Implement performance improvements
Transform and Analyze Data with Microsoft Fabric

Luis Silva
Solution Architect - Data & AI
Optimization strategies
- Optimize design of Fabric items
- Scale up
- Scale out
Optimizing SQL
- Limit the queries to only the columns and operations needed
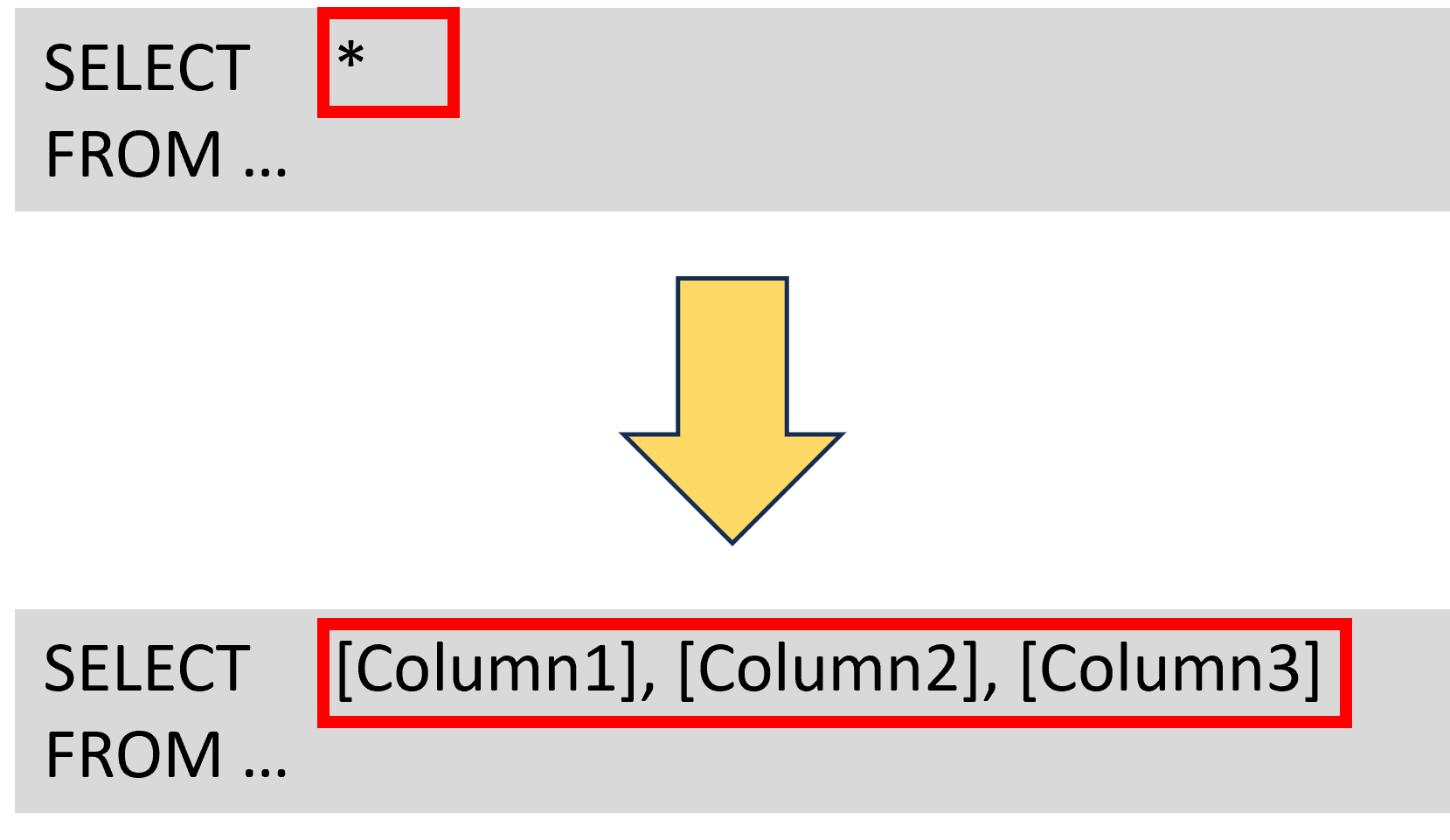
Optimizing SQL
- Limit the queries to only the columns and operations needed
- Use the smallest data types possible
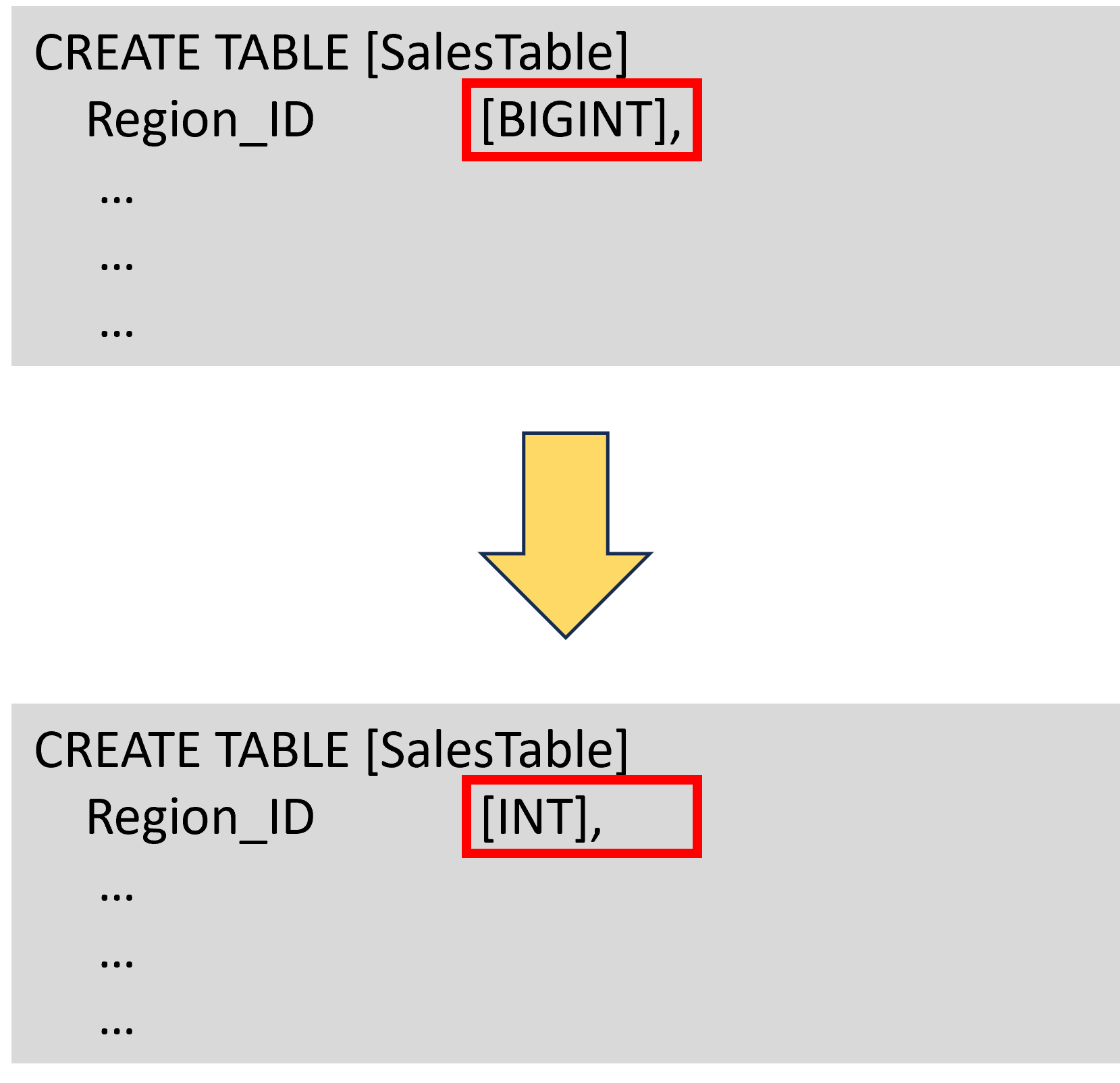
Optimizing SQL
- Limit the queries to only the columns and operations needed
- Use the smallest data types possible
