Implementing Star Schemas
Transform and Analyze Data with Microsoft Fabric

Luis Silva
Solution Architect - Data & AI
Medallion Architecture
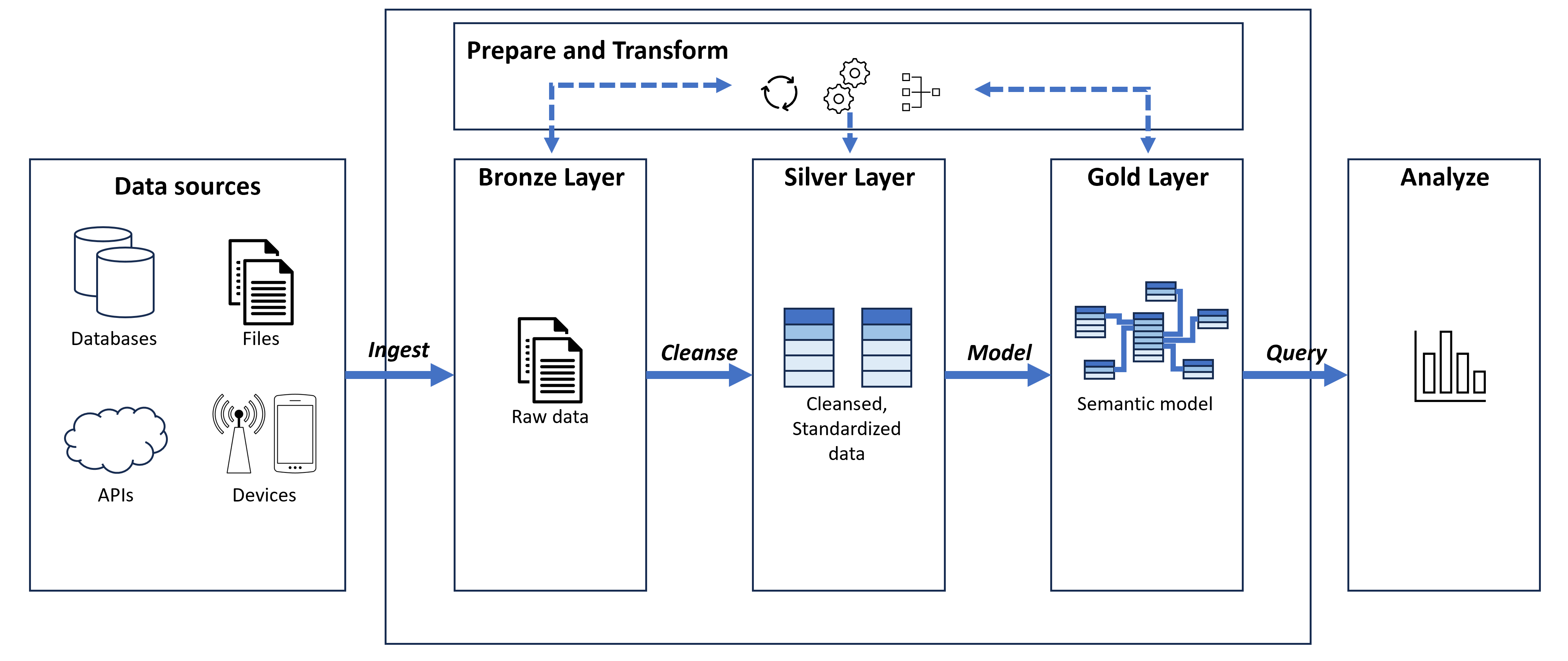
- Design pattern for organization of data
- Three distinct layers that indicate progressive refinement of the data
Medallion Architecture
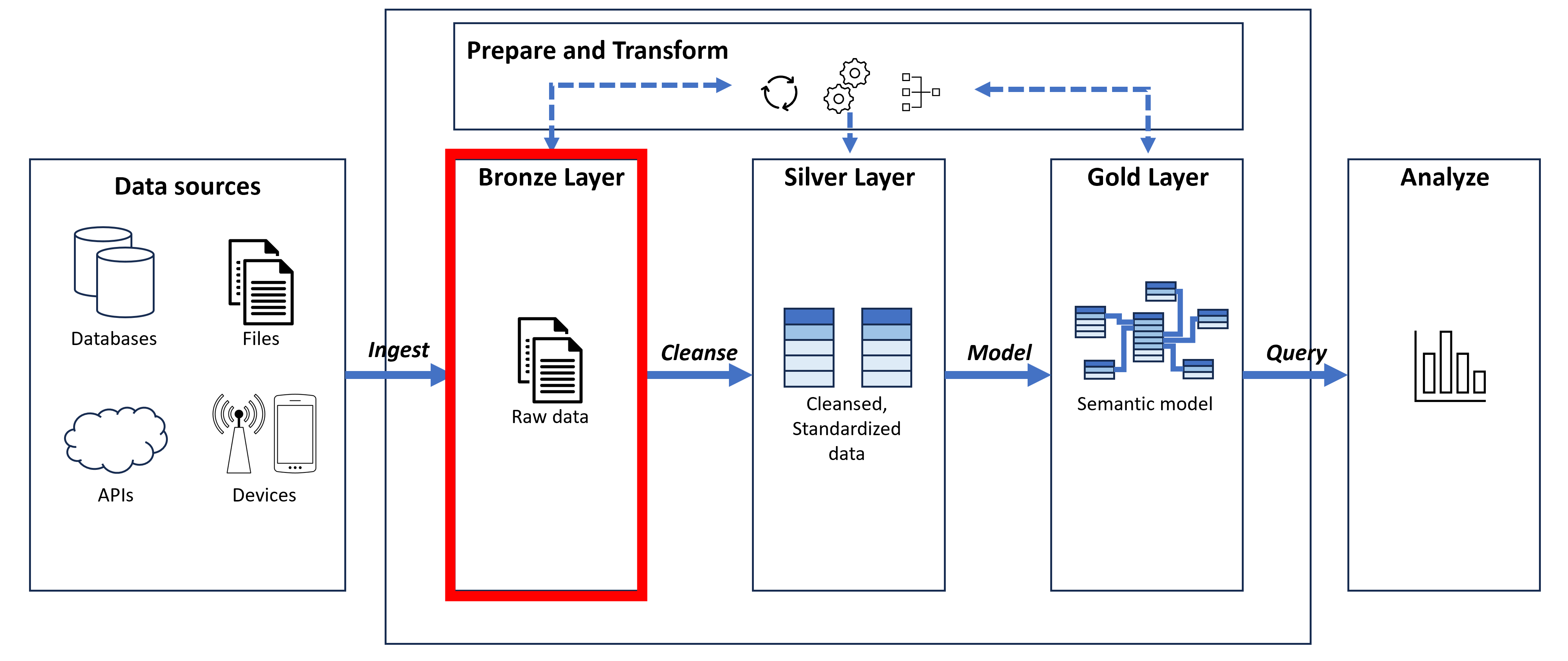
- Bronze layer: Data ingested from the source in its original raw format.
Medallion Architecture
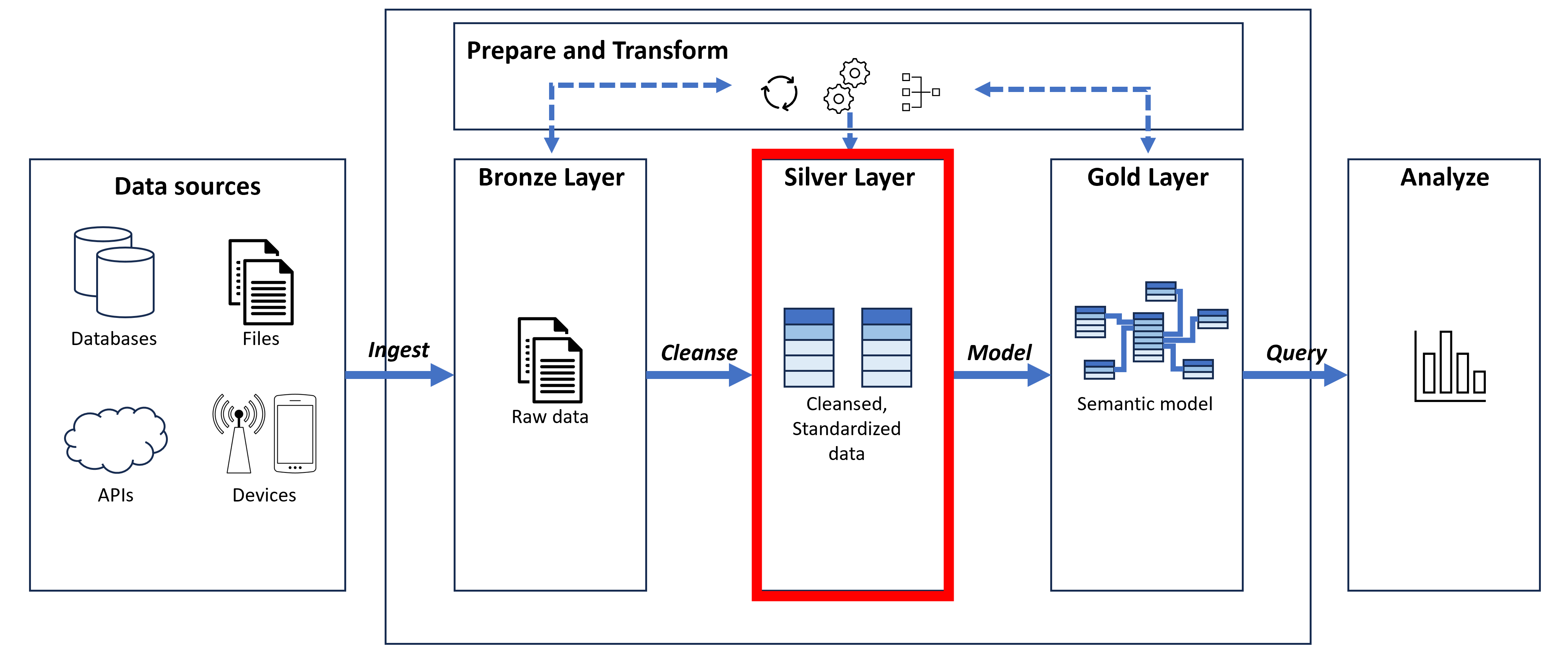
- Silver layer: Cleansed and standardized data.
