What is covariate shift?
Monitoring Machine Learning Concepts

Hakim Elakhrass
Co-founder and CEO of NannyML
Definitions
- covariate variables $=$ input features
- $P(X)$ changes
- joint probability $P(Y|X)$ remains the same
- changes in the joint distribution of the covariates
Why joint probability distribution?
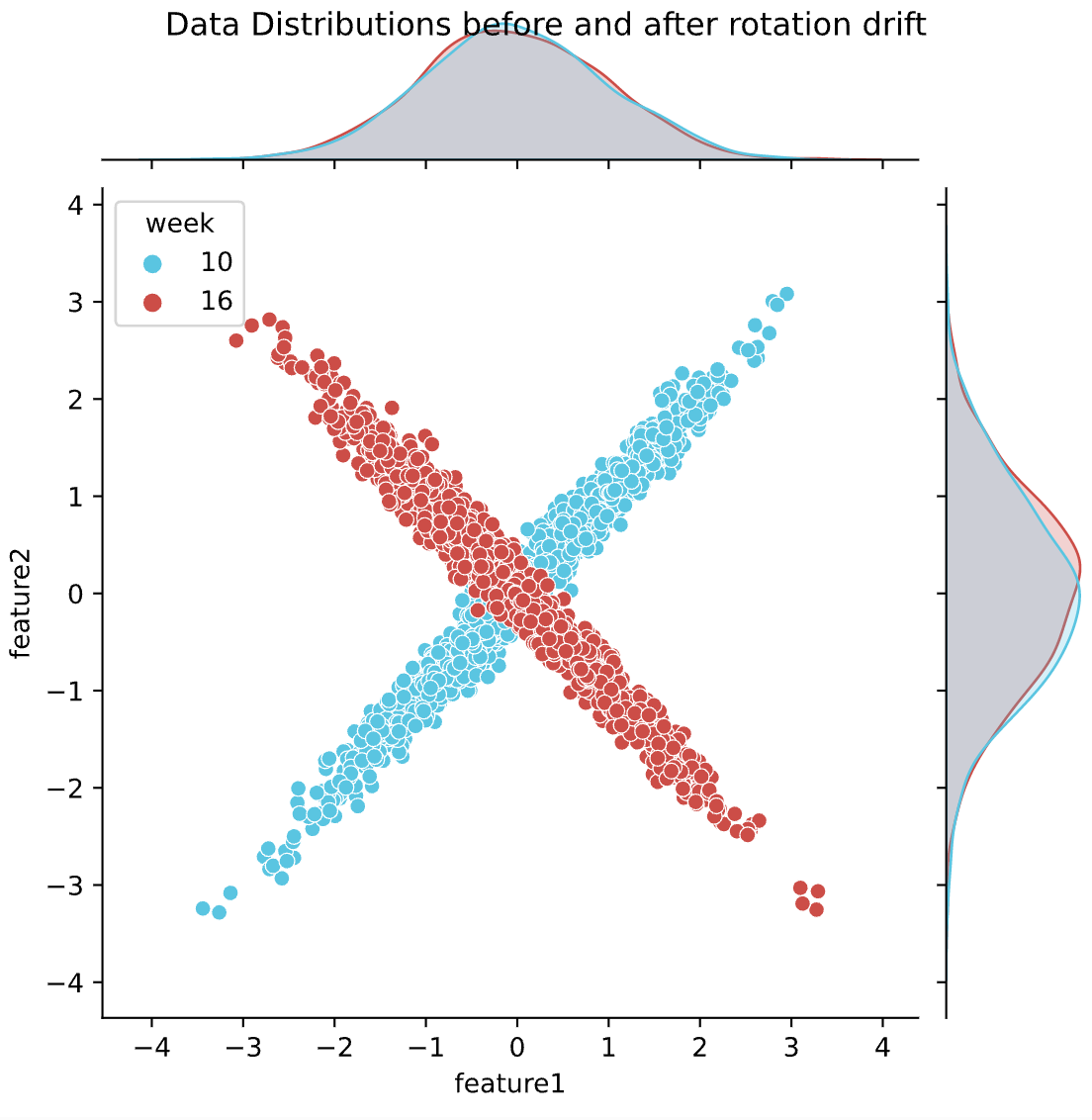
Why does covariate shift occur?
