Die Leistung des Modells bewerten
Einführung in Deep Learning mit PyTorch

Jasmin Ludolf
Senior Data Science Content Developer, DataCamp
Training, Validierung und Test
$$
- Ein Datensatz wird normalerweise in drei Teilmengen aufgeteilt:
| Prozent der Daten | Rolle | |
|---|---|---|
| Training | 80-90 % | Passt die Modellparameter an |
| Validierung | 10-20 % | Passt Hyperparameter an |
| Test | 5-10 % | Bewertet die finale Leistung des Modells |
$$
- Verlust und Genauigkeit bei Training und Validierung verfolgen
Den Trainingsverlust berechnen
$$
Für jede Epoche:
- Verlust über alle Batches im DataLoader summieren
- Mittleren Trainingsverlust am Ende der Epoche berechnen
training_loss = 0.0for inputs, labels in trainloader: # Run the forward pass outputs = model(inputs) # Compute the loss loss = criterion(outputs, labels)# Backpropagation loss.backward() # Compute gradients optimizer.step() # Update weights optimizer.zero_grad() # Reset gradients# Calculate and sum the loss training_loss += loss.item()epoch_loss = training_loss / len(trainloader)
Den Validierungsverlust berechnen
validation_loss = 0.0 model.eval() # Put model in evaluation modewith torch.no_grad(): # Disable gradients for efficiencyfor inputs, labels in validationloader: # Run the forward pass outputs = model(inputs) # Calculate the loss loss = criterion(outputs, labels) validation_loss += loss.item() epoch_loss = validation_loss / len(validationloader) # Compute mean lossmodel.train() # Switch back to training mode
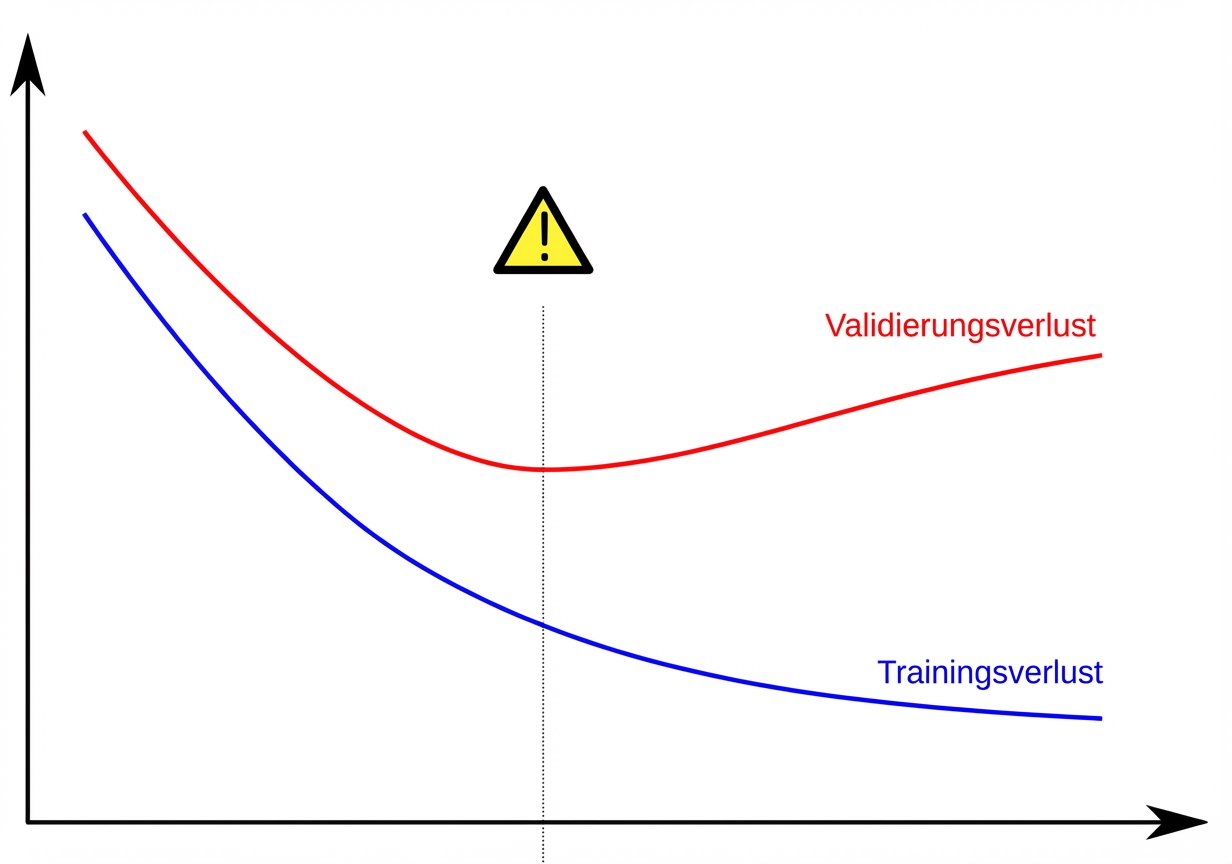
Überanpassung
Berechnung der Genauigkeit mit torchmetrics
import torchmetrics# Create accuracy metric metric = torchmetrics.Accuracy(task="multiclass", num_classes=3)for features, labels in dataloader: outputs = model(features) # Forward pass # Compute batch accuracy (keeping argmax for one-hot labels) metric.update(outputs, labels.argmax(dim=-1))# Compute accuracy over the whole epoch accuracy = metric.compute()# Reset metric for the next epoch metric.reset()
Lass uns üben!
Einführung in Deep Learning mit PyTorch