- Use the star schema design
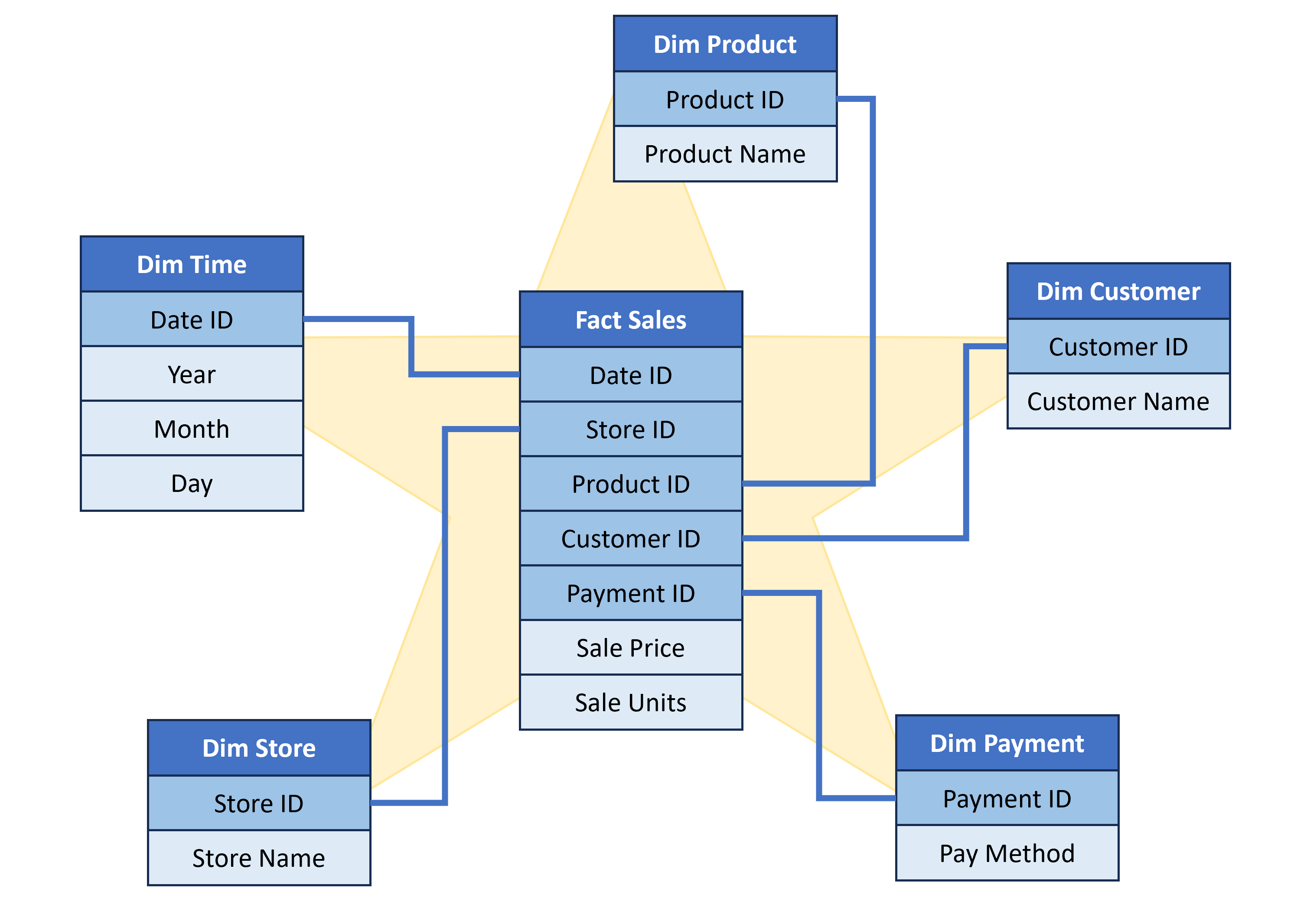
Optimizing SQL
- Limit the queries to only the columns and operations needed
- Use the smallest data types possible
- Use the star schema design
- Use system views to monitor query usage
SELECT *
FROM sys.dm_exec_requests;
Optimizing Notebooks
