Classification
Big Data Fundamentals with PySpark

Upendra Devisetty
Science Analyst, CyVerse
Classification using PySpark MLlib
- Classification is a supervised machine learning algorithm for sorting the input data into different categories
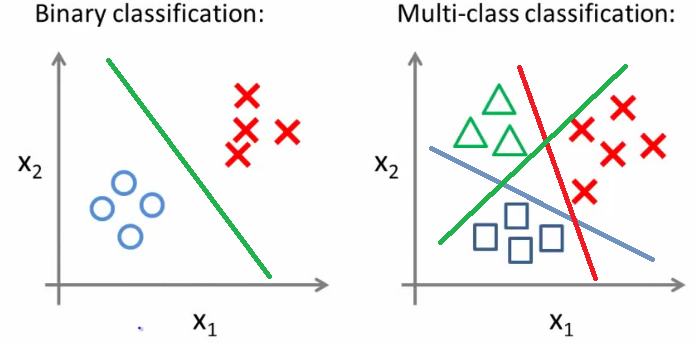
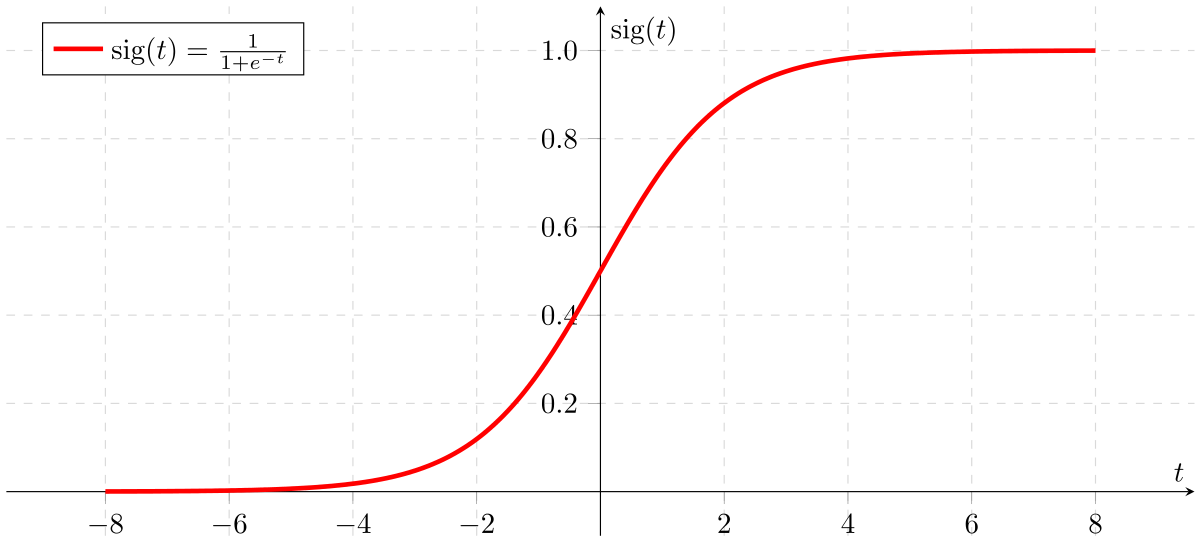
Introduction to Logistic Regression
- Logistic Regression predicts a binary response based on some variables
Working with Vectors
PySpark MLlib contains specific data types Vectors and LabelledPoint
Two types of Vectors
- Dense Vector: store all their entries in an array of floating point numbers
- Sparse Vector: store only the nonzero values and their indices
denseVec = Vectors.dense([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
DenseVector([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
sparseVec = Vectors.sparse(4, {1: 1.0, 3: 5.5})
SparseVector(4, {1: 1.0, 3: 5.5})
LabeledPoint() in PySpark MLlib
A LabeledPoint is a wrapper for input features and predicted value
For binary classification of Logistic Regression, a label is either 0 (negative) or 1 (positive)
positive = LabeledPoint(1.0, [1.0, 0.0, 3.0])
negative = LabeledPoint(0.0, [2.0, 1.0, 1.0])
print(positive)
print(negative)
LabeledPoint(1.0, [1.0,0.0,3.0])
LabeledPoint(0.0, [2.0,1.0,1.0])
HashingTF() in PySpark MLlib
HashingTF()algorithm is used to map feature value to indices in the feature vector
from pyspark.mllib.feature import HashingTF
sentence = "hello hello world"
words = sentence.split()
tf = HashingTF(10000)
tf.transform(words)
SparseVector(10000, {3065: 1.0, 6861: 2.0})
Logistic Regression using LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS
- Logistic Regression using Pyspark MLlib is achieved using LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS class
data = [
LabeledPoint(0.0, [0.0, 1.0]),
LabeledPoint(1.0, [1.0, 0.0]),
]
RDD = sc.parallelize(data)
lrm = LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS.train(RDD)
lrm.predict([1.0, 0.0])
lrm.predict([0.0, 1.0])
1
0
Final Slide
Big Data Fundamentals with PySpark

