Erzeugung neuer Merkmale
Explorative Datenanalyse in Python

George Boorman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
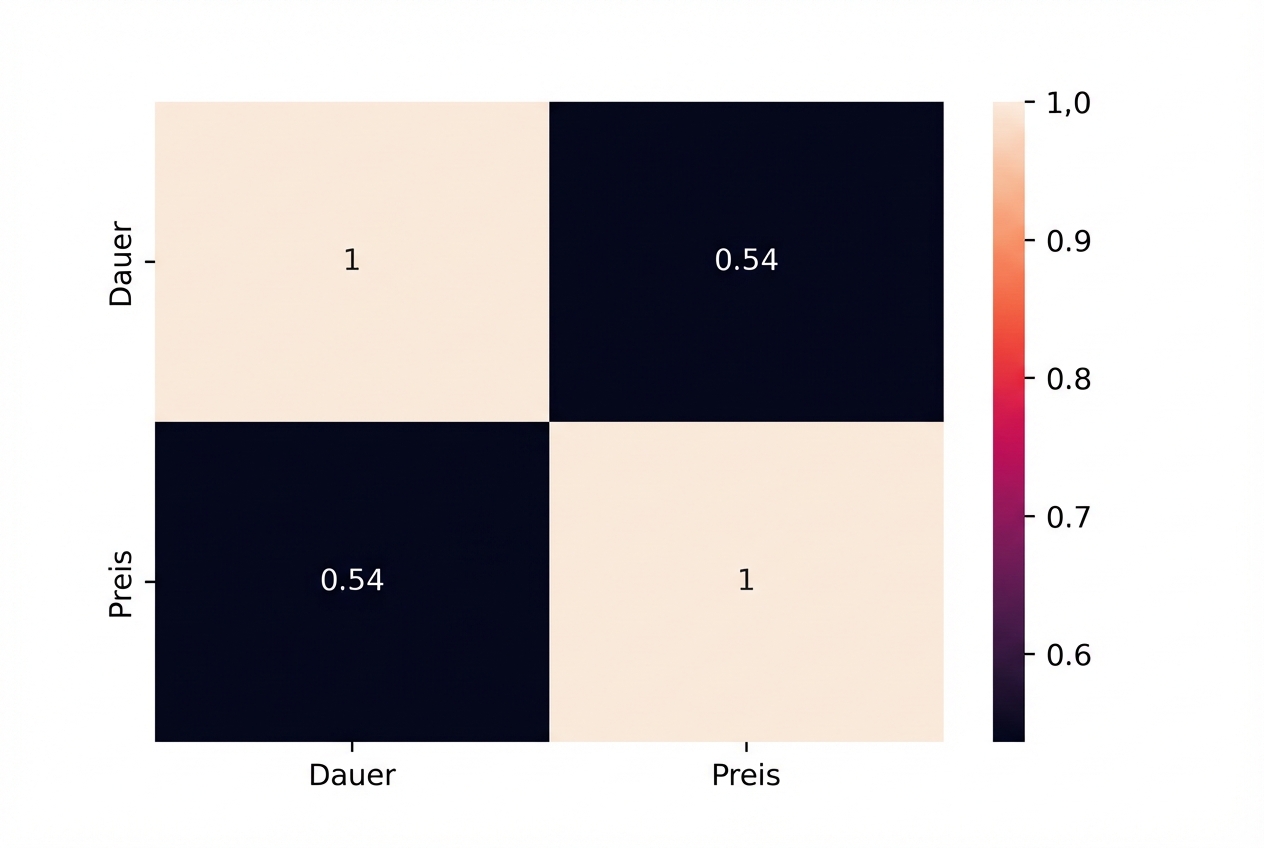
Korrelation
sns.heatmap(planes.corr(numeric_only=True), annot=True)
plt.show()
Datentypen anzeigen
print(planes.dtypes)
Airline object
Date_of_Journey datetime64[ns]
Source object
Destination object
Route object
Dep_Time datetime64[ns]
Arrival_Time datetime64[ns]
Duration float64
Total_Stops object
Additional_Info object
Price float64
dtype: object
Gesamtzahl der Zwischenstopps
print(planes["Total_Stops"].value_counts())
1 stop 4107
non-stop 2584
2 stops 1127
3 stops 29
4 stops 1
Name: Total_Stops, dtype: int64
Gesamtzahl der Zwischenstopp bereinigen
planes["Total_Stops"] = planes["Total_Stops"].str.replace(" stops", "")planes["Total_Stops"] = planes["Total_Stops"].str.replace(" stop", "")planes["Total_Stops"] = planes["Total_Stops"].str.replace("non-stop", "0")planes["Total_Stops"] = planes["Total_Stops"].astype(int)
