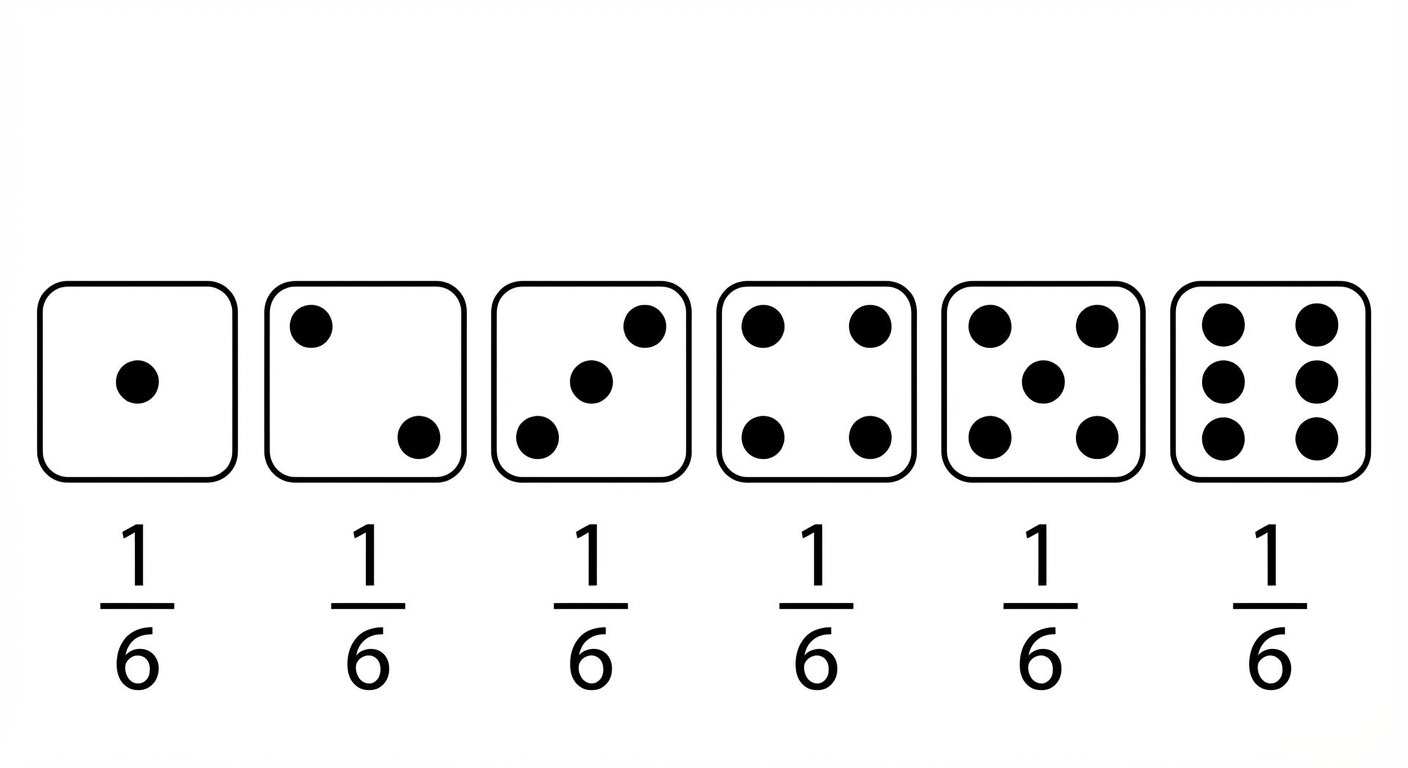
Beschreibt die Wahrscheinlichkeit eines jeden möglichen Ergebnisses in einem Szenario
Erwartungswert: Die Mittelwert einer Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilung
Erwarteter Wert eines fairen Würfelwurfs = $(1 \times \frac{1}{6}) + (2 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(3 