NumPy data types
Introduction to NumPy

Izzy Weber
Core Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
NumPy vs. Python data types
Sample Python data types:
intfloat
Sample NumPy data types:
np.int64np.int32np.float64np.float32
Bits and bytes
The number 10436 represented in binary is:

np.int32 can store 4,294,967,296 integers:
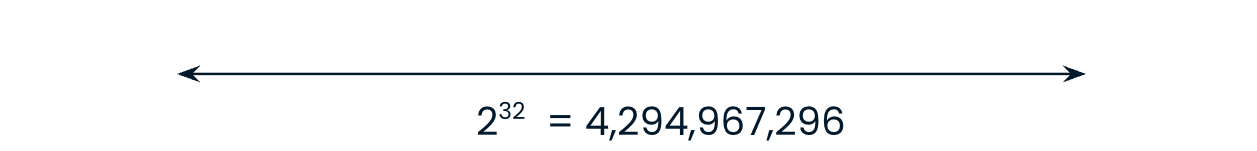
Bits and bytes
The number 10436 represented in binary is:

np.int32 can store 4,294,967,296 integers:

The .dtype attribute
np.array([1.32, 5.78, 175.55]).dtype
dtype('float64')
Default data types
int_array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
int_array.dtype
dtype('int64')
String data
np.array(["Introduction", "to", "NumPy"]).dtype
dtype('<U12')
dtype as an argument
float32_array = np.array([1.32, 5.78, 175.55], dtype=np.float32)
float32_array.dtype
dtype('float32')
Type conversion
boolean_array = np.array([[True, False], [False, False]], dtype=np.bool_)
boolean_array.astype(np.int32)
array([[1, 0],
[0, 0]], dtype=int32)
Type coercion
np.array([True, "Boop", 42, 42.42])
array(['True', 'Boop', '42', '42.42'], dtype='<U5')
Type coercion hierarchy
Adding a float to an array of integers will change all integers into floats:
np.array([0, 42, 42.42]).dtype
dtype('float64')
Adding an integer to an array of booleans will change all booleans in to integers:
np.array([True, False, 42]).dtype
dtype('int64')
Let's practice!
Introduction to NumPy

