DAX for creating tables and columns
DAX Functions in Power BI

Carl Rosseel
Curriculum Manager at DataCamp
DAX stands for data analysis expressions
- DAX is a formula expression language used in multiple Microsoft analytics tools

- DAX formulas include functions, operators and values to perform advanced calculations
- DAX formulas are used in:
- Measures
- Calculated columns
- Calculated tables
- Row-level security
The power of DAX
- It opens up new capabilities:
- Joins, filters, measures, and calculated fields become part of your toolbox
- DAX + Power Query = a powerful data analysis tool:
- Dive deeper into the data and extract key insights
- Use DAX for rapid prototyping
Measures vs calculated columns
Calculated Columns:
- Calculated on data import
- Visible in Table and Report view
COST = Orders[Sales] - Orders[Profit]
| Order_ID | Sales | Profit | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3151 | $77.88 | $3.89 | $73.99 |
| 3152 | $6.63 | $1.79 | $4.84 |
| 3153 | $22.72 | $10.22 | $12.50 |
| 3154 | $45.36 | $21.77 | $23.59 |
Measures vs calculated columns
Calculated Columns:
- Calculated on data import
- Visible in Table and Report view
COST = Orders[Sales] - Orders[Profit]
| Order_ID | Sales | Profit | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3151 | $77.88 | $3.89 | $73.99 |
| 3152 | $6.63 | $1.79 | $4.84 |
| 3153 | $22.72 | $10.22 | $12.50 |
| 3154 | $45.36 | $21.77 | $23.59 |
Measures:
- Calculated at query run-time
- Visible only in report pane
Total Sales = SUM(Orders[Sales])
| Region | Total Sales |
|---|---|
| Central | $501,239.89 |
| East | $678,781.24 |
| West | $391,721.91 |
| South | $725.457.82 |
| Total | $2,297,200.86 |
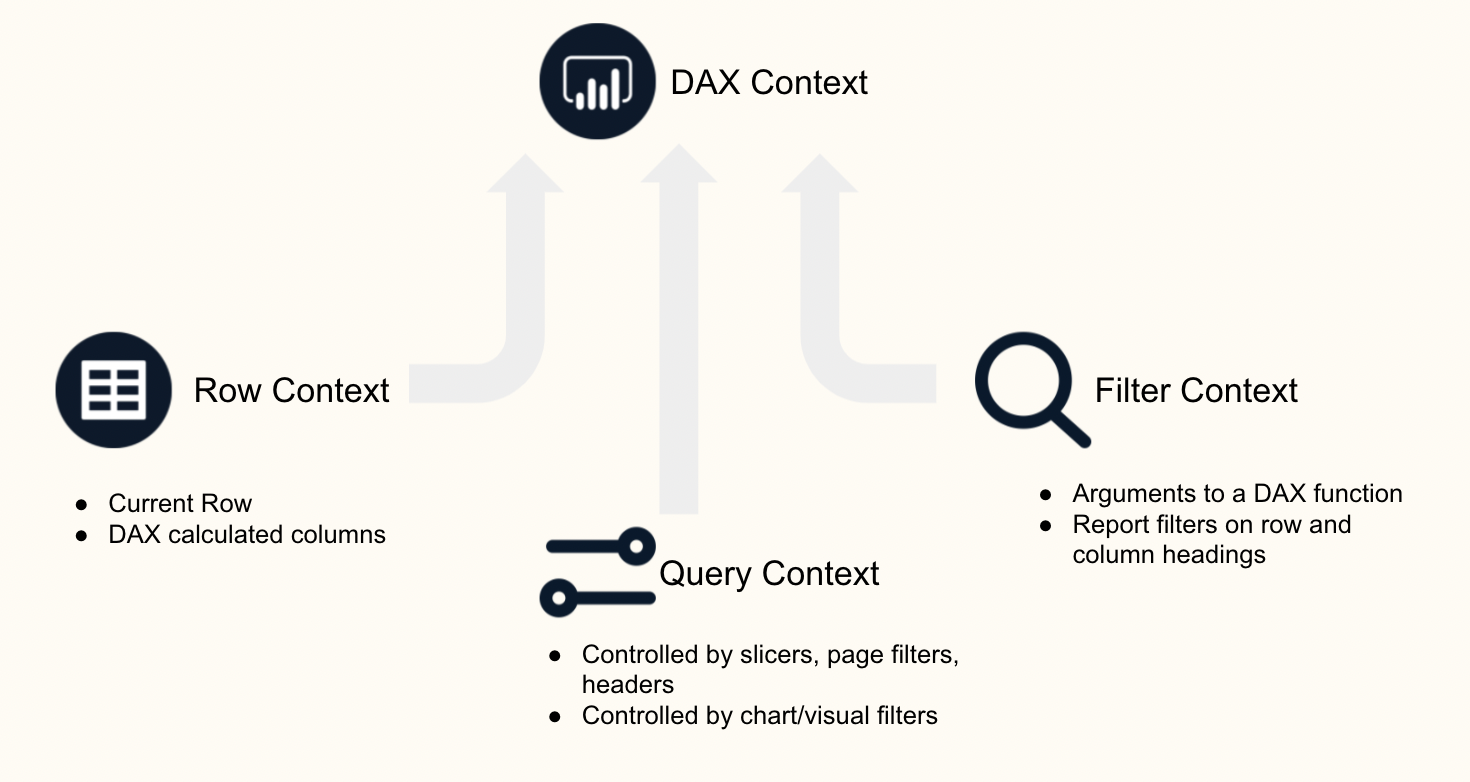
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
There are three types of context: row, query, and filter context
- Row context: (1)
- "The current row"
- DAX calculated columns
COST = Orders[Sales] - Orders[Profit]
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
There are three types of context: row, query, and filter context
- Row context: (1)
- "The current row"
- DAX calculated columns