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(4 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(5 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(6 \times \frac{1}{6}) = 3,5$
Warum sind Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen wichtig?
- Hilf uns, Risiken zu quantifizieren und Entscheidungen zu treffen
- Wird häufig bei Hypothesentests verwendet
- Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass die Ergebnisse zufällig entstanden sind

Visualisierung einer Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilung
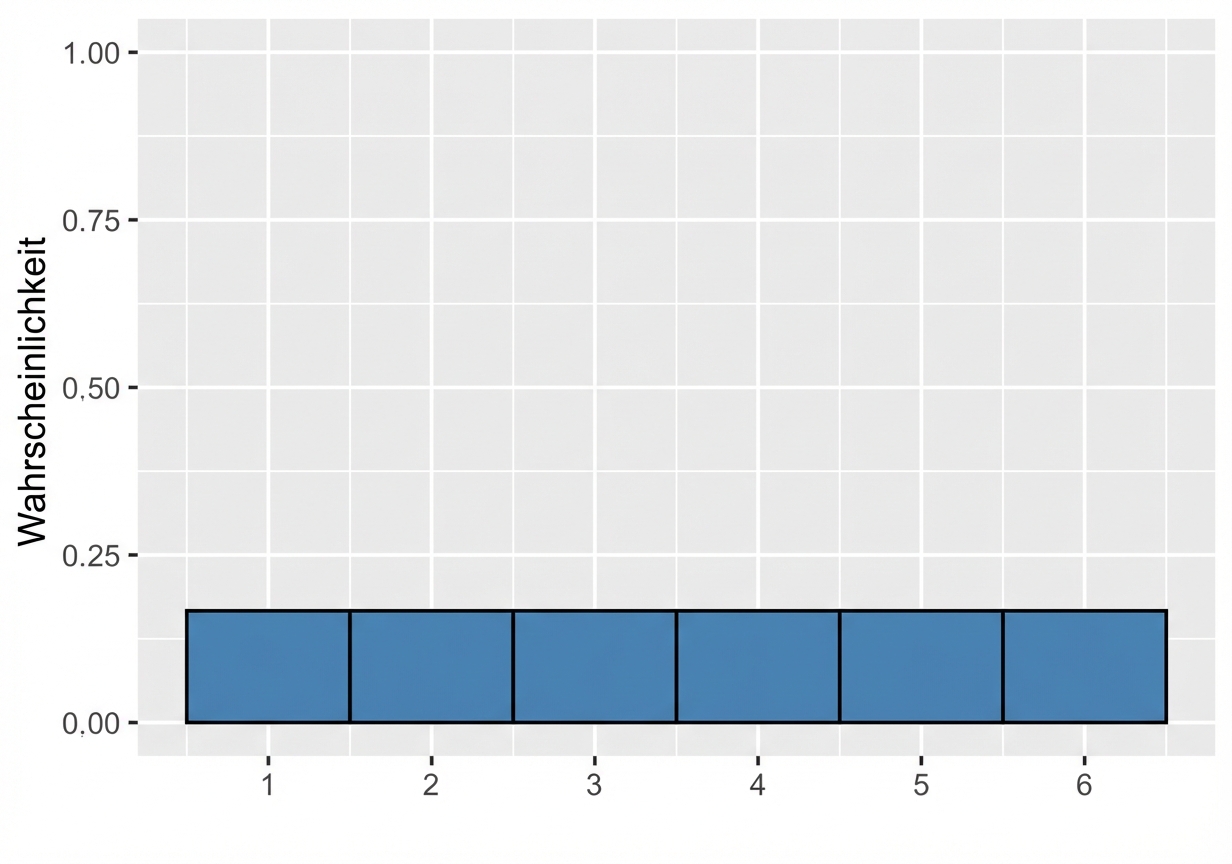
Wahrscheinlichkeit = Fläche
$$P(\text{Würfelwurf}) \le 2 = ~?$$
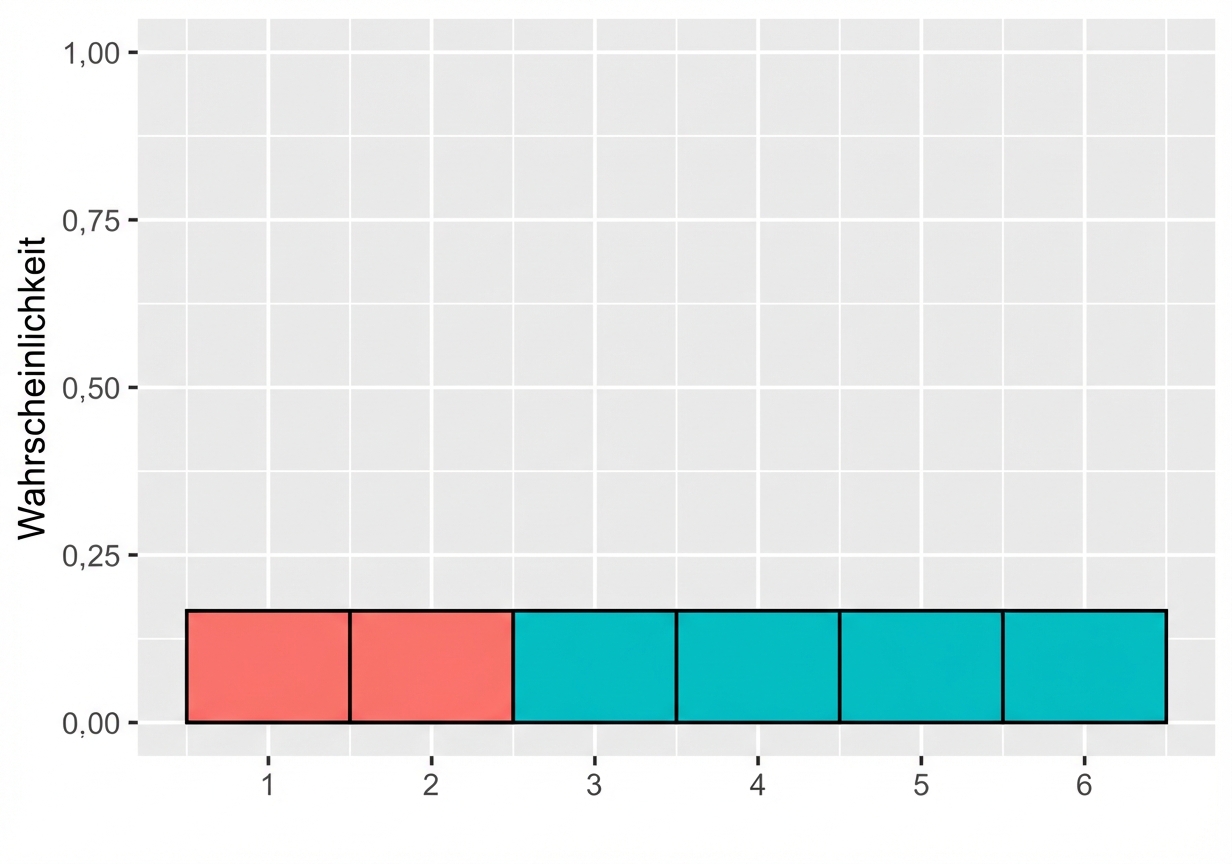
Wahrscheinlichkeit = Fläche
$$P(\text{Würfelwurf}) \le 2 = 1/3$$
