What are the chances?
Introduction to Statistics in R

Maggie Matsui
Content Developer, DataCamp
Measuring chance
What's the probability of an event?
$$ P(\text{event}) = \frac{\text{\# ways event can happen}}{\text{total \# of possible outcomes}} $$
Example: a coin flip
$$ P(\text{heads}) = \frac{\text{1 way to get heads}}{\text{2 possible outcomes}} = \frac{1}{2} = 50\%$$
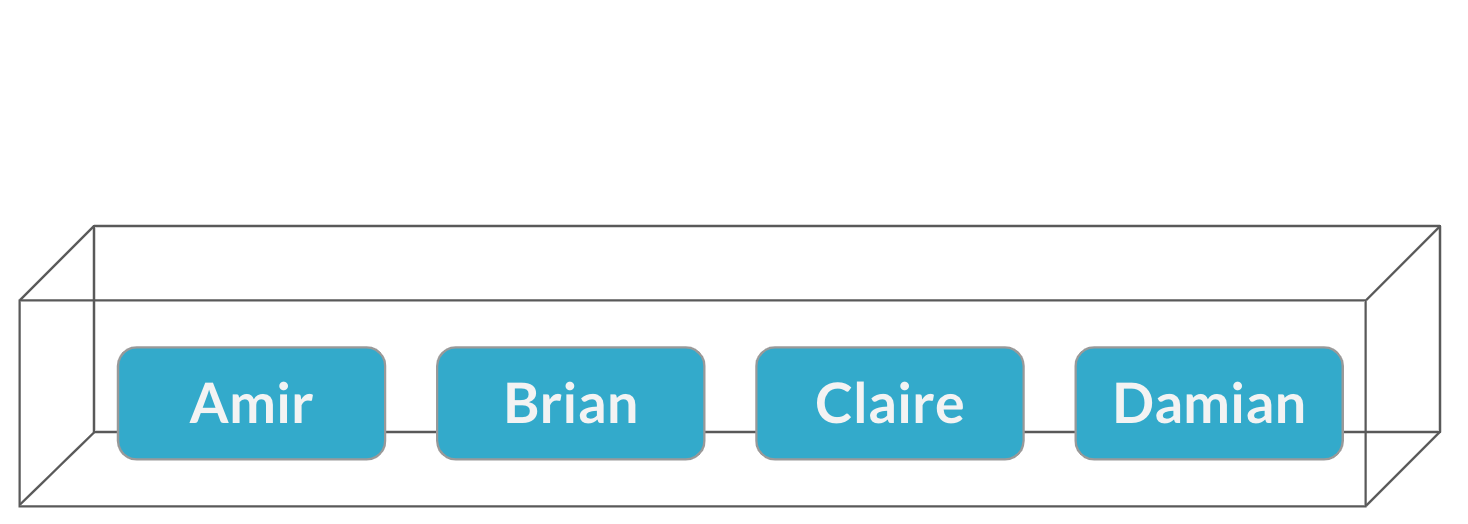
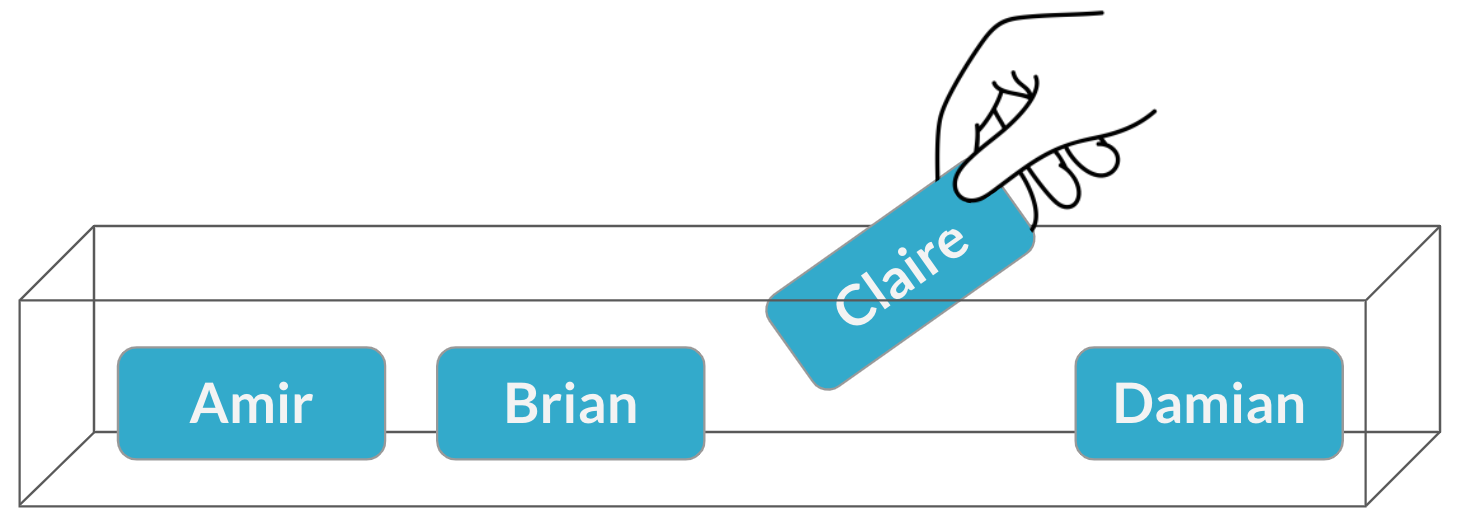
Assigning salespeople
Assigning salespeople
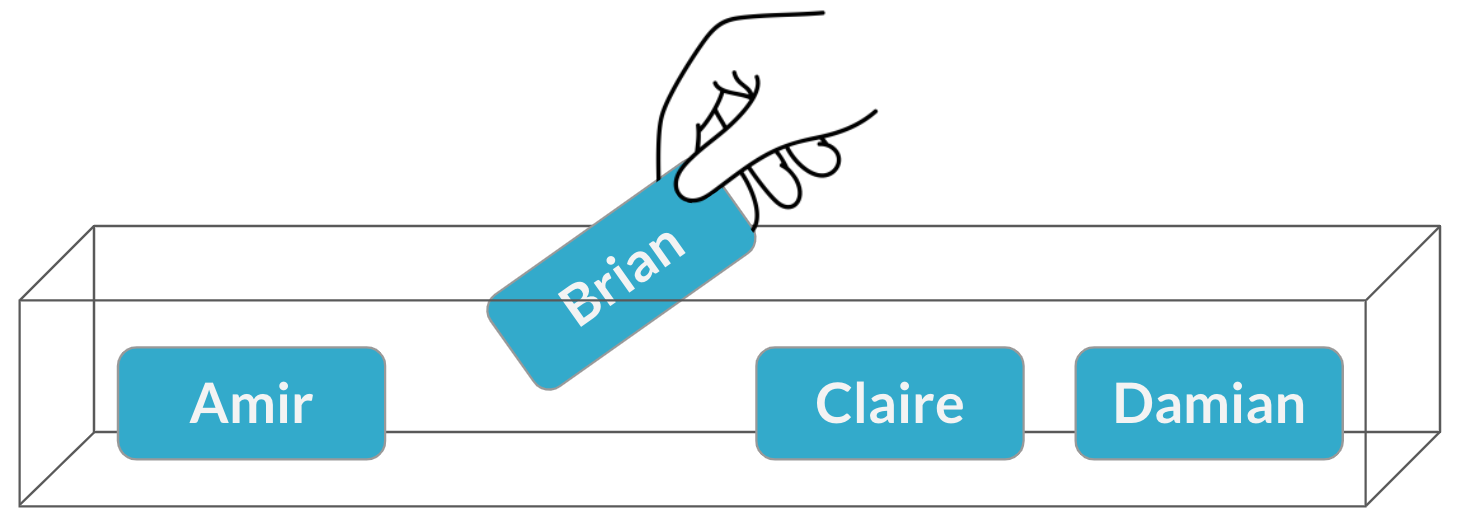