Medallion Architecture
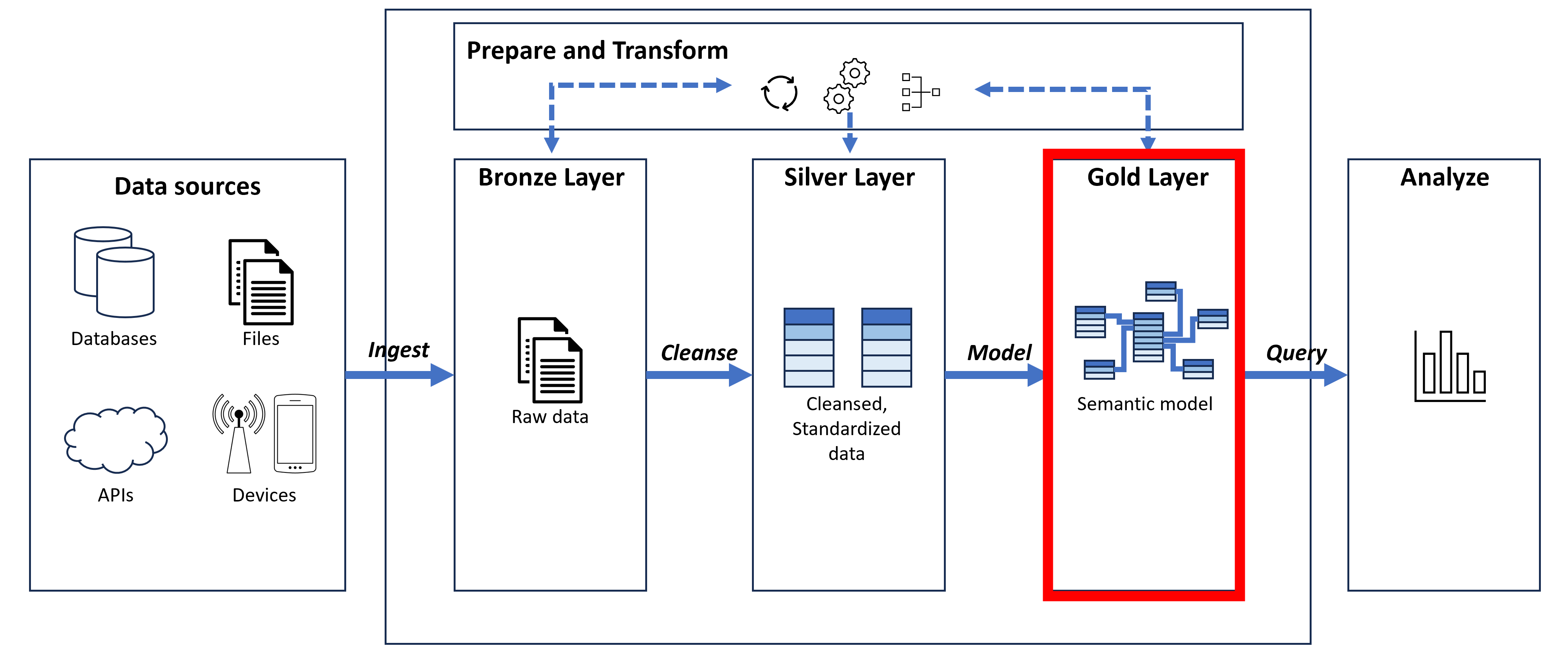
- Gold layer: Data in a format suitable for analytics, usually star schema.
Medallion Architecture in Fabric
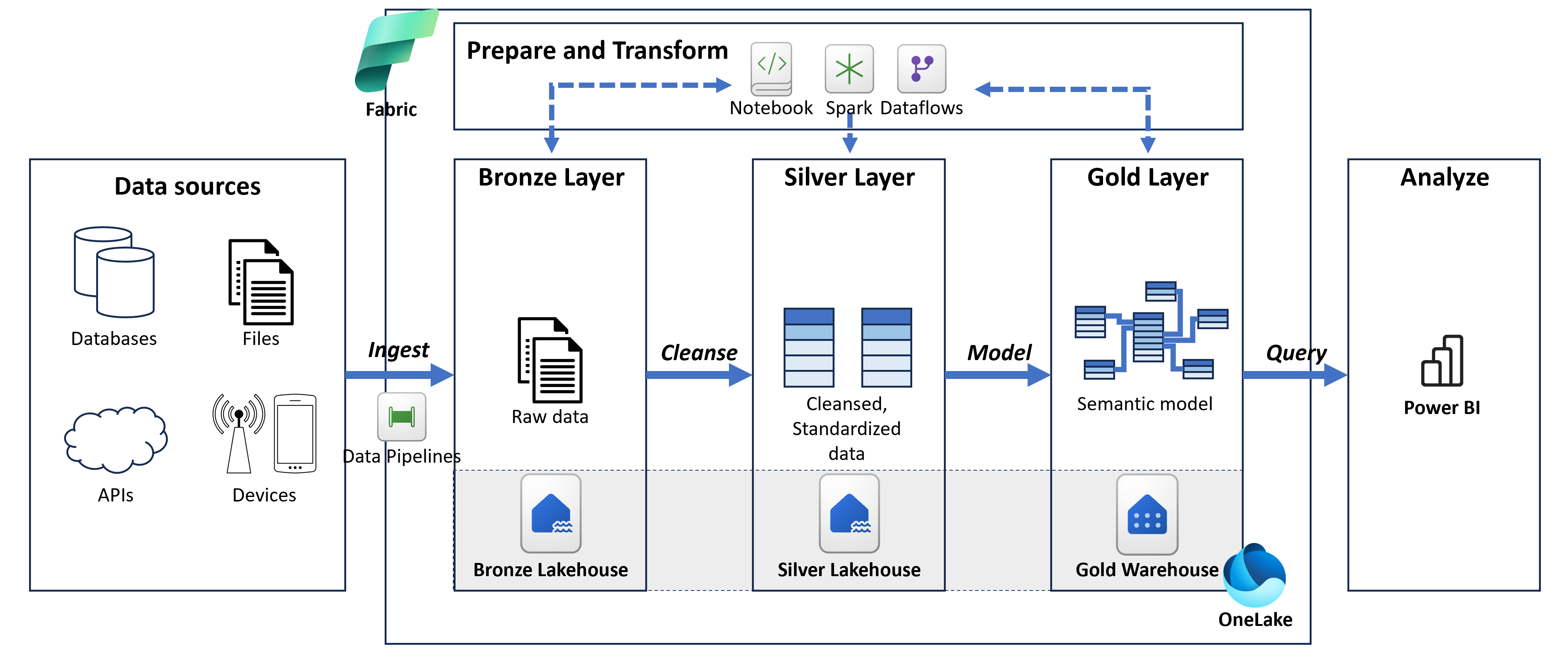
- Bronze layer: Lakehouse
- Silver layer: Lakehouse