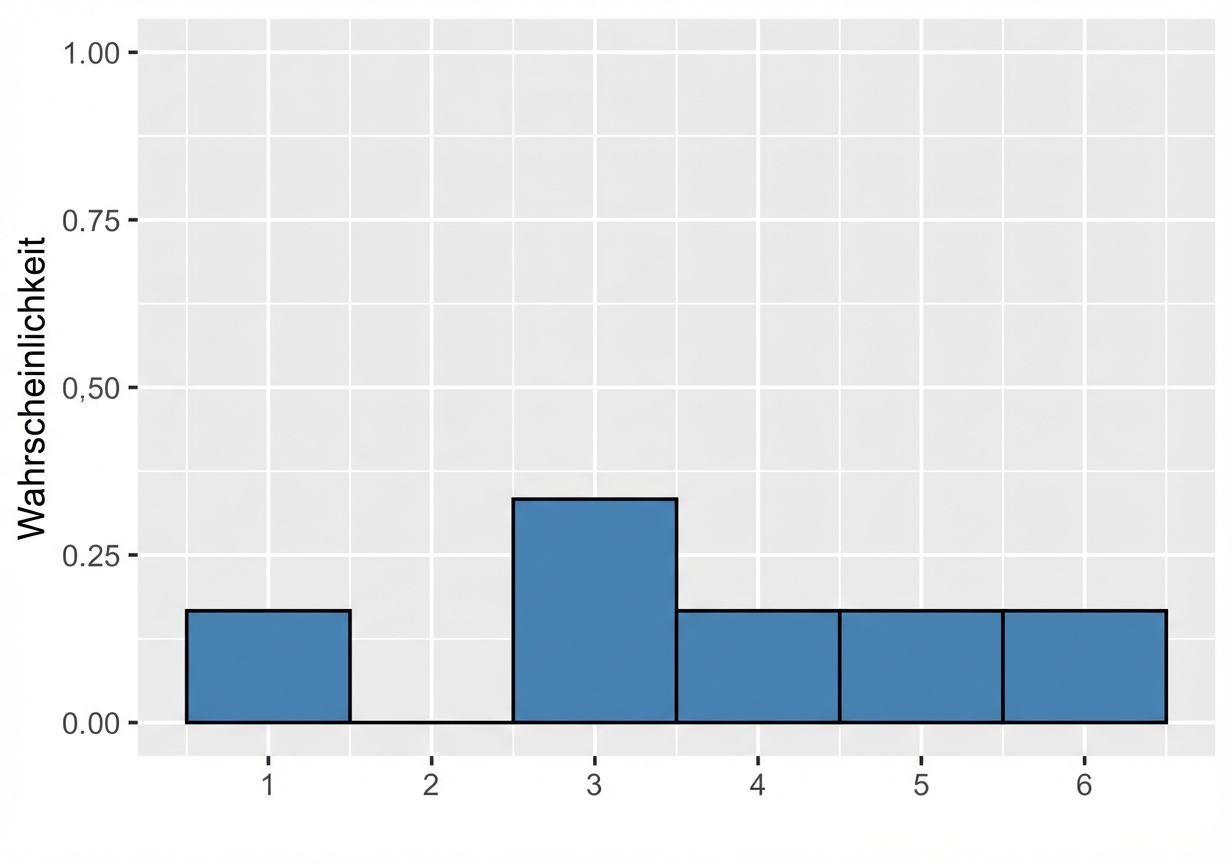
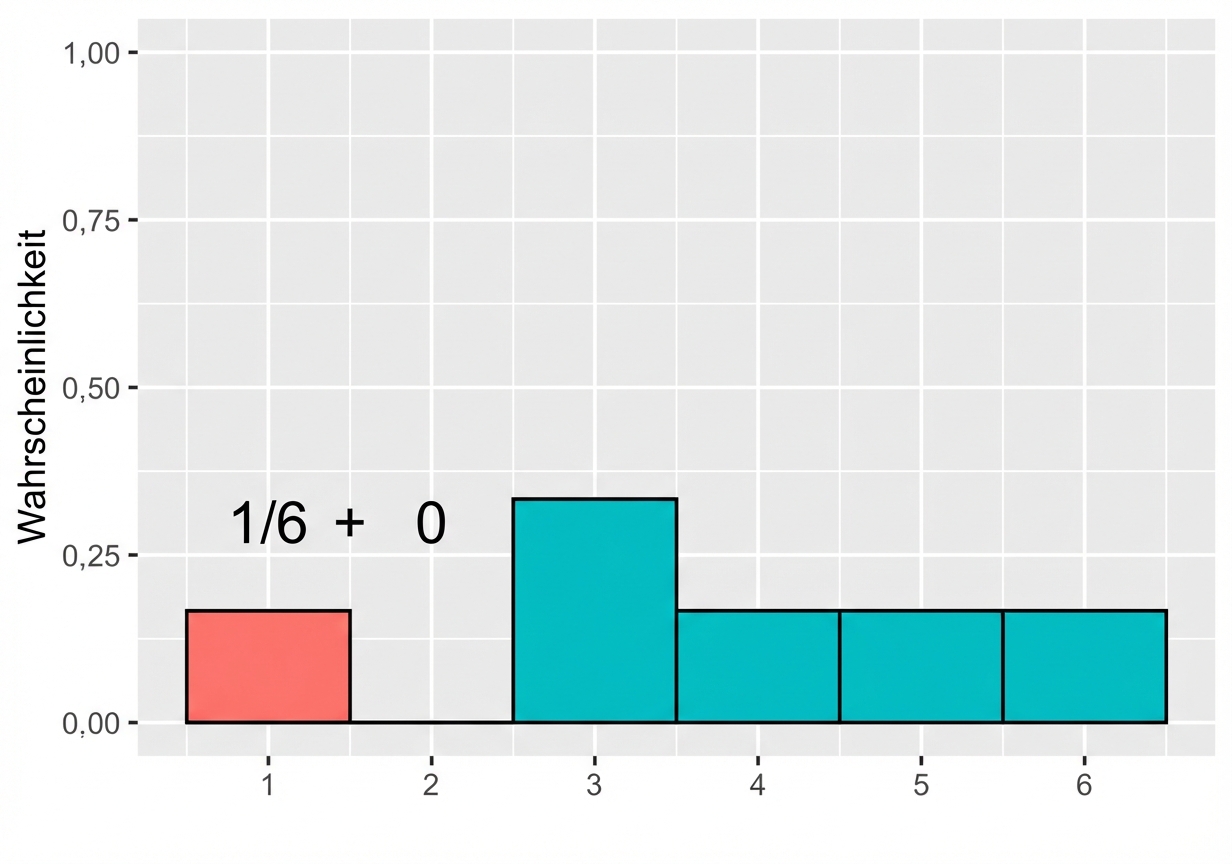
Ungerader Würfel
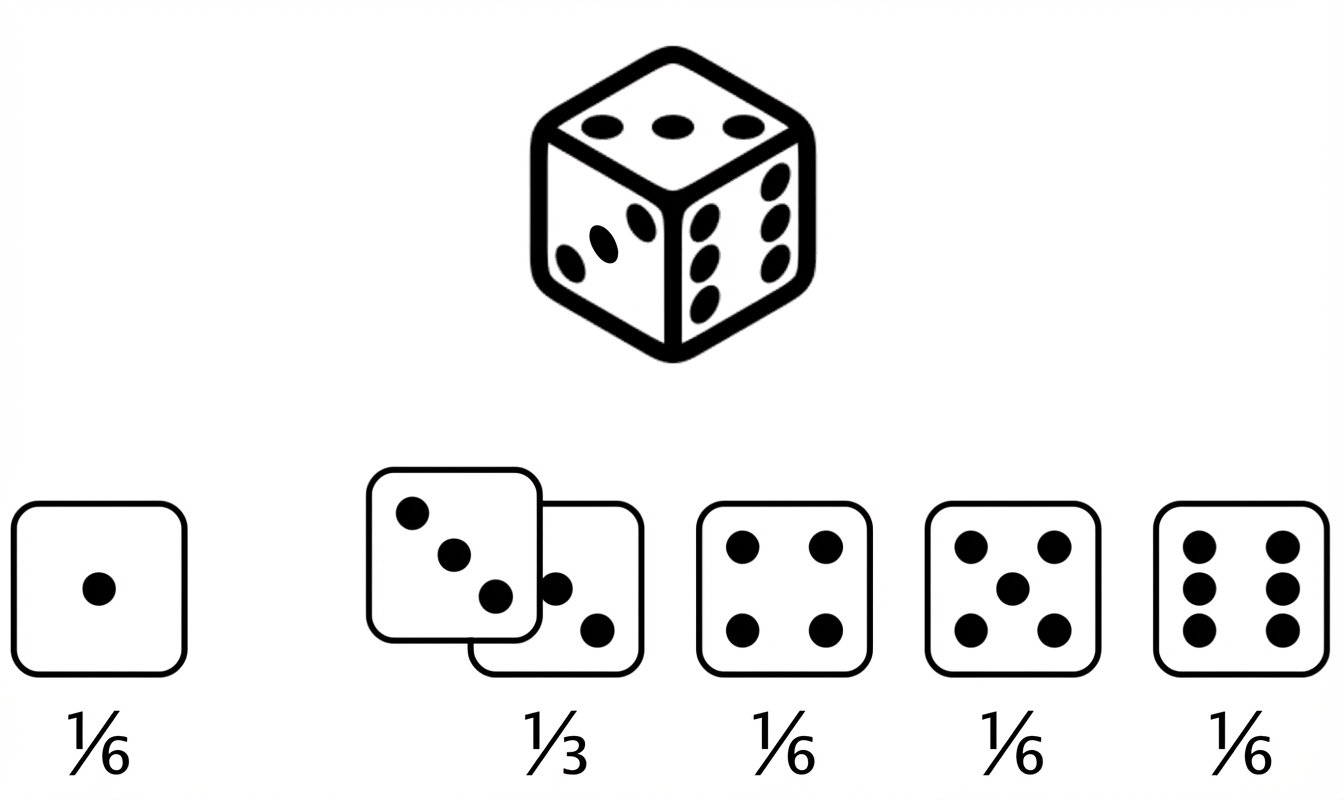
Erwarteter Wert eines ungeraden Würfelwurfs = $(1 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(2 \times 0) +(3 \times \frac{1}{3}) +(4 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(5 \times \frac{1}{6}) +(6 \times \frac{1}{6}) = 3,67 $