- Leverage the Spark History Server
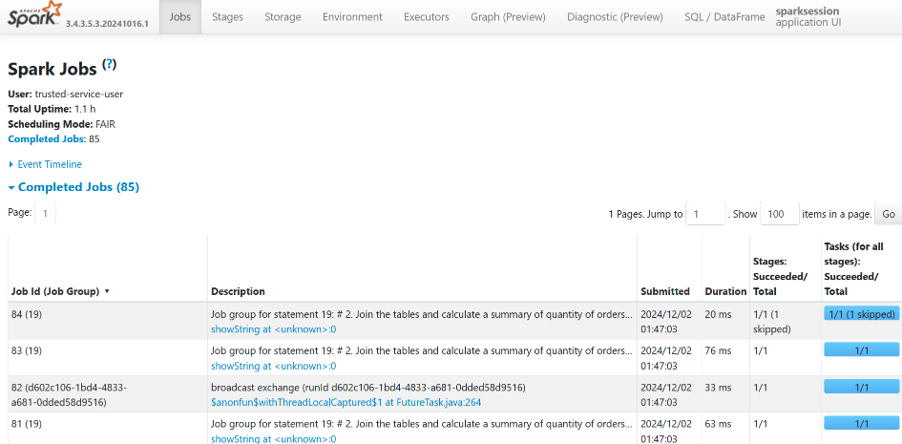
Optimizing Notebooks
- Leverage the Spark History Server
- Stop active Spark sessions when not in use
Optimizing Notebooks
- Leverage the Spark History Server
- Stop active Spark sessions when not in use