- Gold layer: Lakehouse or Warehouse
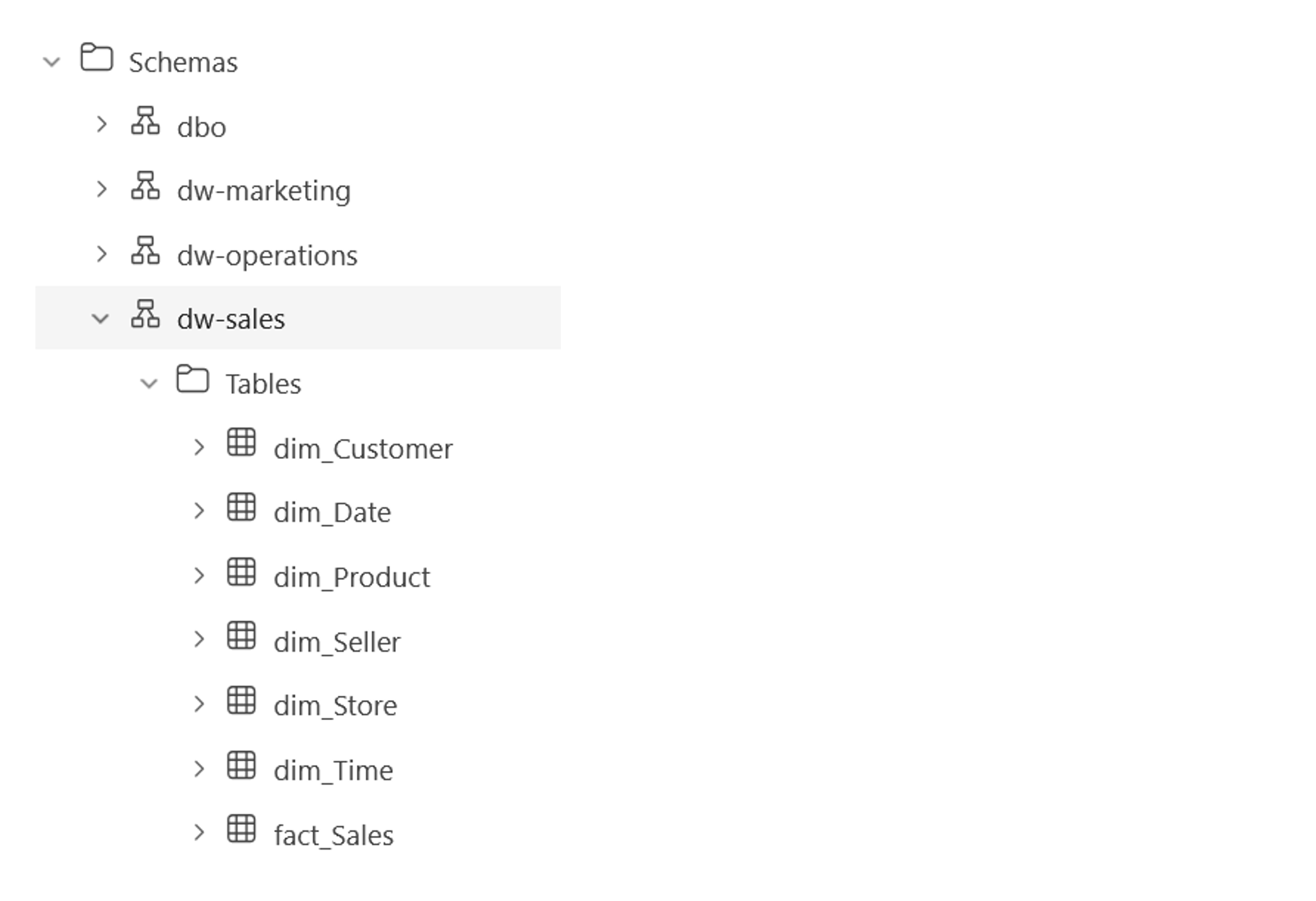
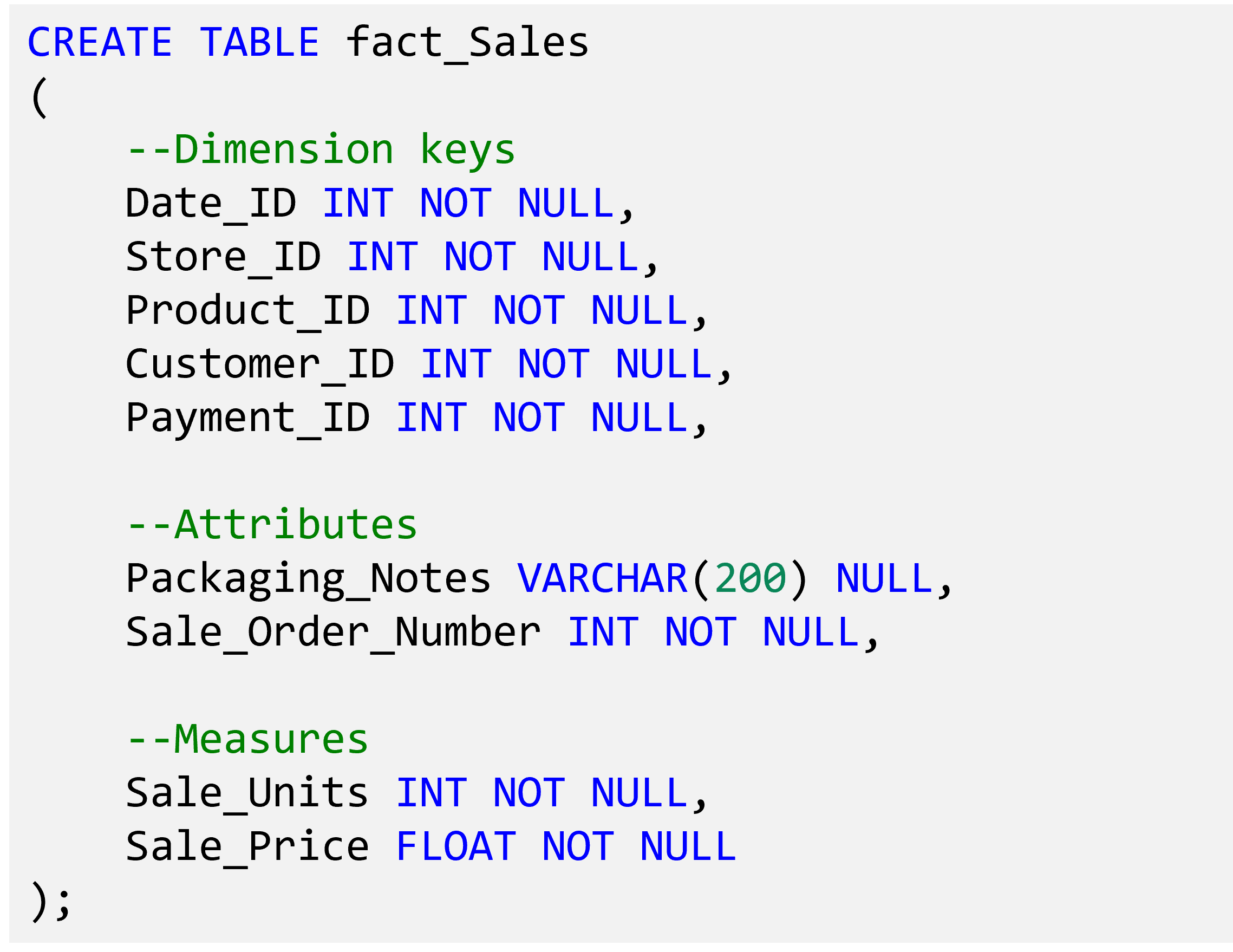
Implementing a star schema
- Use T-SQL CREATE TABLE statement to define the tables.
- Fabric supports the most commonly used T-SQL data types.