$$P(\text{Brian}) = \frac{1}{4} = 25\%$$
Sampling from a data frame
sales_counts
name n_sales
1 Amir 178
2 Brian 126
3 Claire 75
4 Damian 69
sales_counts %>%
sample_n(1)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
sales_counts %>%
sample_n(1)
name n_sales
1 Claire 75
Setting a random seed
set.seed(5)sales_counts %>% sample_n(1)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
set.seed(5)sales_counts %>% sample_n(1)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
A second meeting
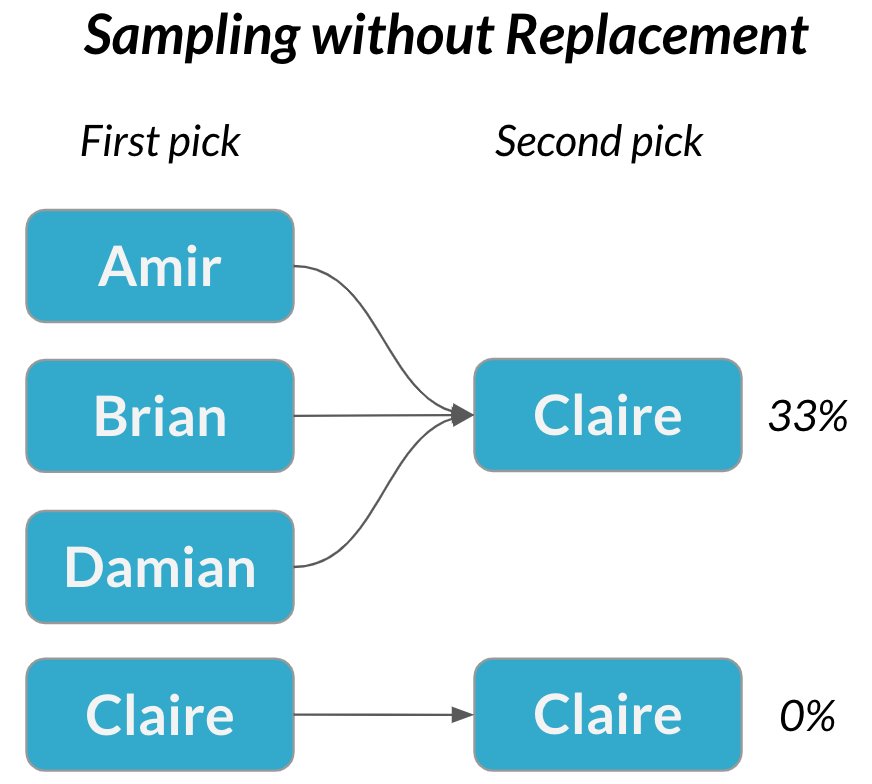