COST = Orders[Sales] - Orders[Profit]
| Order_ID | Sales | Pofit | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3151 | $77.88 | $3.89 | $73.99 |
| 3152 | $6.63 | $1.79 | $4.84 |
| 3153 | $22.72 | $10.22 | $12.50 |
| 3154 | 45.36 | $21.77 | $23.59 |
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
There are three types of context: row, query, and filter context
- Query context: (2)
- Refers to the subset of data that is implicitly retrieved for a formula
- Controlled by slicers, page filters, table columns and row headers
- Controlled by chart/visual filters
- Applies after row context
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
- Query context: (2)
- Example: Filter data by Region.
| Region | Total Sales |
|---|---|
| Central | $501,239 |
| East | $678,781 |
| West | $391,721 |
| South | $725.457 |
- Query context: (2)
- Example: Filter data by State.
| State | Total Sales |
|---|---|
| Alabama | $13,724 |
| Arizona | $38,710 |
| Arkansas | $7,669 |
| California | $381,306 |
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
There are three types of context: row, query, and filter context
- Filter Context: (3)
- The set of values allowed in each column, or in the values retrieved from a related table
- By using arguments to a formula or by using report filters on row and column headings
- Applies after query context
Context allows you to perform dynamic analysis
There are three types of context: row, query, and filter context.
- Filter Context (3)
Total Costs East = CALCULATE([Total Costs], Orders[Region] = 'East')
| Region | Total costs | Total costs East |
|---|---|---|
| Central | $617,039 | |
| East | $587,258 | $587,258 |
| West | $461,534 | |
| South | $344,972 | |
| Total | $2,010,804 | $587,258 |
Context in a nutshell
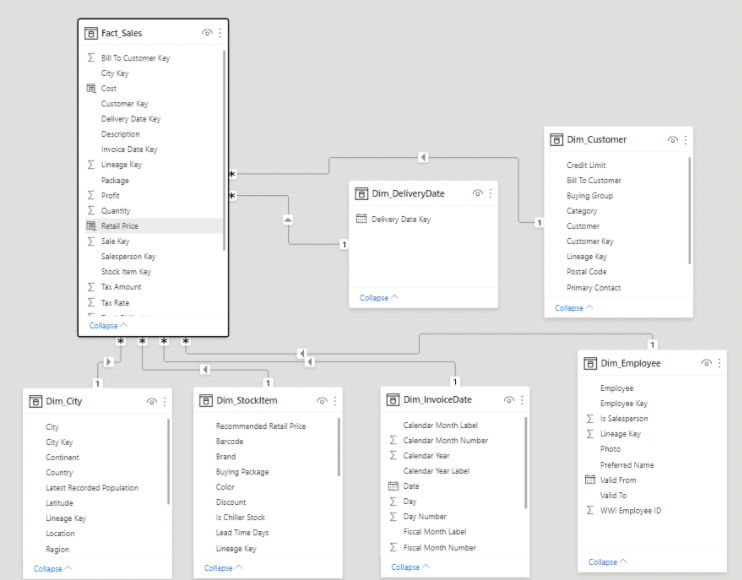
World wide importers dataset
- A fictitious wholesaler who imports and distributes novelty goods
- The dataset consists of:
- A fact table that detailing sales transactions
- Multiple other dimension tables:
- Dates
- Customers
- Cities
- Employees
- Stock Items
Let's practice!
DAX Functions in Power BI