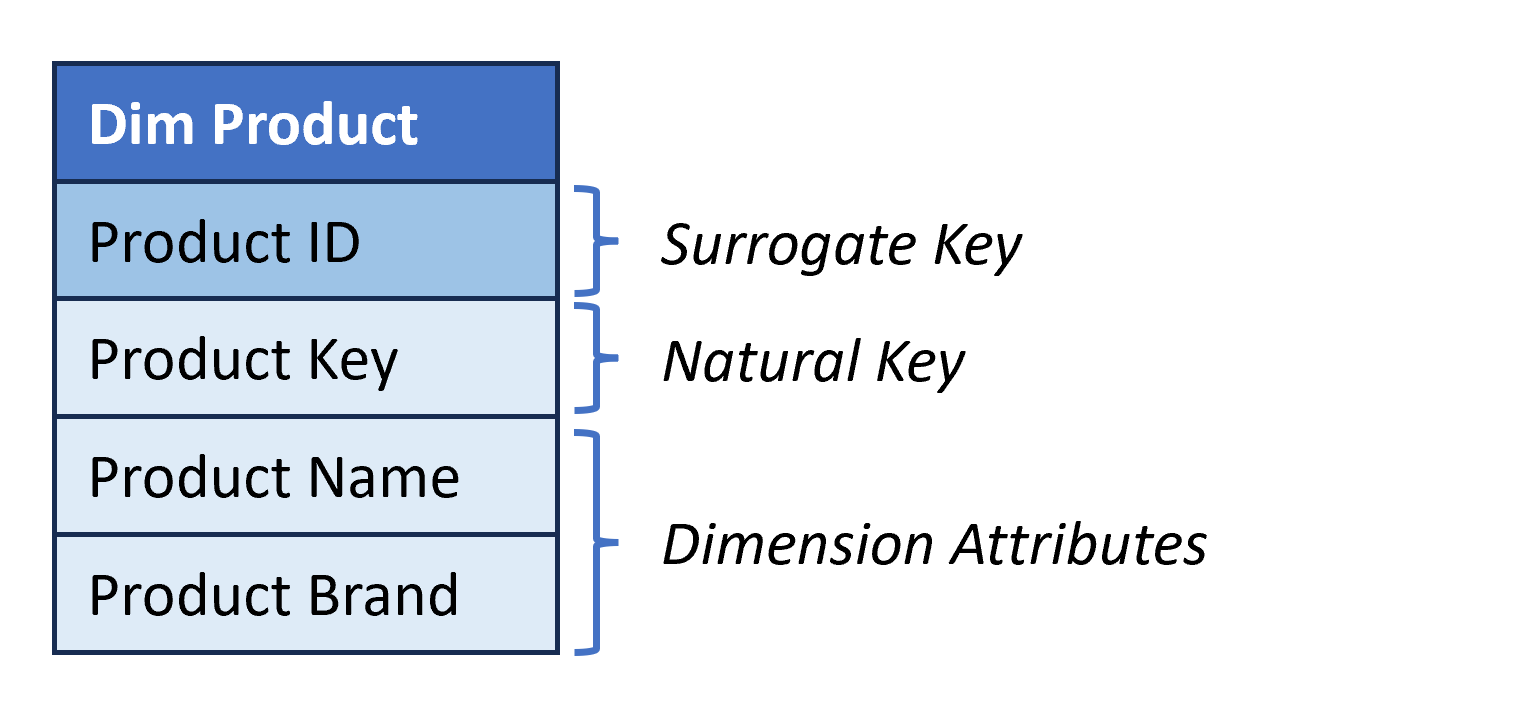
Dimension table structure
- Describe business entities (e.g., products).
- Usually have the following columns:
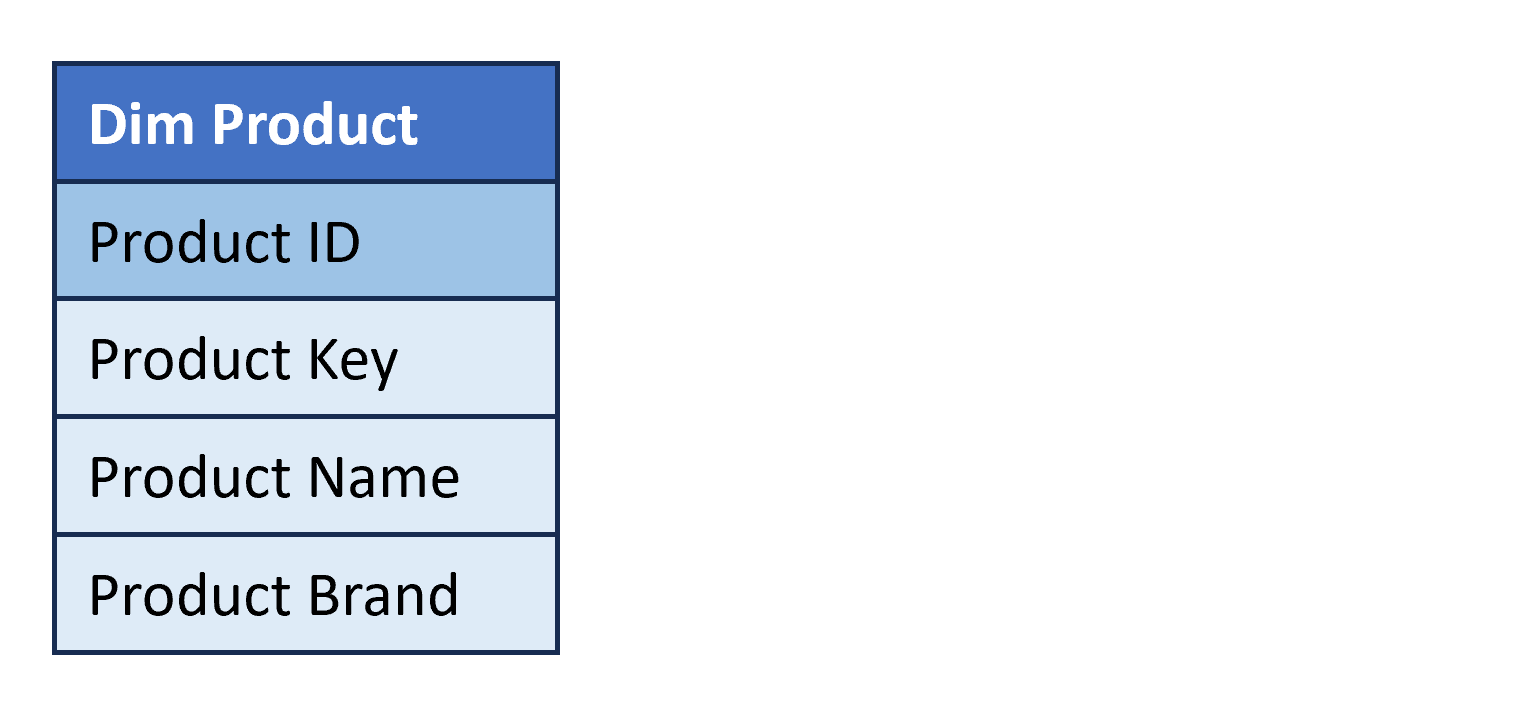
Dimension table structure
- Describe business entities (e.g., products).
- Usually have the following columns:
- Surrogate Key. Single-column unique identifier for dimension items.
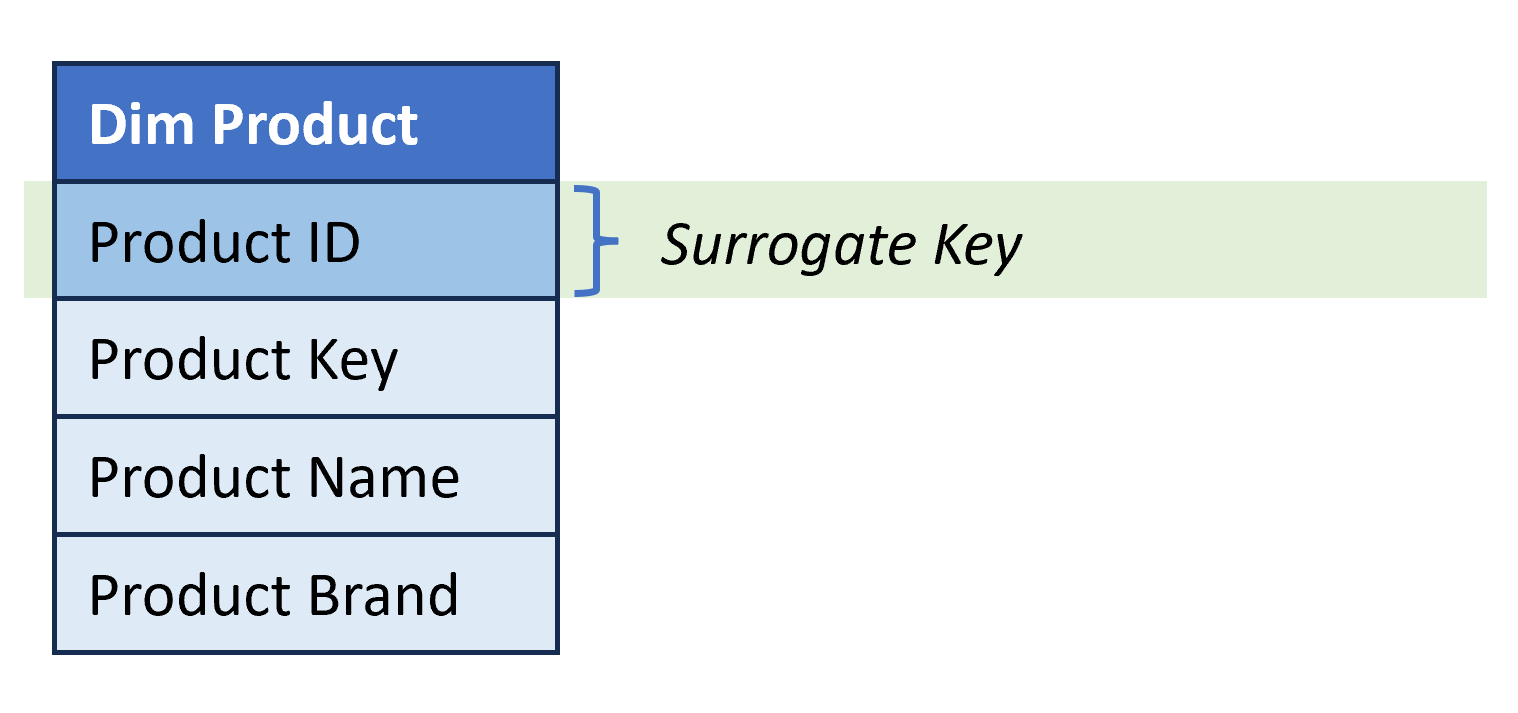
Dimension table structure
- Describe business entities (e.g., products).