Sampling without replacement

A second meeting
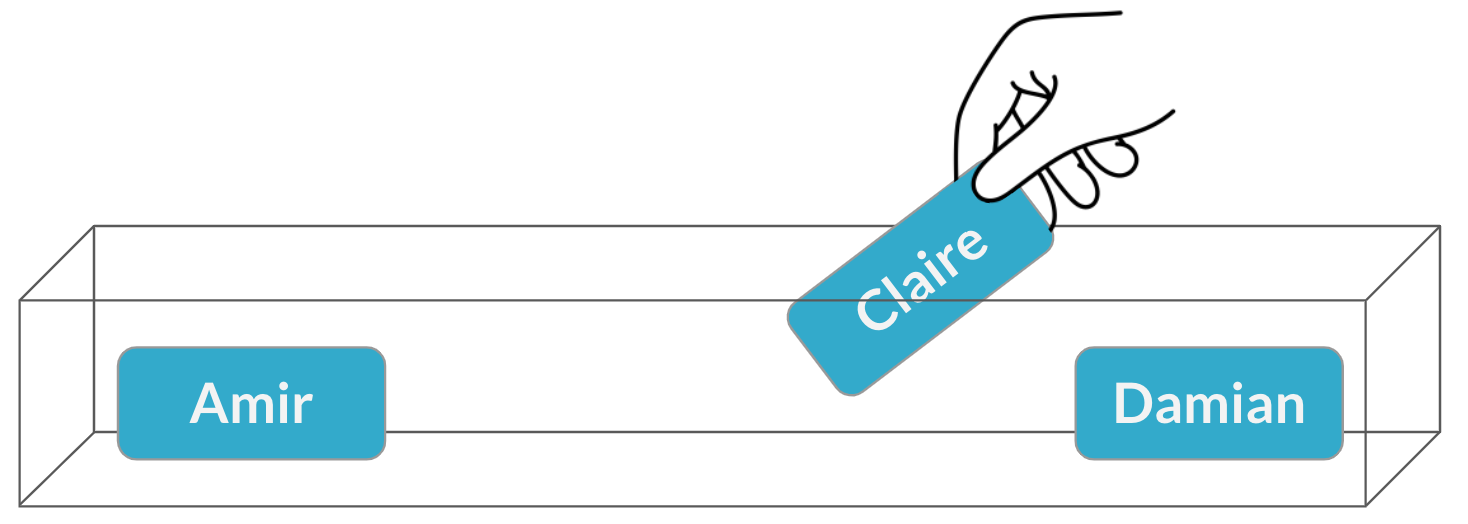
$$P(\text{Claire}) = \frac{1}{3} = 33\%$$
Sampling twice in R
sales_counts %>%
sample_n(2)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
2 Claire 75
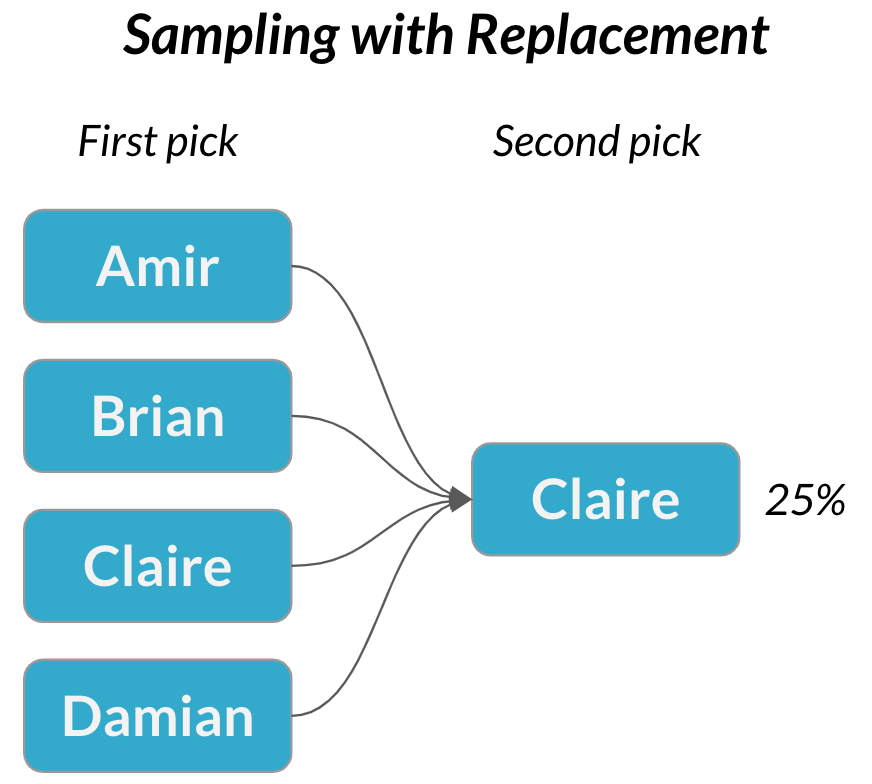
Sampling with replacement
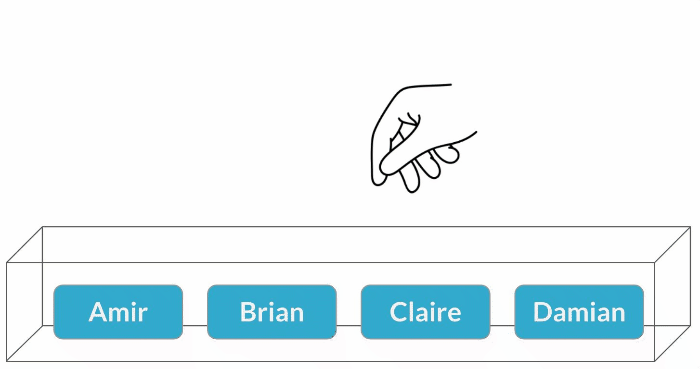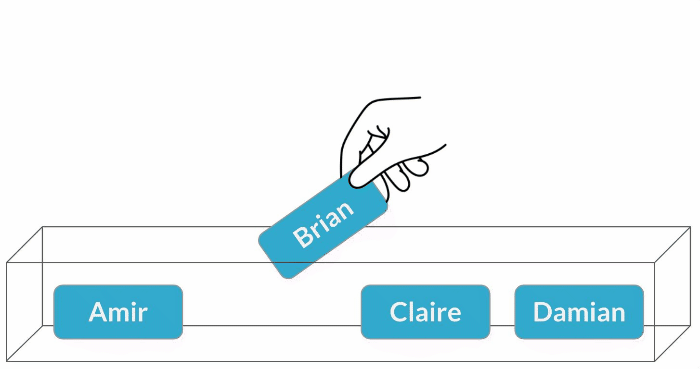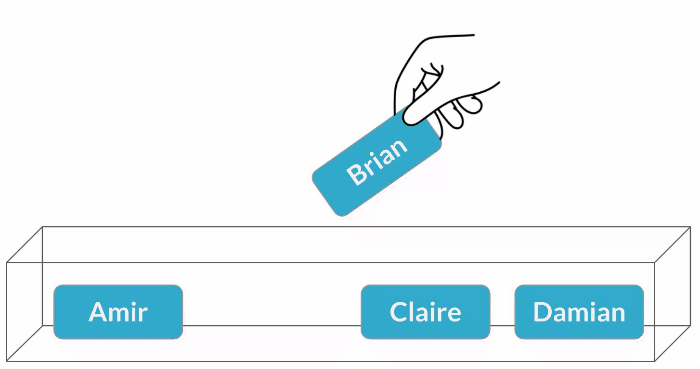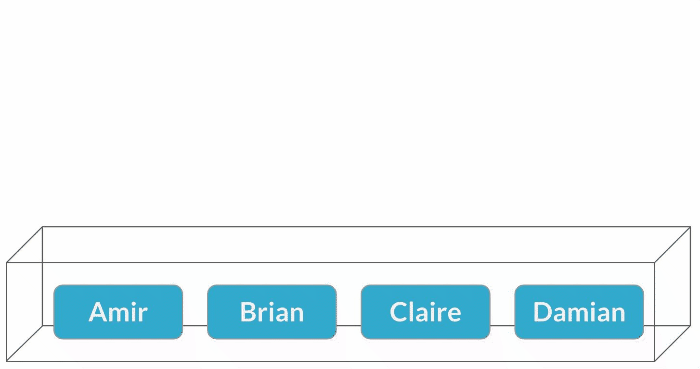
Sampling with replacement
$$P(\text{Claire}) = \frac{1}{4} = 25\%$$