Visualisieren ungleichverteilter Wahrscheinlichkeiten
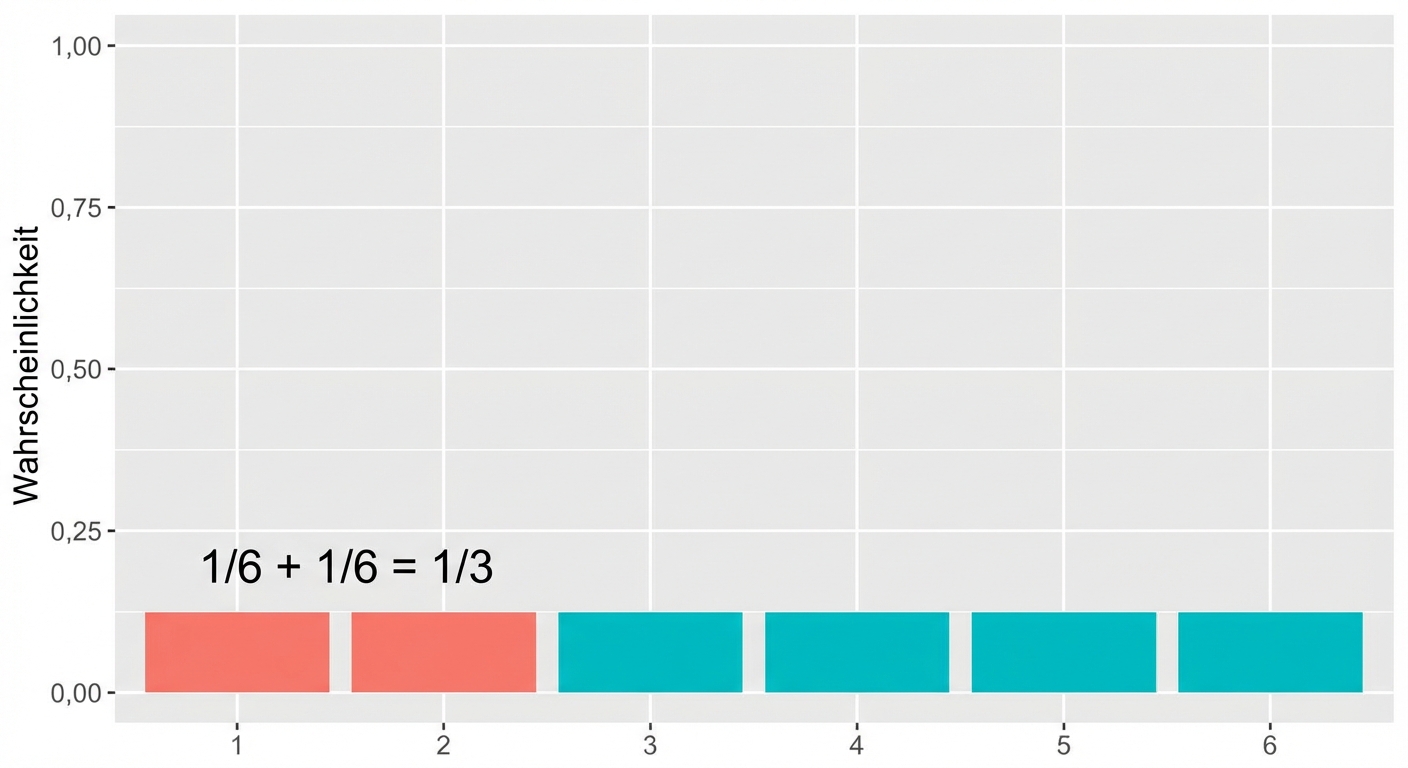
Hinzufügen von Flächen
$$P(\text{Ungerader Würfelwurf}) \le 2 = ~?$$
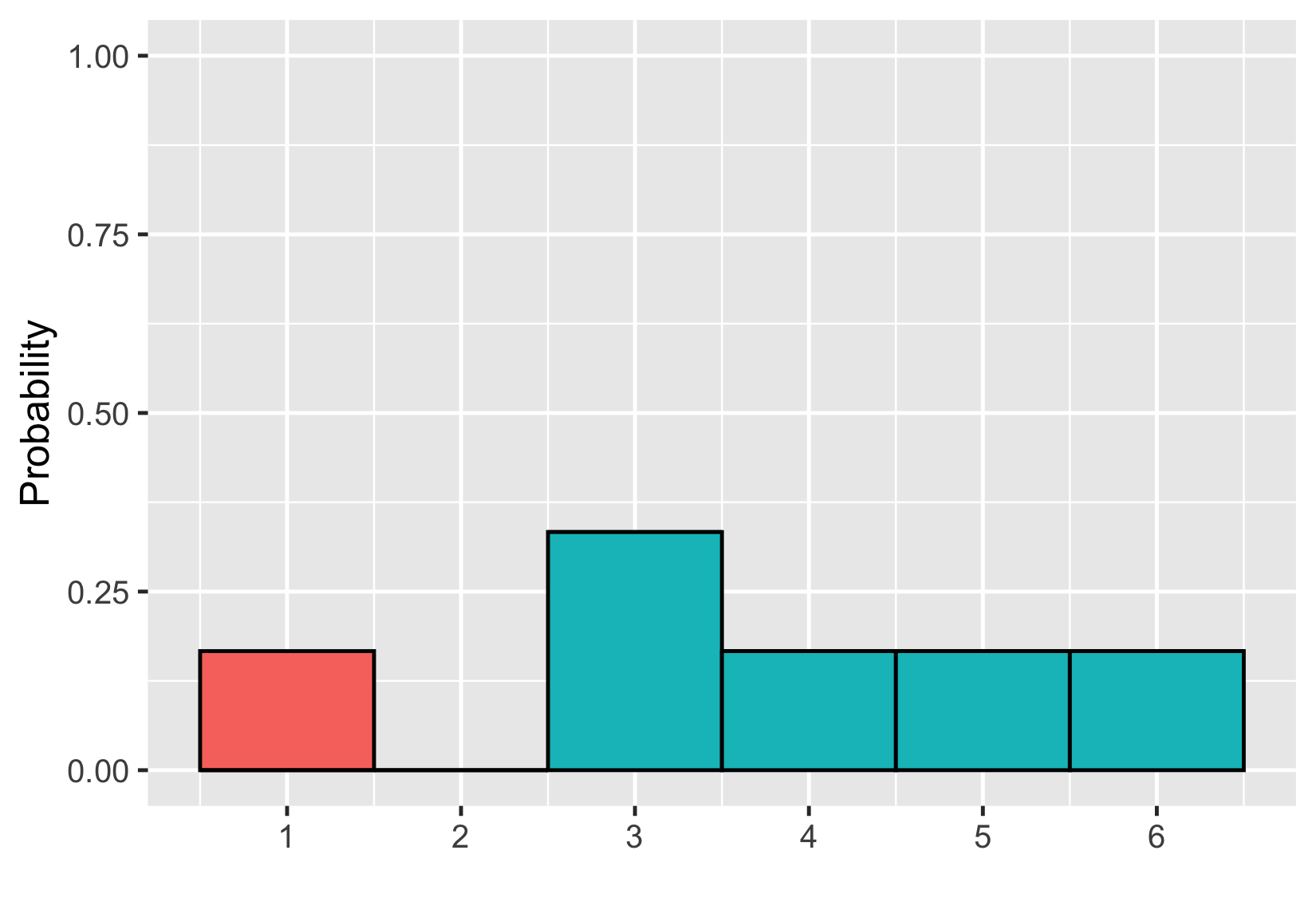
Hinzufügen von Flächen
$$P(\text{Ungerader Würfelwurf}) \le 2 = 1/6$$
Diskrete Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen
Beschreibe Wahrscheinlichkeiten für diskrete Ergebnisse
Fairer Würfel
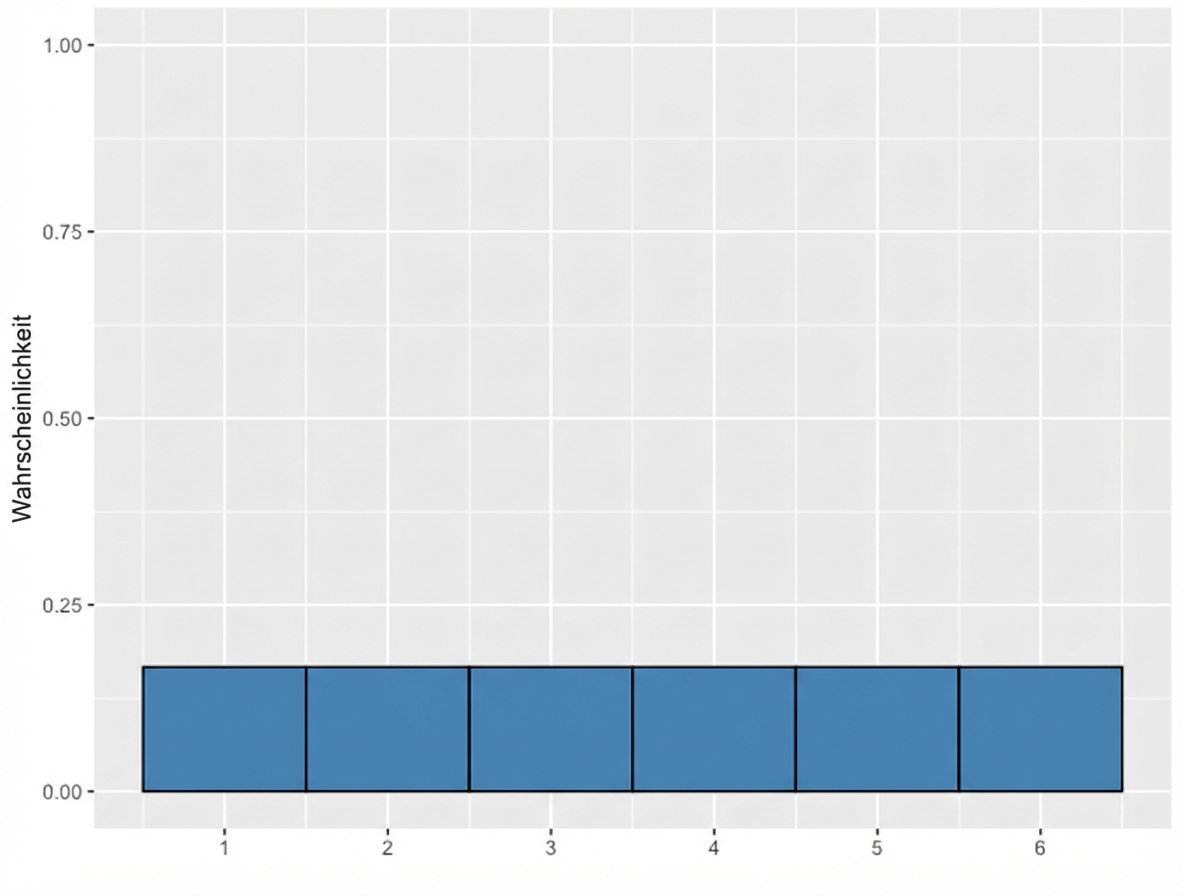
Diskrete Gleichverteilung
Ungerader Würfel
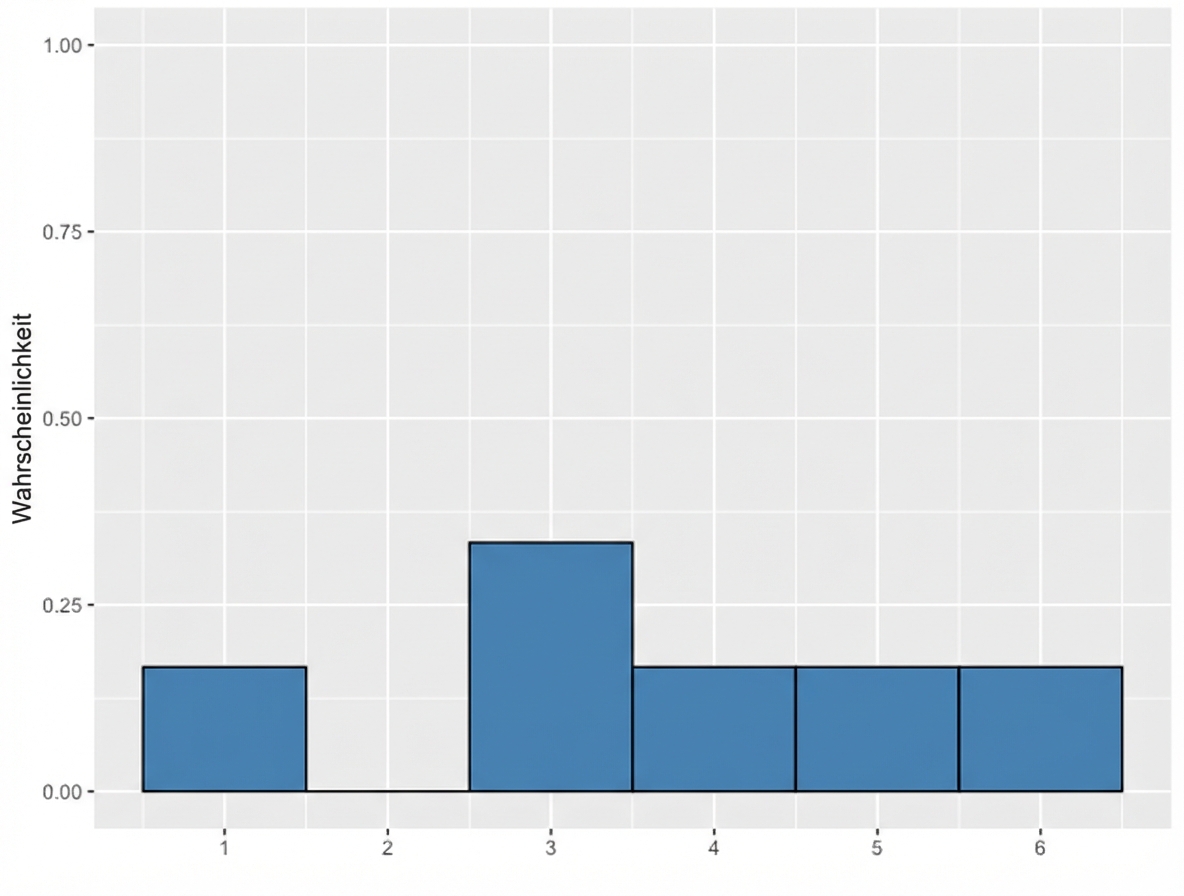
Stichproben aus einer diskreten Verteilung
| Wurf | Ergebnis |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 6 |
$ {Mittelwert} = 3,5 $