- When joining data, reduce the amount of data in memory prior to executing the join
Optimizing dataflows
- Minimize expensive operations like sorting
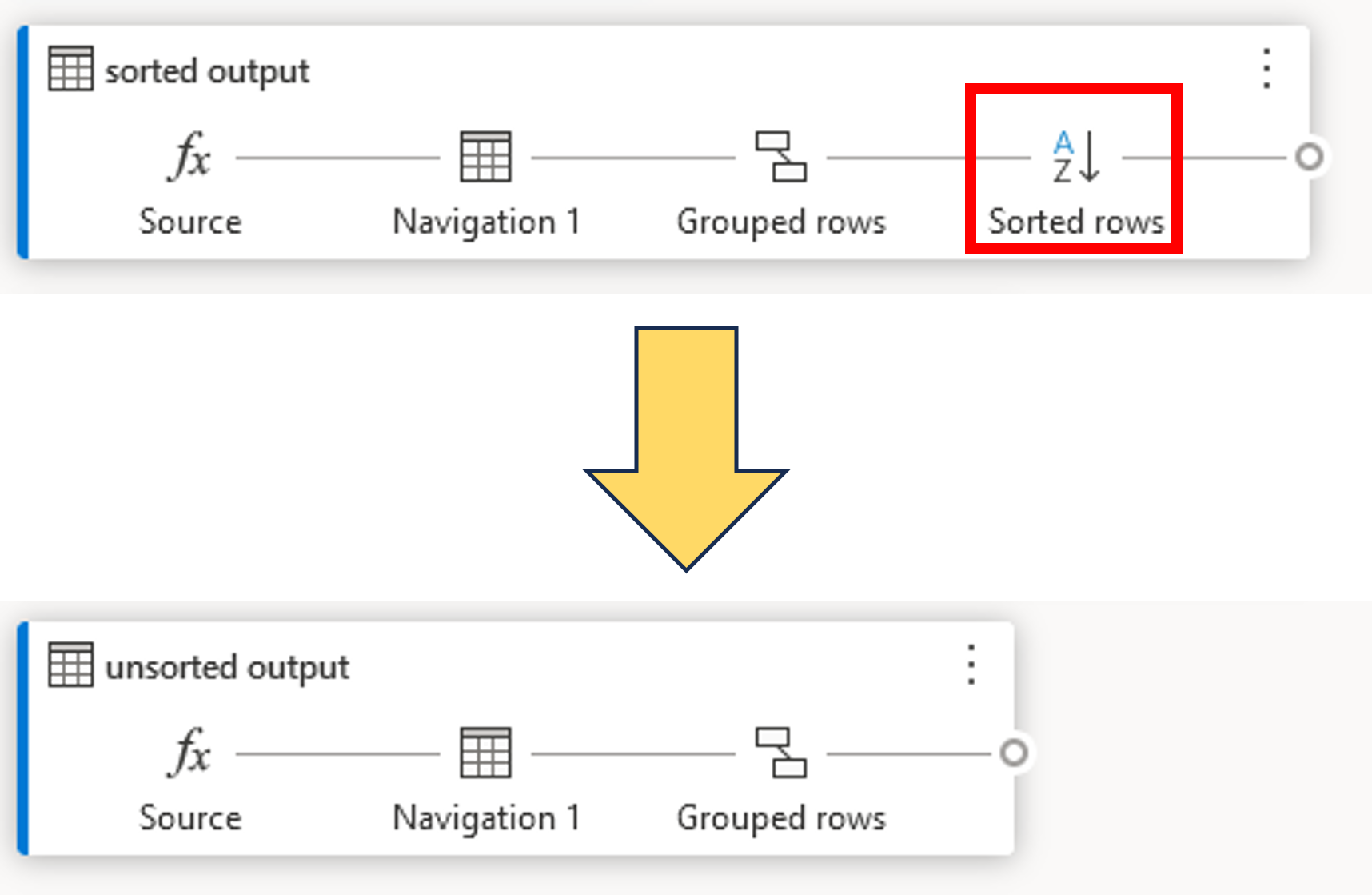
Optimizing dataflows
- Minimize expensive operations like sorting
- Query folding
- Offload processing tasks to the data source