Sampling with replacement in R
sales_counts %>%
sample_n(2, replace = TRUE)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
2 Claire 75
5 meetings:
sample(sales_team, 5, replace = TRUE)
name n_sales
1 Brian 126
2 Claire 75
3 Brian 126
4 Brian 126
5 Amir 178
Independent events
Two events are independent if the probability of the second event isn't affected by the outcome of the first event.
Independent events
Two events are independent if the probability of the second event isn't affected by the outcome of the first event.
Sampling with replacement = each pick is independent
Dependent events
Two events are dependent if the probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event.
Dependent events
Two events are dependent if the probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event.
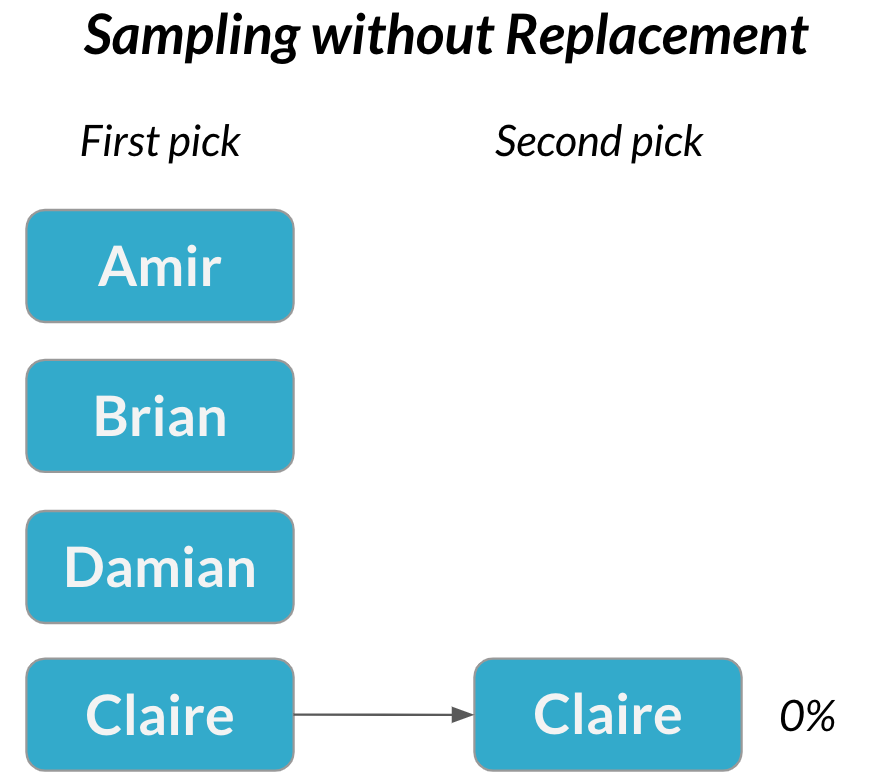
Dependent events
Two events are dependent if the probability of the second event is affected by the outcome of the first event.
Sampling without replacement = each pick is dependent
Let's practice!
Introduction to Statistics in R