| Wurf | Ergebnis |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 3 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 |
| 10 | 5 |
Visualisieren einer Stichprobe
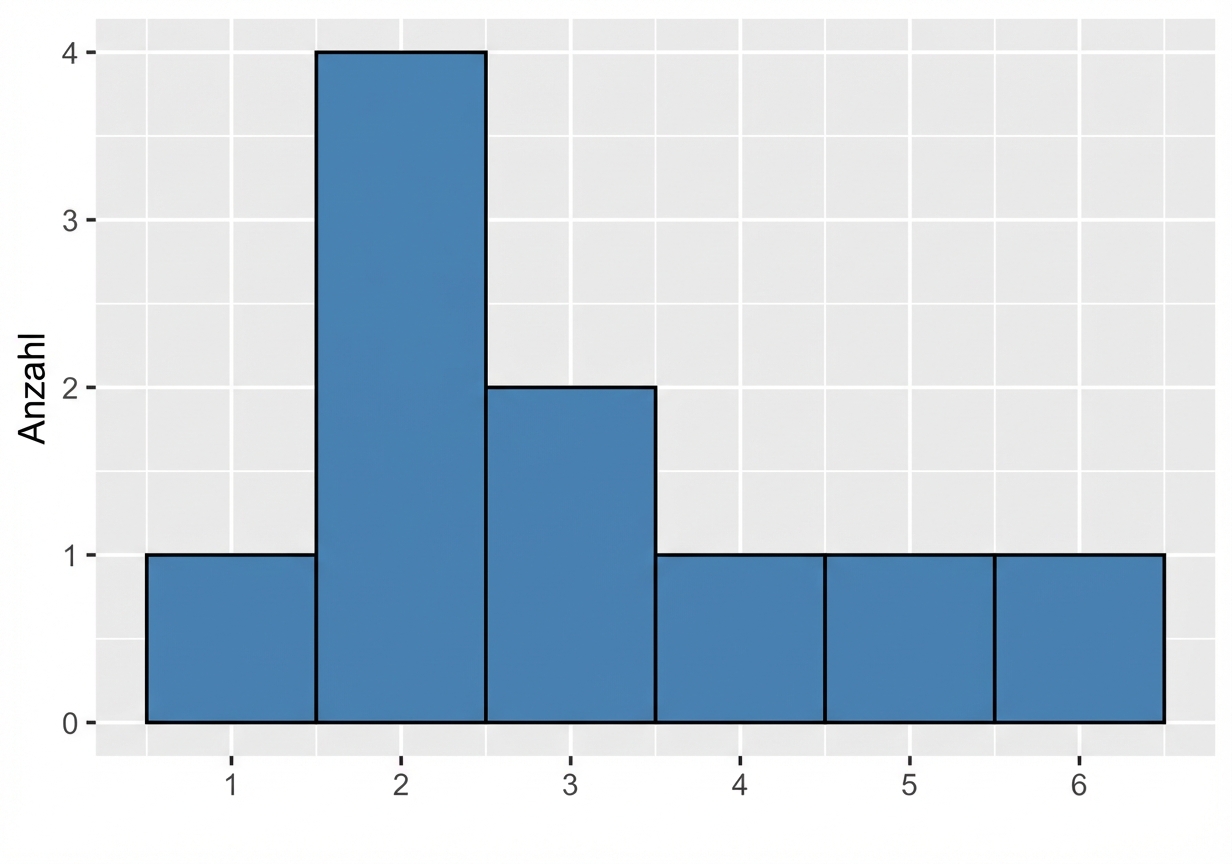
Stichprobenverteilung vs. theoretische Verteilung

$ {Mittelwert} = 3,0 $

$ {Mittelwert} = 3,5 $
Eine größere Stichprobe
Stichprobe mit 100 Würfen
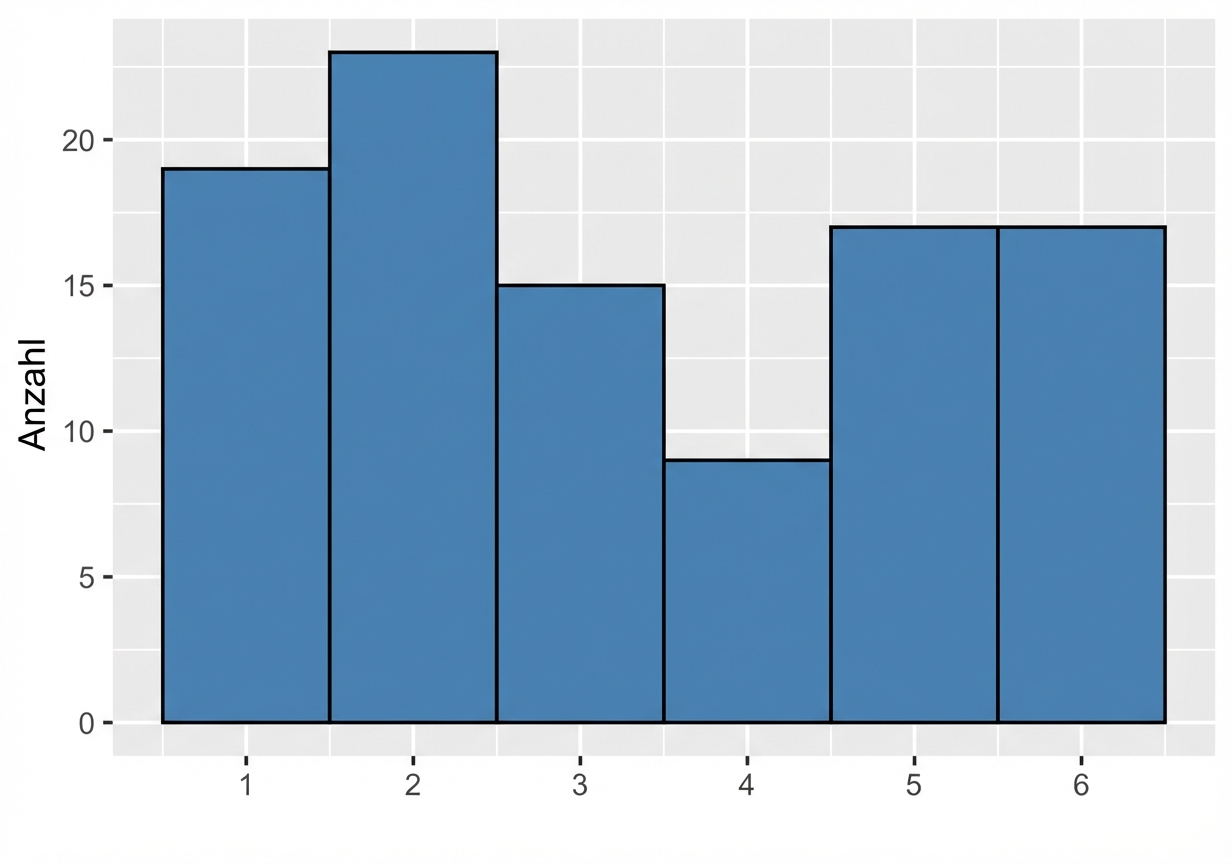
$ {Mittelwert} = 3,33 $