- Usually have the following columns:
- Surrogate Key. Single-column unique identifier for dimension items.
- Natural Key (Business Key). Single-column unique identifier that comes from source systems.
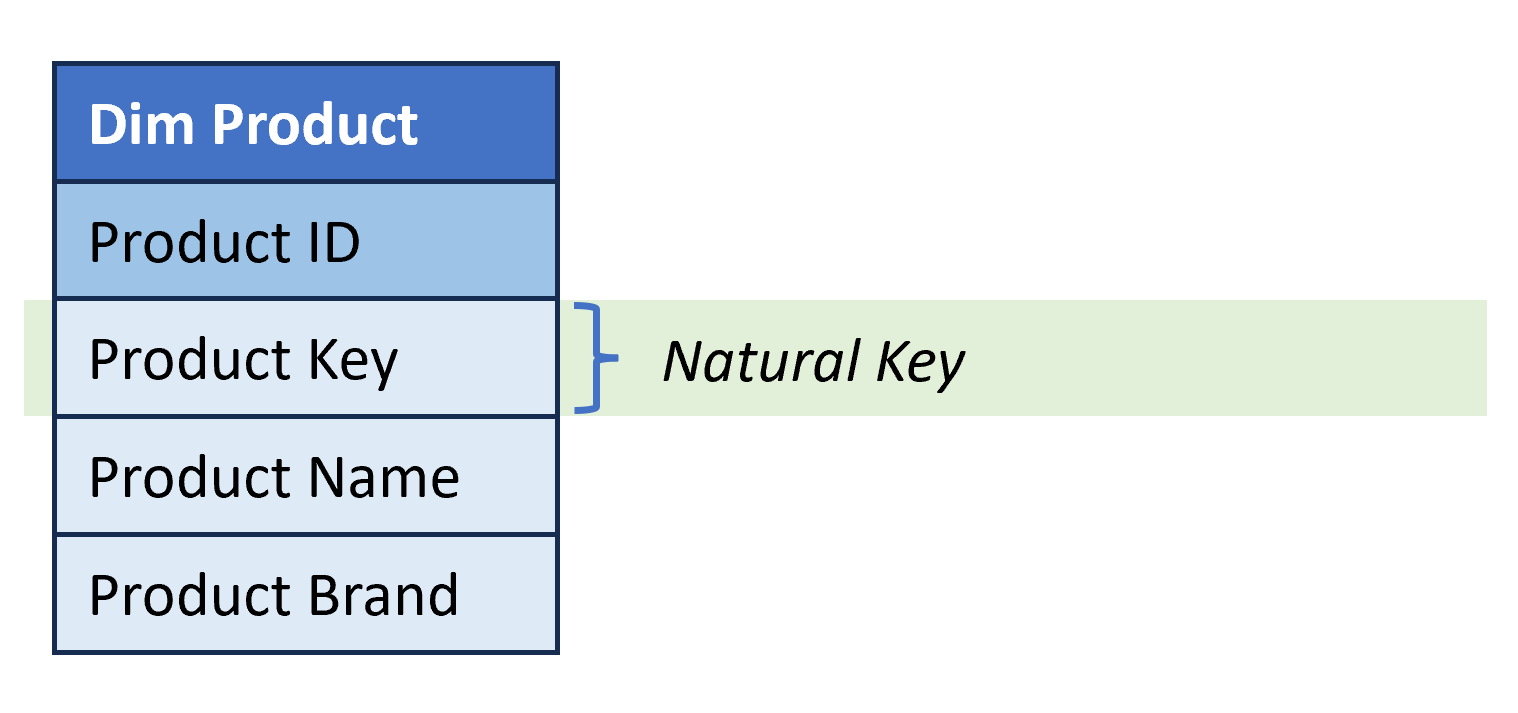
Dimension table structure
- Describe business entities (e.g., products).
- Usually have the following columns:
- Surrogate Key. Single-column unique identifier for dimension items.