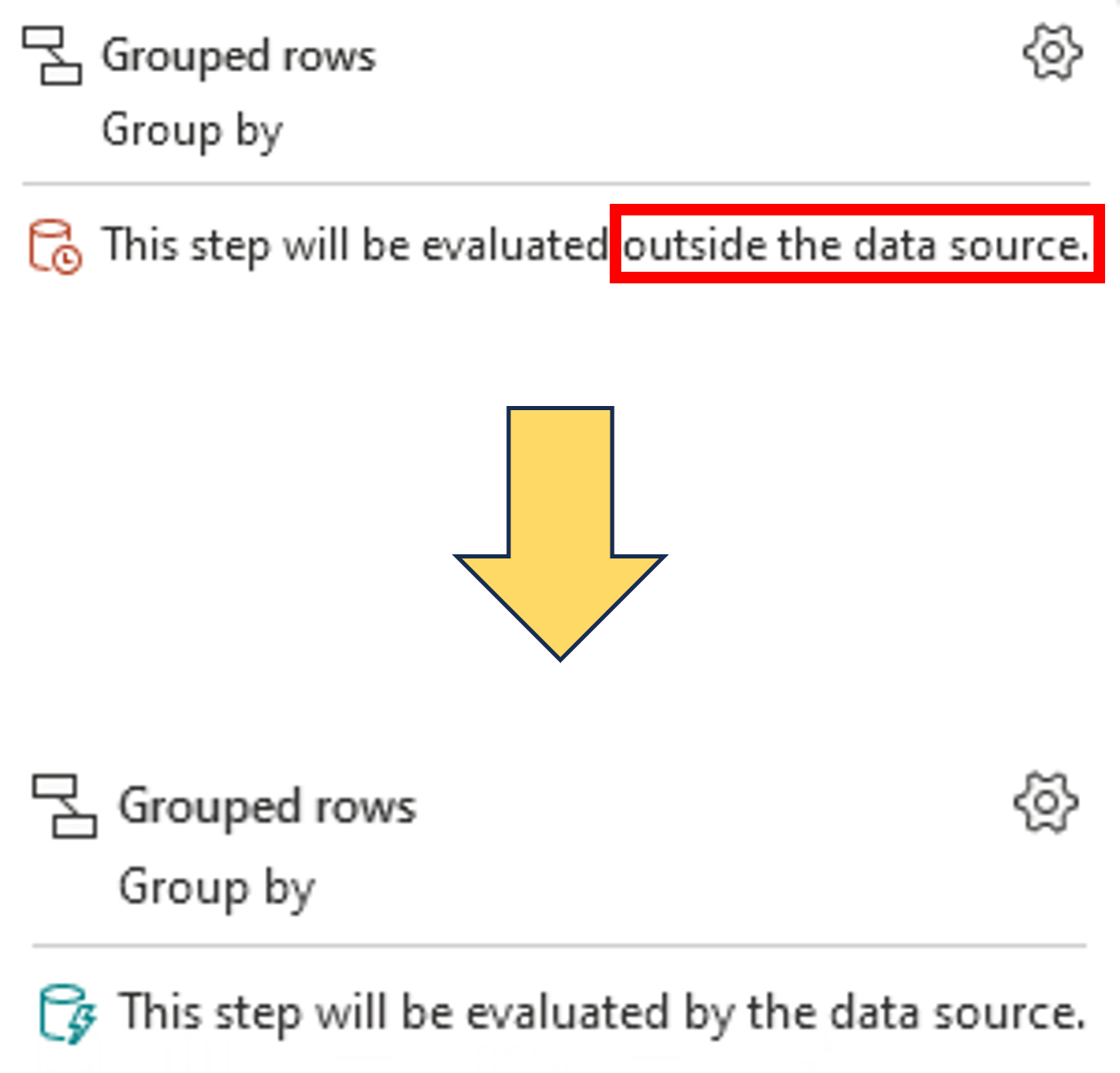
Optimizing dataflows
- Minimize expensive operations like sorting
- Query folding
- Offload processing tasks to the data source
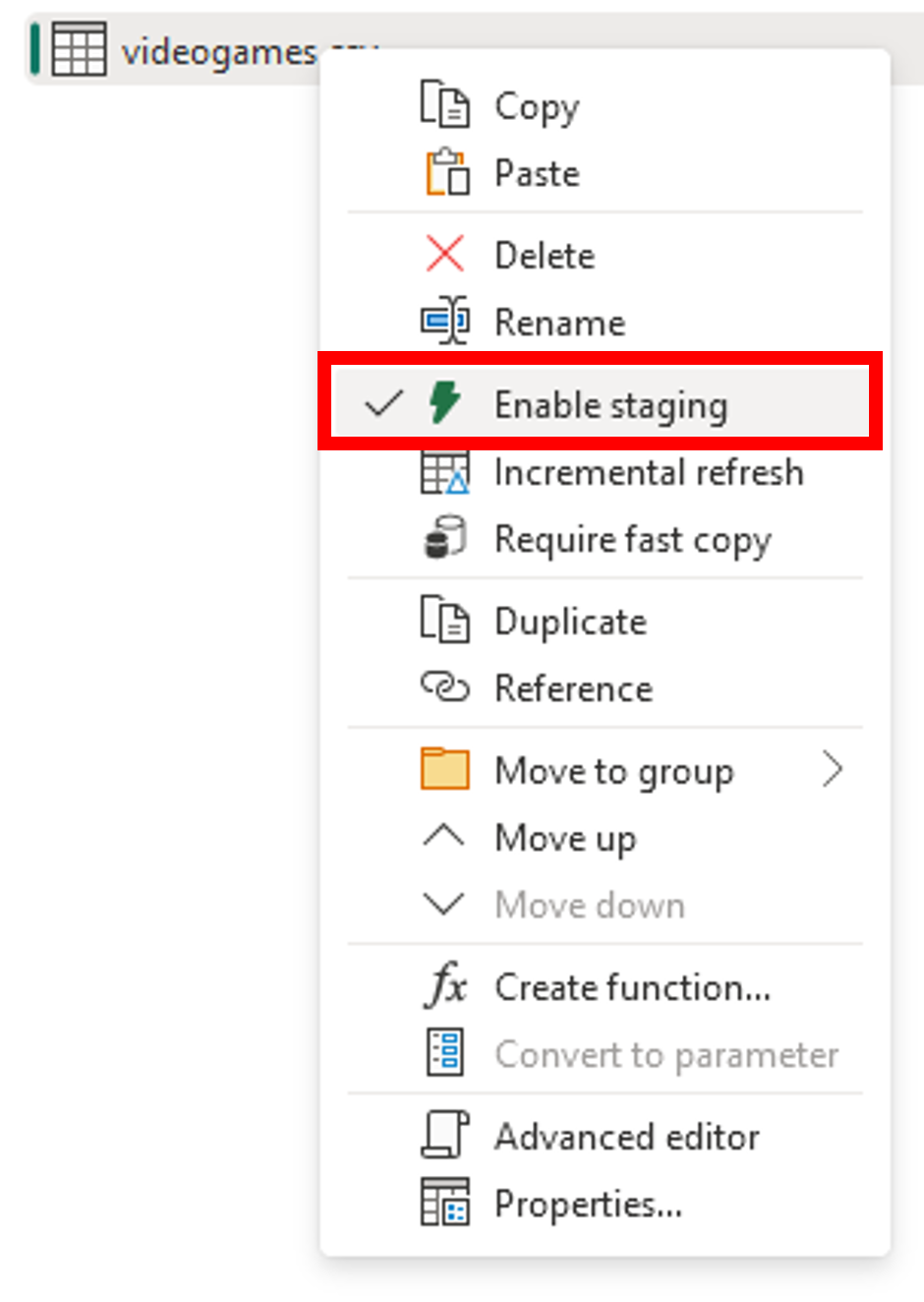
- Staging On/Off
- Disable for small data loads or simpler transformations
