Custom models
Introduction to MLflow

Weston Bassler
Senior MLOps Engineer
Example use cases
NLP - Tokenizer(s)
Classification - Label encoder
Pre/Post processing
Not a built-in flavor

1 unsplash.com
Custom Python models
Built in Flavor -
python_functionmlflow.pyfuncsave_model()log_model()load_model()
Custom model class
Custom model class
MyClass(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel)
PythonModel class
load_context()- loads artifacts whenmlflow.pyfunc.load_model()is calledpredict()- takes model input and performs user defined evaluation
Python class
# Class class MyPythonClass:# Function that prints Hello! def my_func(): print("Hello!")
# Create a new Object x = MyPythonClass()# Excute my_func function x.my_func()
"Hello!"
Example custom Class
import mlflow.pyfunc # Define the model class class CustomPredict(mlflow.pyfunc.PythonModel):# Load artifacts def load_context(self, context): self.model = mlflow.sklearn.load_model(context.artifacts["custom_model"])# Evaluate input using custom_function() def predict(self, context, model_input): prediction = self.model.predict(model_input) return custom_function(prediction)
Saving and logging a custom model
# Save model to local filesystem
mlflow.pyfunc.save_model(path="custom_model", python_model=CustomPredict())
# Log model to MLflow Tracking
mlflow.pyfunc.log_model(artifact_path="custom_model", python_model=CustomPredict())
Loading custom models
# Load model from local filesystem
mlflow.pyfunc.load_model("local")
# Load model from MLflow Tracking
mlflow.pyfunc.load_model("runs:/run_id/tracking_path")
Model Evaluation
mlflow.evaluate()- Performance based on a datasetRegression and Classification models
Evaluation Example
# Training Data X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \ train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.7,random_state=0)# Linear Regression model lr = LinearRegression() lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Dataset eval_data = X_test eval_data["test_label"] = y_test# Evaluate model with Dataset mlflow.evaluate( "runs:/run_id/model", eval_data, targets="test_label", model_type="regressor" )
Tracking UI
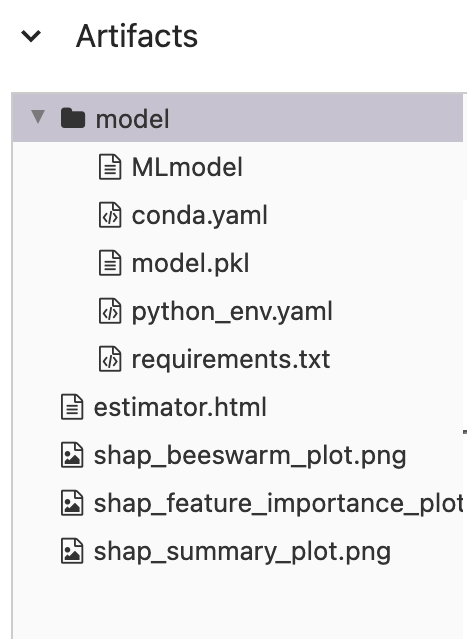

1 shap.readthedocs.io
Let's practice!
Introduction to MLflow