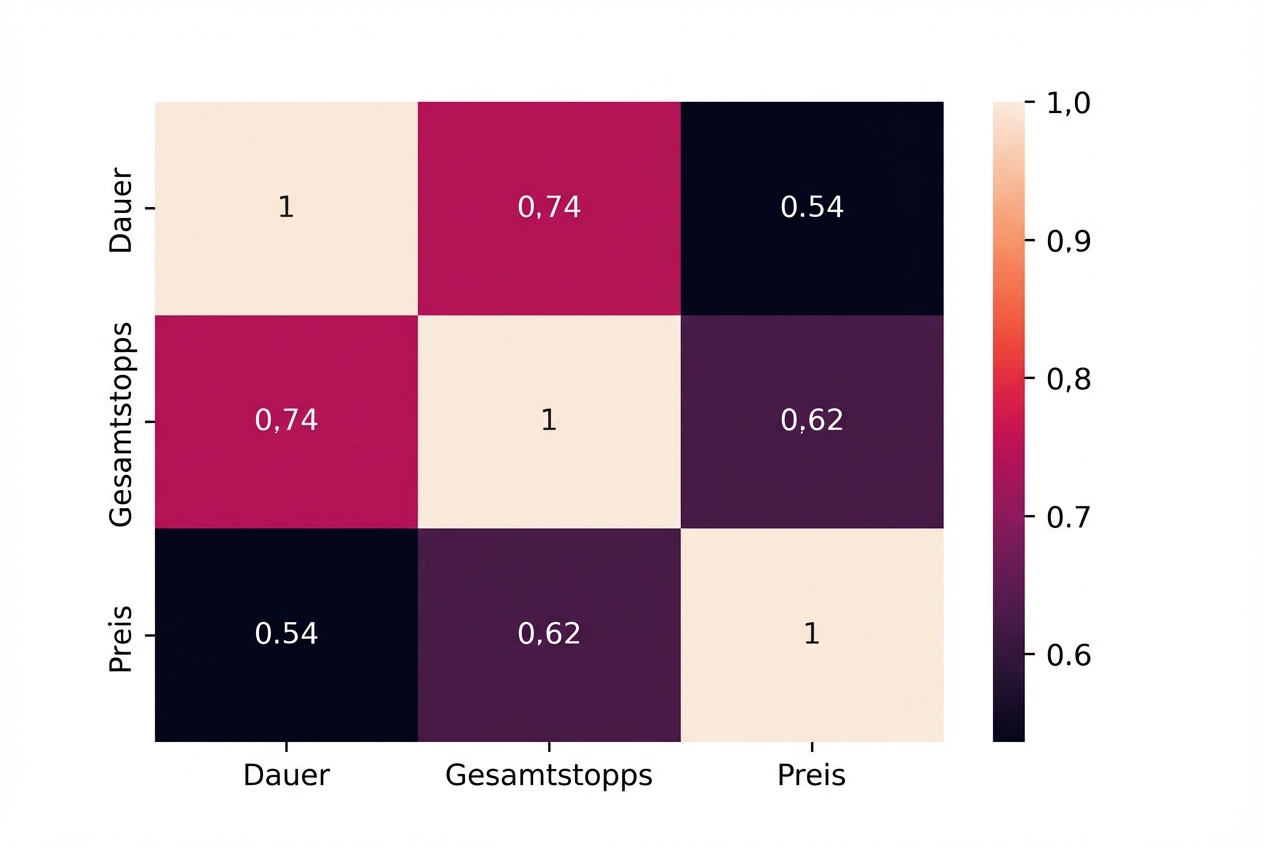
Korrelation
sns.heatmap(planes.corr(numeric_only=True), annot=True)
plt.show()
Datumsangaben
print(planes.dtypes)
Airline object
Date_of_Journey datetime64[ns]
Source object
Destination object
Route object
Dep_Time datetime64[ns]
Arrival_Time datetime64[ns]
Duration float64
Total_Stops int64
Additional_Info object
Price float64
dtype: object
Extraktion des Monats und Wochentags
planes["month"] = planes["Date_of_Journey"].dt.monthplanes["weekday"] = planes["Date_of_Journey"].dt.weekdayprint(planes[["month", "weekday", "Date_of_Journey"]].head())
month weekday Date_of_Journey
0 9 4 2019-09-06
1 12 3 2019-12-05
2 1 3 2019-01-03
3 6 0 2019-06-24
4 12 1 2019-12-03
Abflug- und Ankunftszeiten
planes["Dep_Hour"] = planes["Dep_Time"].dt.hour