- Enable for larger data loads or more complex transformations
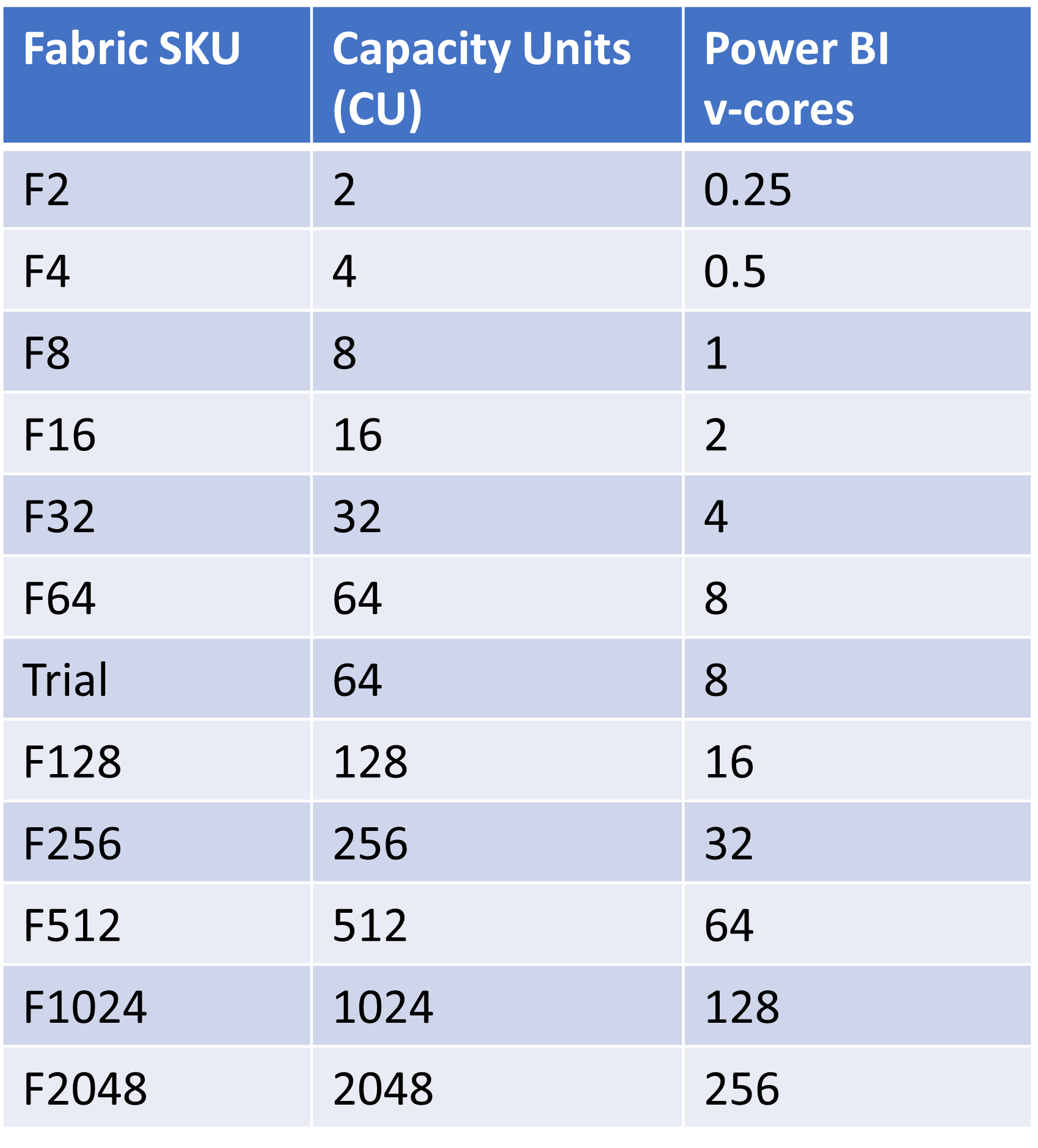
Scale Up
- Increase the SKU size
- Higher SKU = more compute capacity
 v
v
Scale Up
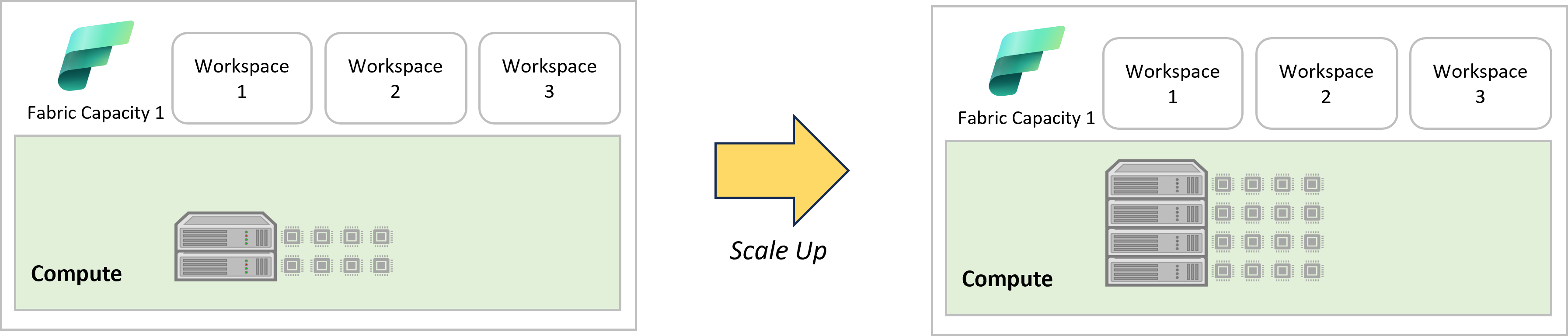
Example: Scale up from F64 (8 v-cores) to F128 (16 v-cores)