Potential reasons for covariate shift:
- The real world is not stationary - patterns and trends evolve
- Changes in data sources - variations in how data is collected between testing and production
- Evolution of the system and environment
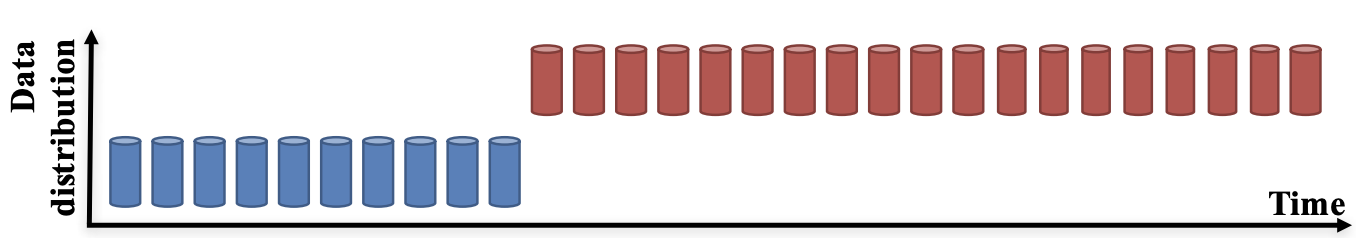
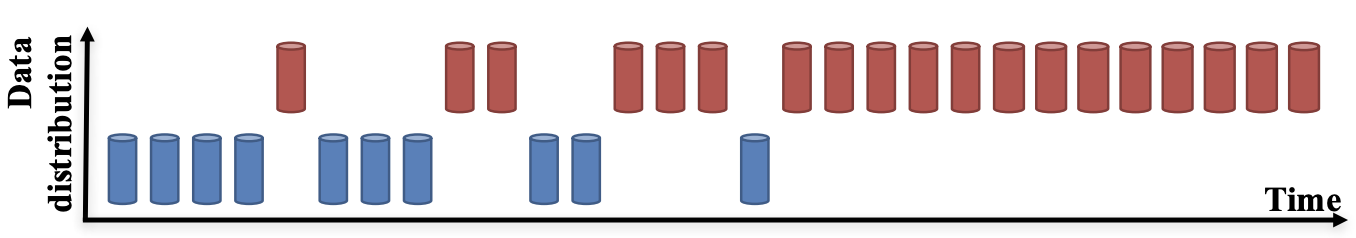
How does covariate shift occur?
Dynamics of the changes in the distribution:
- Sudden
- Gradual
- Seasonal

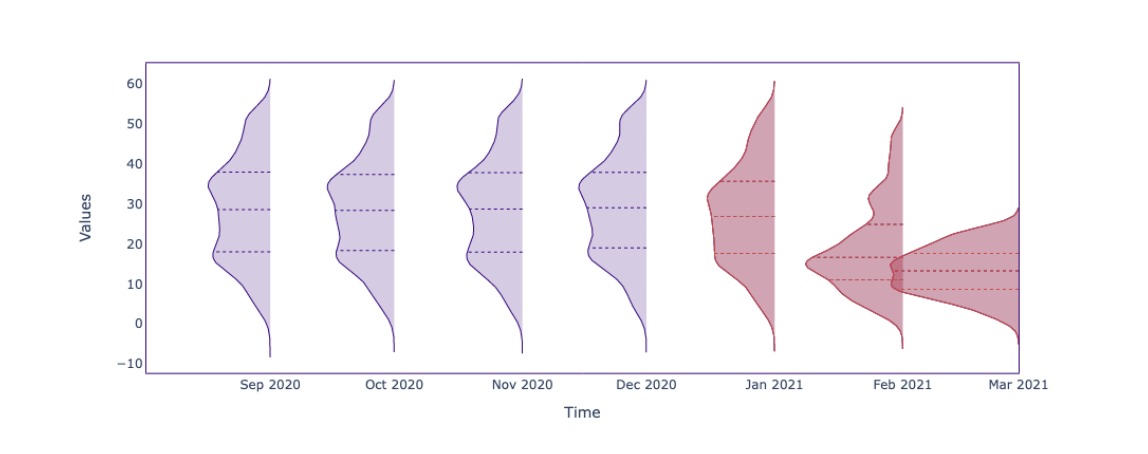
How to detect the covariate shift?
Univariate method
Multivariate method
1 https://app.datacamp.com/learn/courses/dimensionality-reduction-in-python
Let's practice!
Monitoring Machine Learning Concepts

