Creating a sampling distribution
Sampling in Python

James Chapman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Same code, different answer
coffee_ratings.sample(n=30)['total_cup_points'].mean()
82.53066666666668
coffee_ratings.sample(n=30)['total_cup_points'].mean()
81.97566666666667
coffee_ratings.sample(n=30)['total_cup_points'].mean()
82.68
coffee_ratings.sample(n=30)['total_cup_points'].mean()
81.675
Same code, 1000 times
mean_cup_points_1000 = []for i in range(1000): mean_cup_points_1000.append( coffee_ratings.sample(n=30)['total_cup_points'].mean() )print(mean_cup_points_1000)
[82.11933333333333, 82.55300000000001, 82.07266666666668, 81.76966666666667,
...
82.74166666666666, 82.45033333333335, 81.77199999999999, 82.8163333333333]
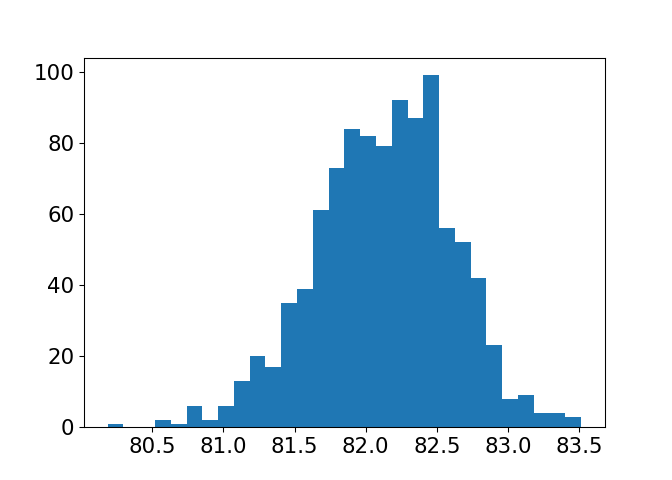
Distribution of sample means for size 30
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.hist(mean_cup_points_1000, bins=30)
plt.show()
A sampling distribution is a distribution of replicates of point estimates.
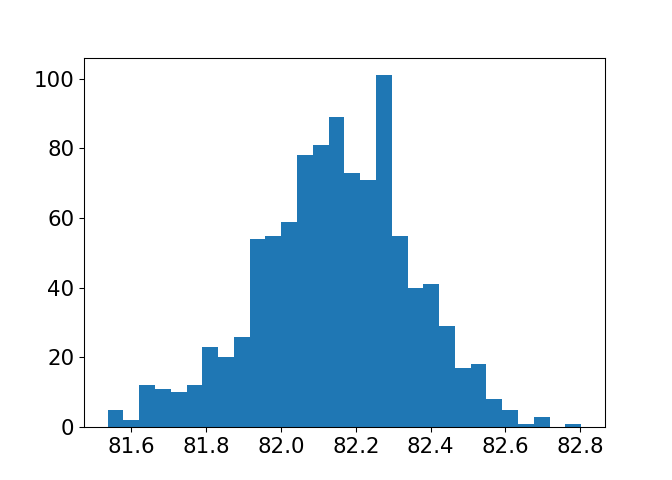
Different sample sizes
Sample size: 6
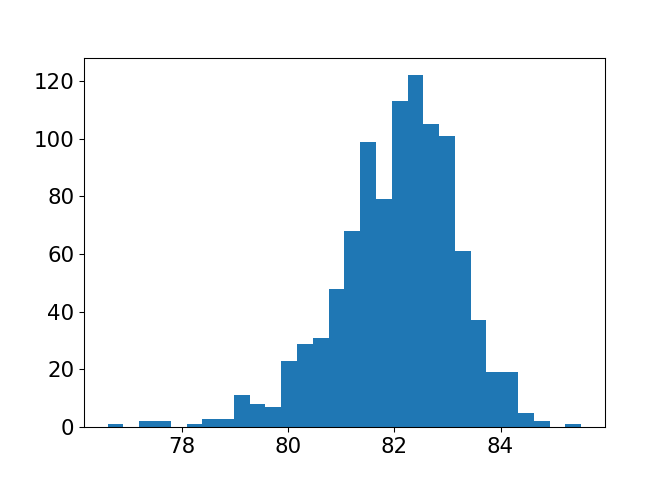
Sample size: 150
Let's practice!
Sampling in Python