- Natural Key (Business Key). Single-column unique identifier that comes from source systems.
- Dimension Attributes. One or more columns that are used to filter data and provide context to the data stored in the fact table.
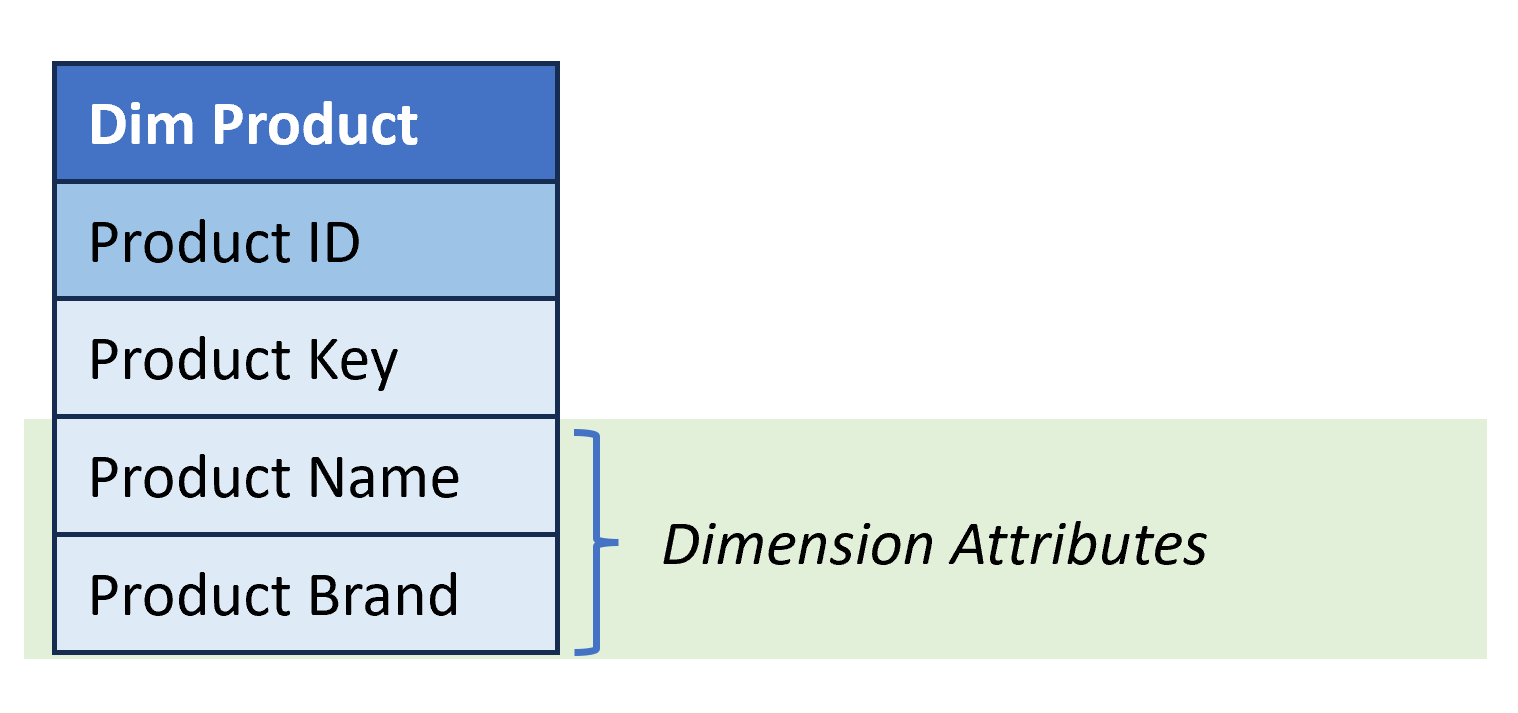
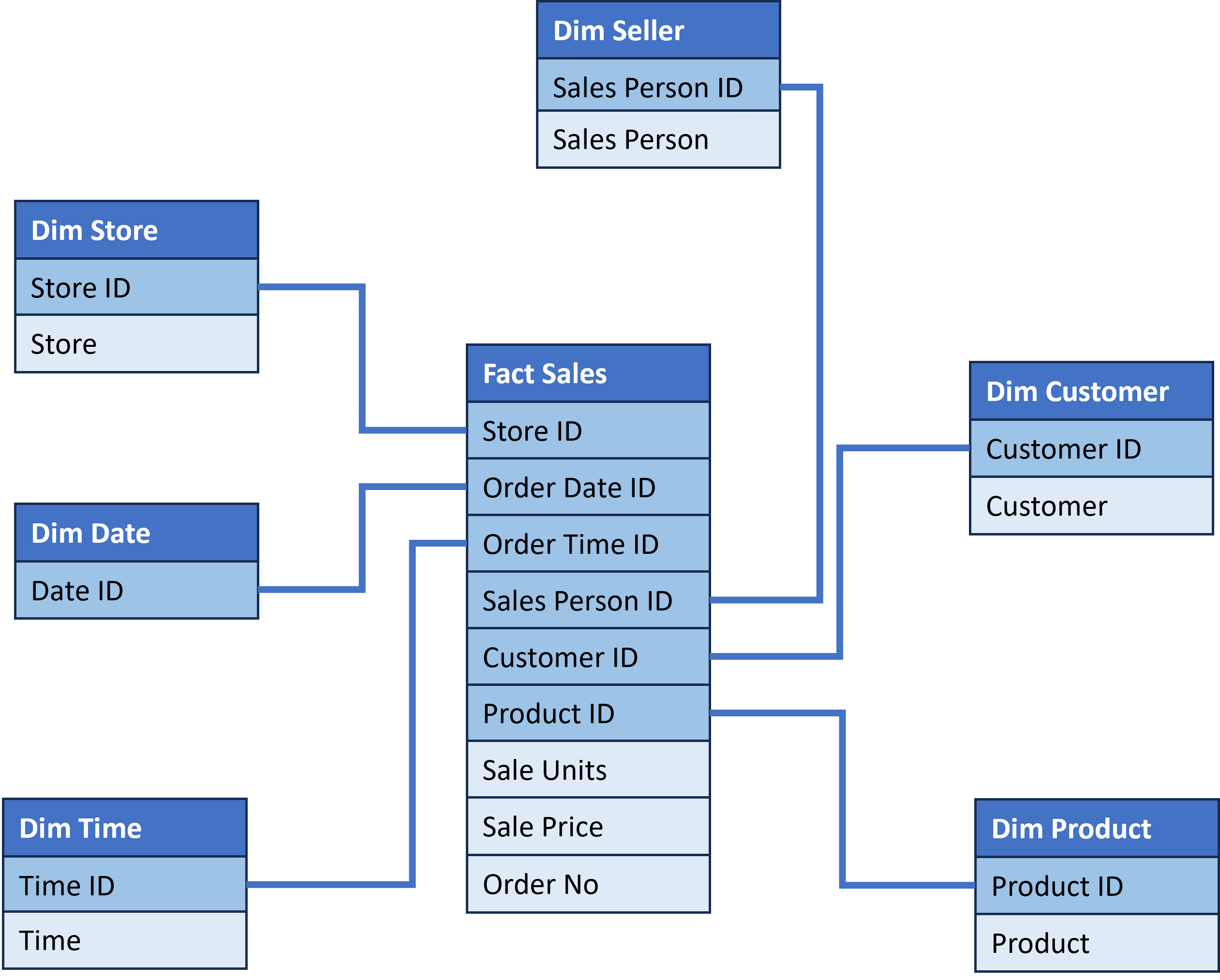
Building dimension tables
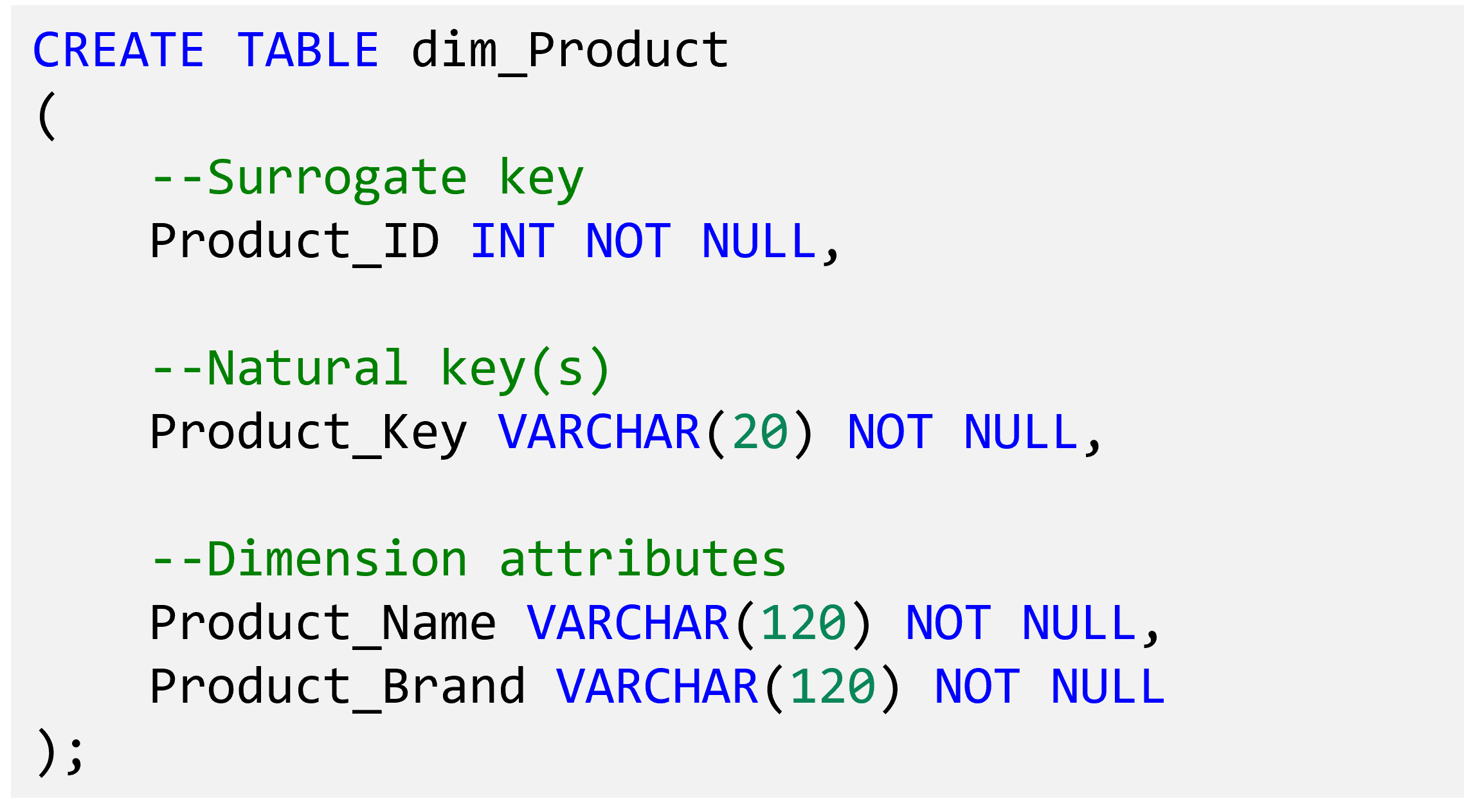
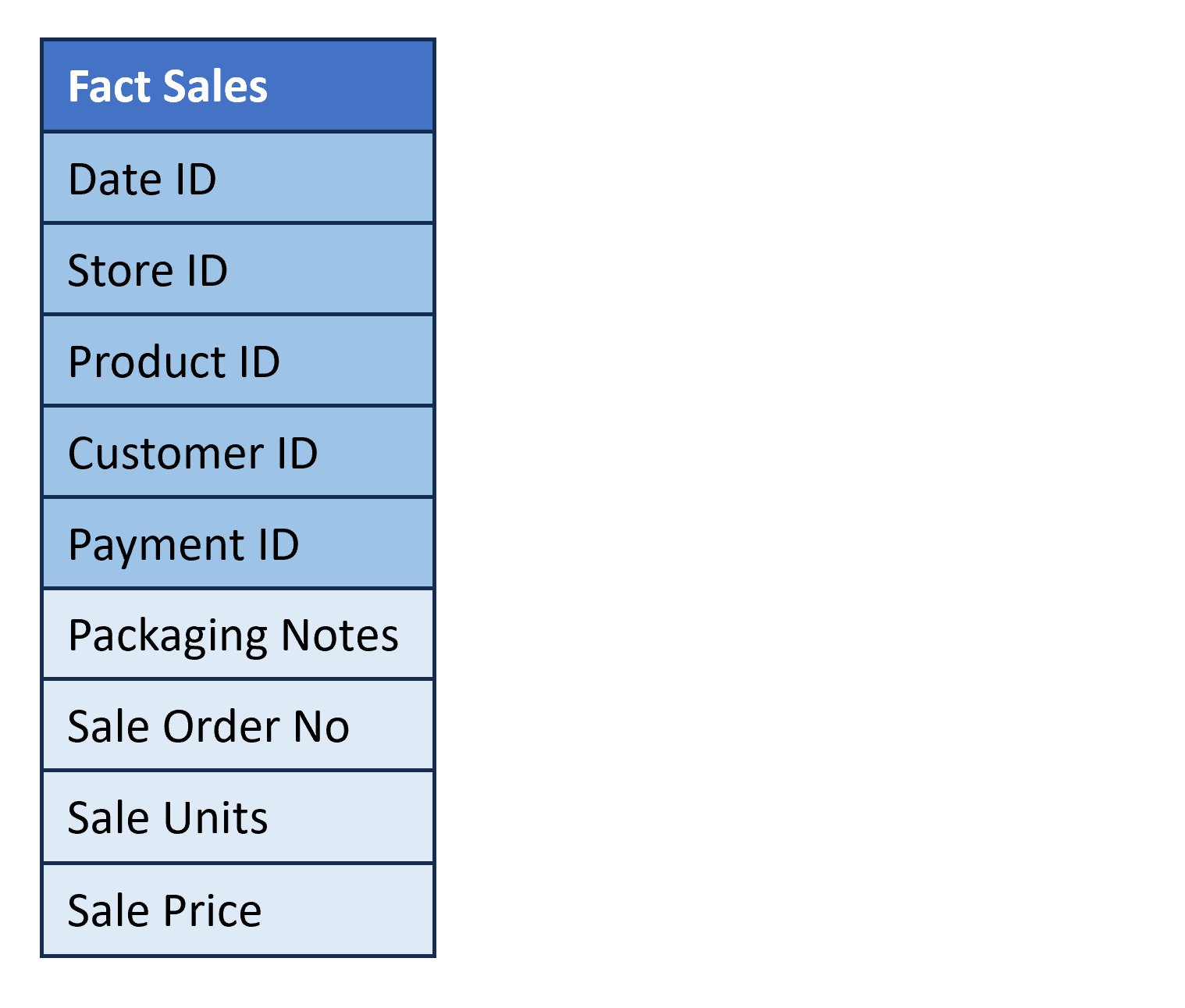
Fact table structure
- Describe business events (e.g., sale of a product).