Eine noch größere Stichprobe
Stichprobe mit 1000 Würfen
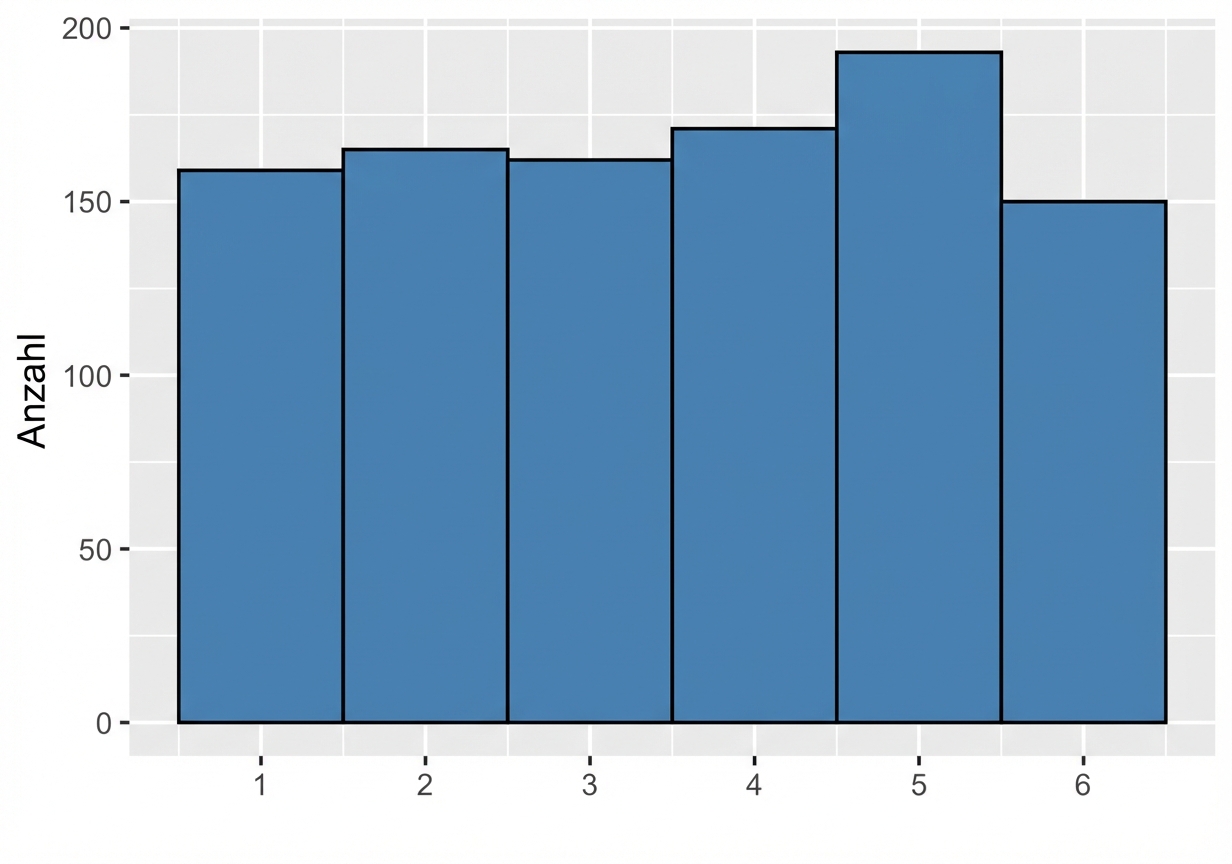
$ {Mittelwert} = 3,52 $
Gesetz der großen Zahlen
Mit zunehmender Stichprobengröße nähert sich der Stichprobenmittelwert dem Erwartungswert an.
| Stichprobengröße | Mittelwert |
|---|---|
| 10 | 3,00 |
| 100 | 3,33 |
| 1.000 | 3,52 |
Lass uns üben!
Einführung in die Statistik