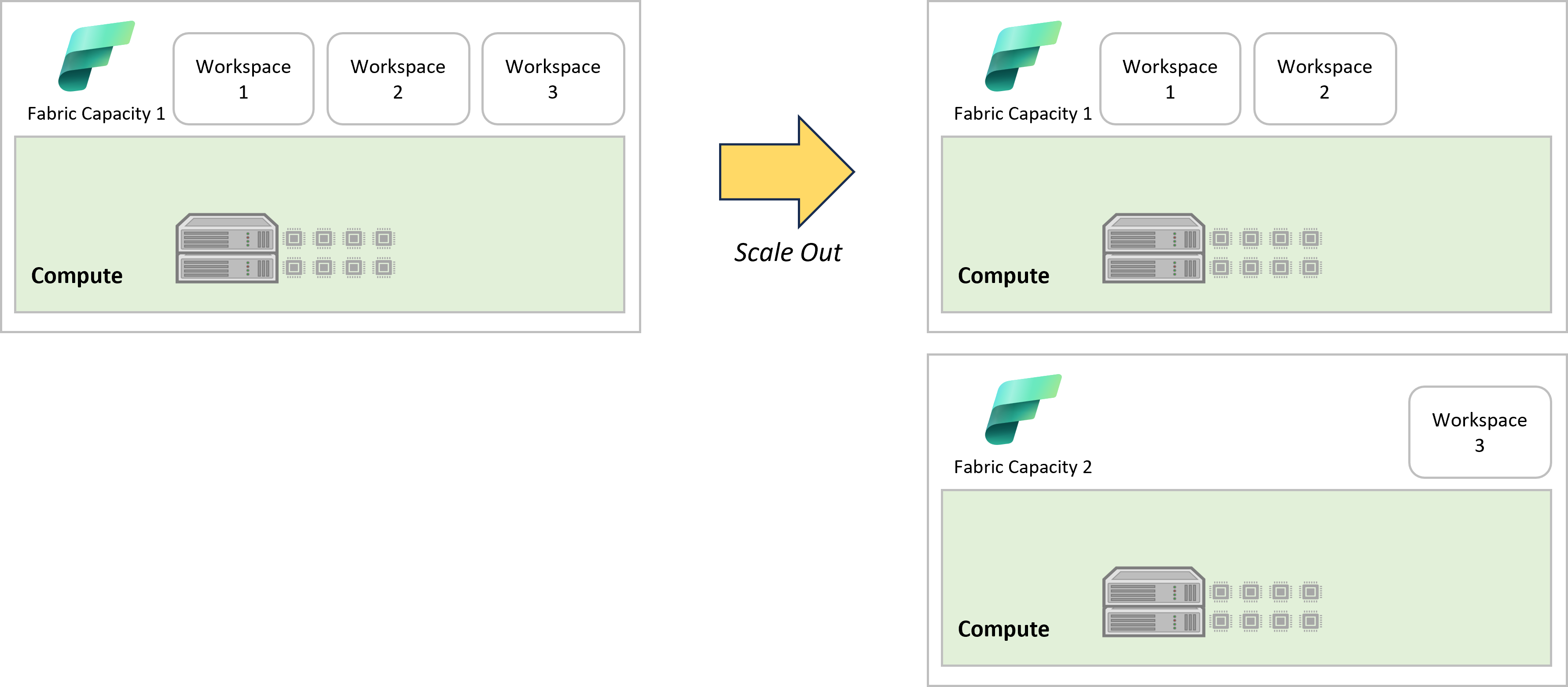
Scale Out
- Move some items to a different Fabric capacity.
- Isolate workloads
- Production vs non-production
- Different areas of the business, for example a separate capacity for executive reporting
Scale Out
Let's practice!
Transform and Analyze Data with Microsoft Fabric