- Columns:
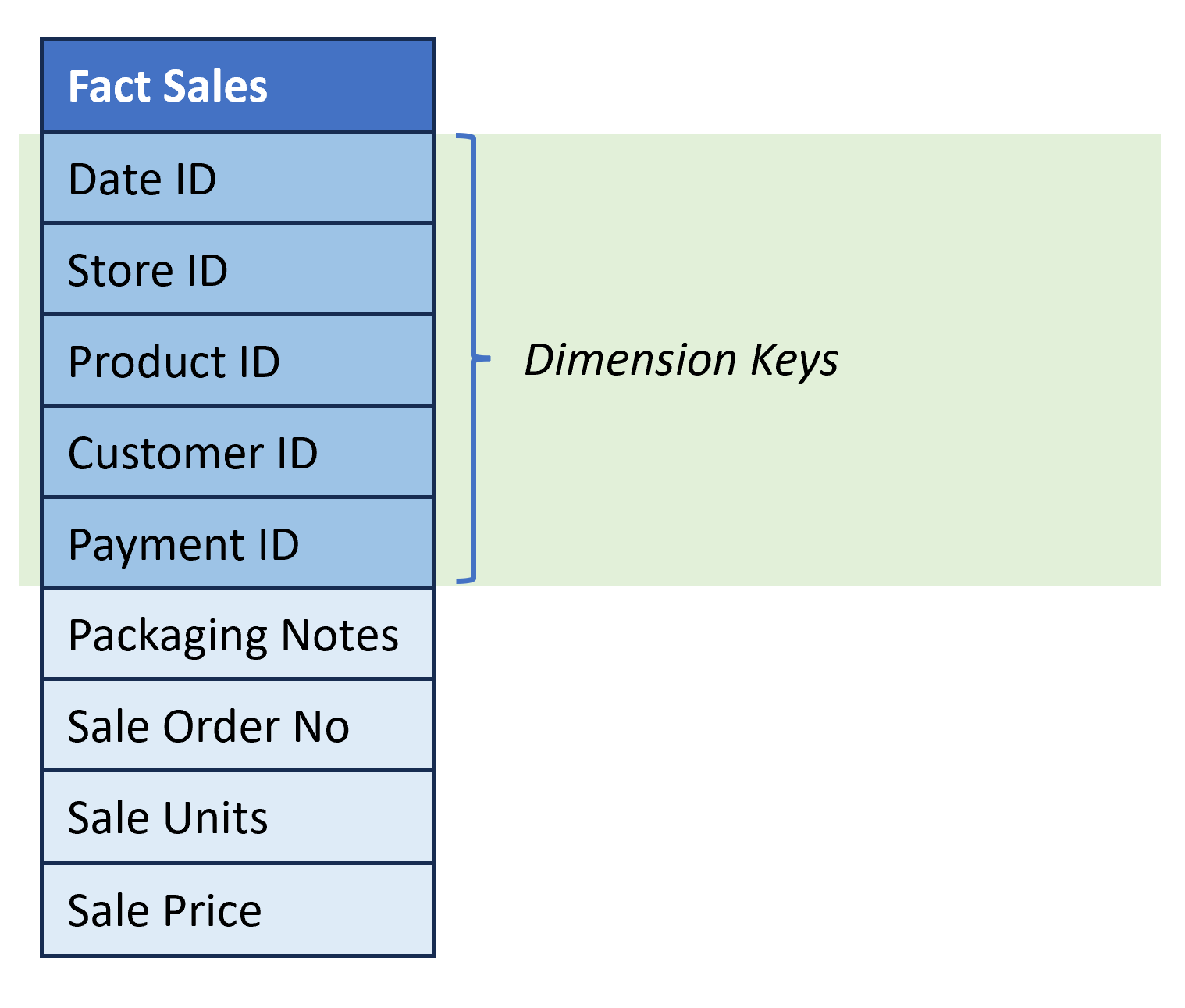
Fact table structure
- Describe business events (e.g., sale of a product).
- Columns:
- Dimension Keys. References to the surrogate keys of the dimension tables.
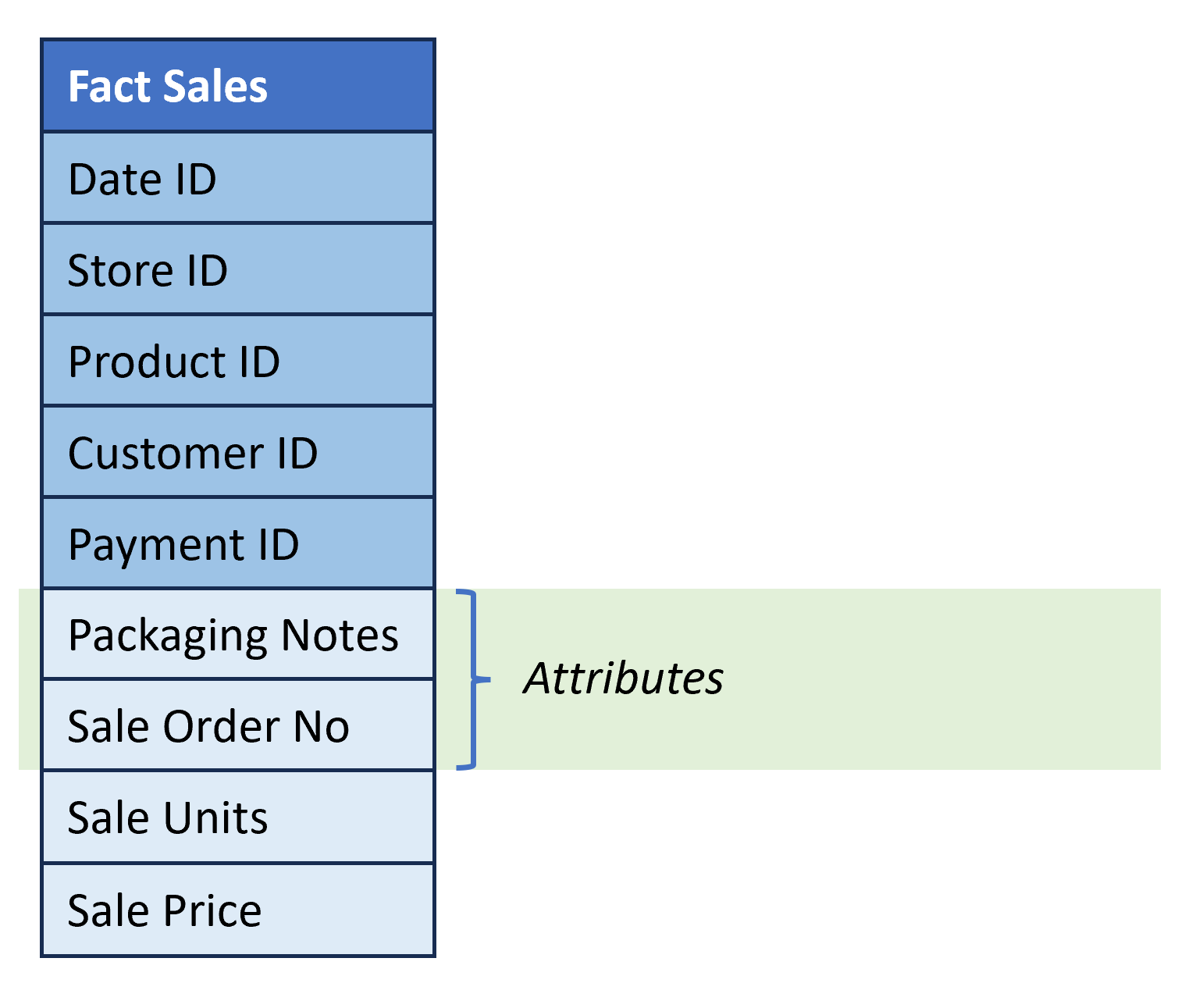
Fact table structure
- Describe business events (e.g., sale of a product).
- Columns:
- Dimension Keys. References to the surrogate keys of the dimension tables.
- Attributes. Provide additional information about the fact but are neither a dimension or a numerical measure.
Fact table structure
- Describe business events (e.g., sale of a product).
- Columns:
- Dimension Keys. References to the surrogate keys of the dimension tables.
- Attributes. Provide additional information about the fact but are neither a dimension or a numerical measure.
- Measures. Quantify something about the fact; they are numeric and commonly additive, e.g., number of units, dollar amount, etc.
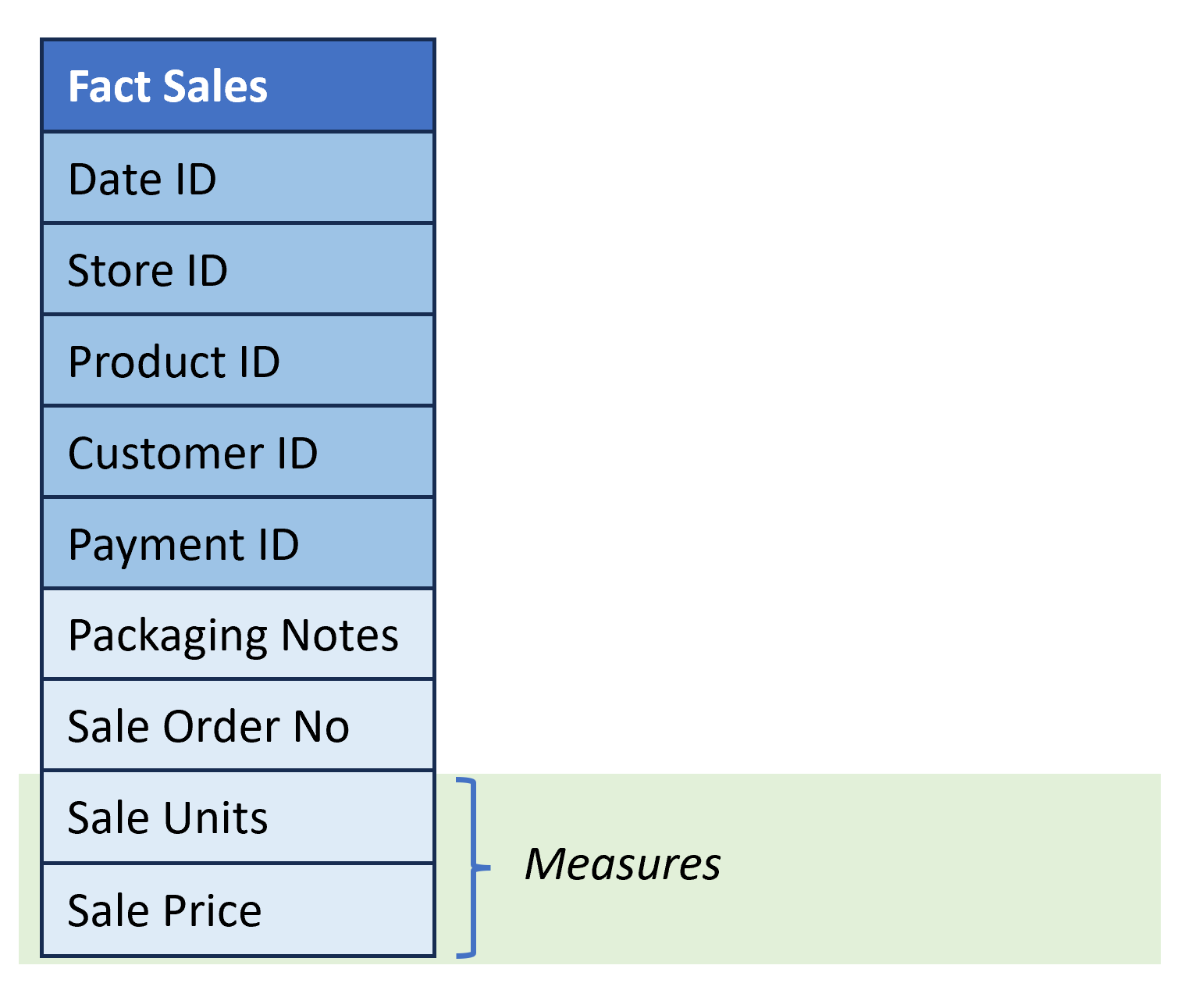
Building fact tables
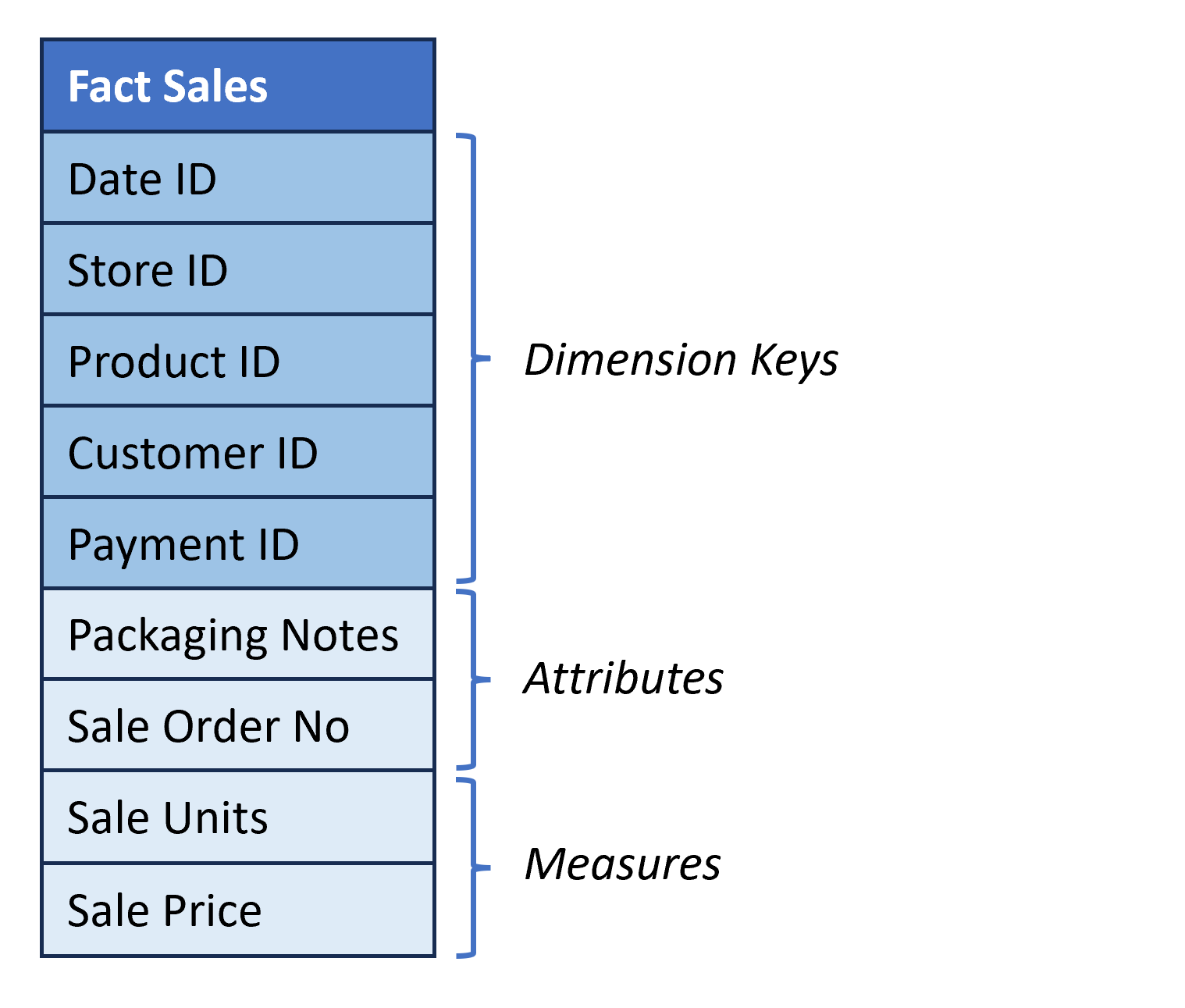
Let's practice!
Transform and Analyze Data with Microsoft Fabric