planes["Arrival_Hour"] = planes["Arrival_Time"].dt.hour
Korrelation
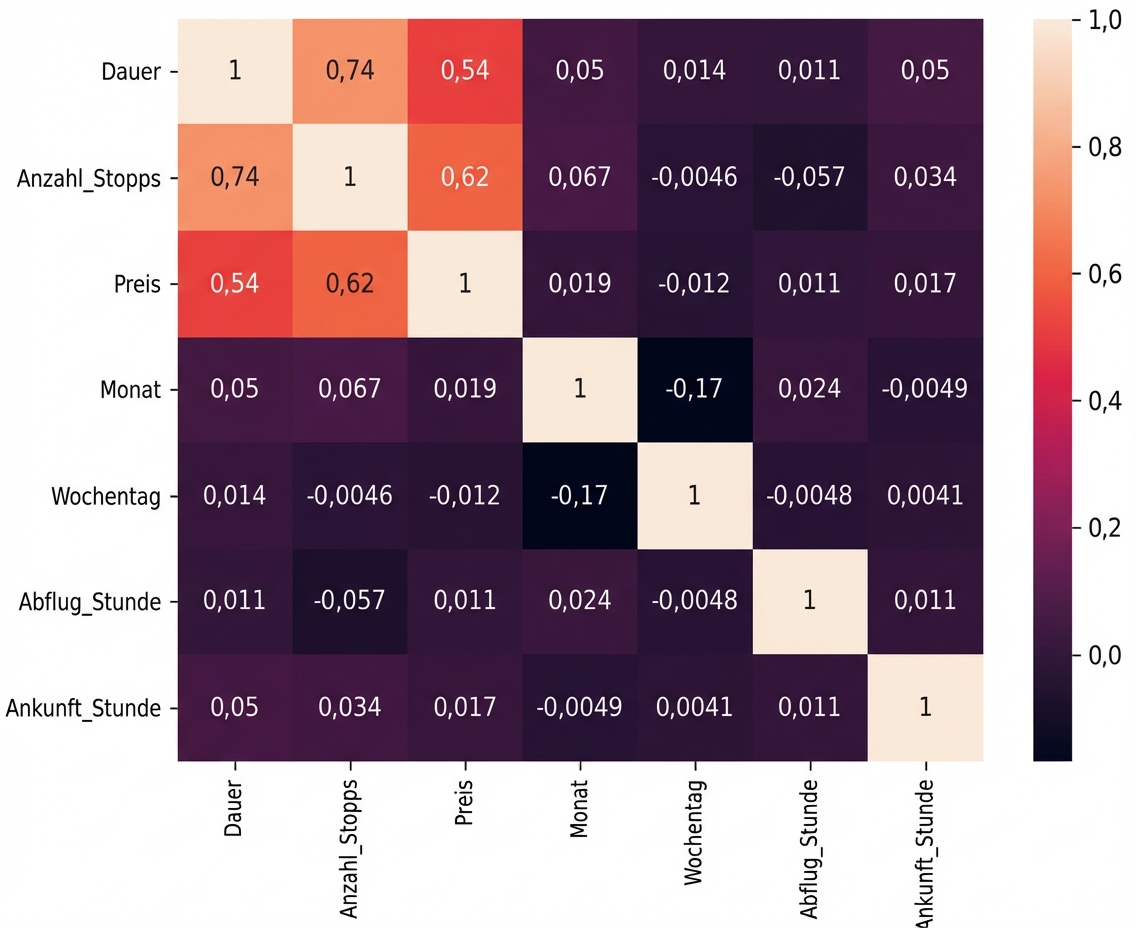
Kategorien erstellen
print(planes["Price"].describe())
count 7848.000000
mean 9035.413609
std 4429.822081
min 1759.000000
25% 5228.000000
50% 8355.000000
75% 12373.000000
max 54826.000000
Name: Price, dtype: float64
| Bereich | Buchungsklasse |
|---|---|
| <= 5228 | Economy |
| > 5228 <= 8355 | Premium Economy |
| > 8335 <= 12373 | Business Class |
| > 12373 | First Class |
Deskriptive Statistik
twenty_fifth = planes["Price"].quantile(0.25)median = planes["Price"].median()seventy_fifth = planes["Price"].quantile(0.75)maximum = planes["Price"].max()
Labels und Bins
labels = ["Economy", "Premium Economy", "Business Class", "First Class"]bins = [0, twenty_fifth, median, seventy_fifth, maximum]
pd.cut()

planes["Price_Category"] = pd.cut(
pd.cut()
planes["Price_Category"] = pd.cut(planes["Price"],
pd.cut()
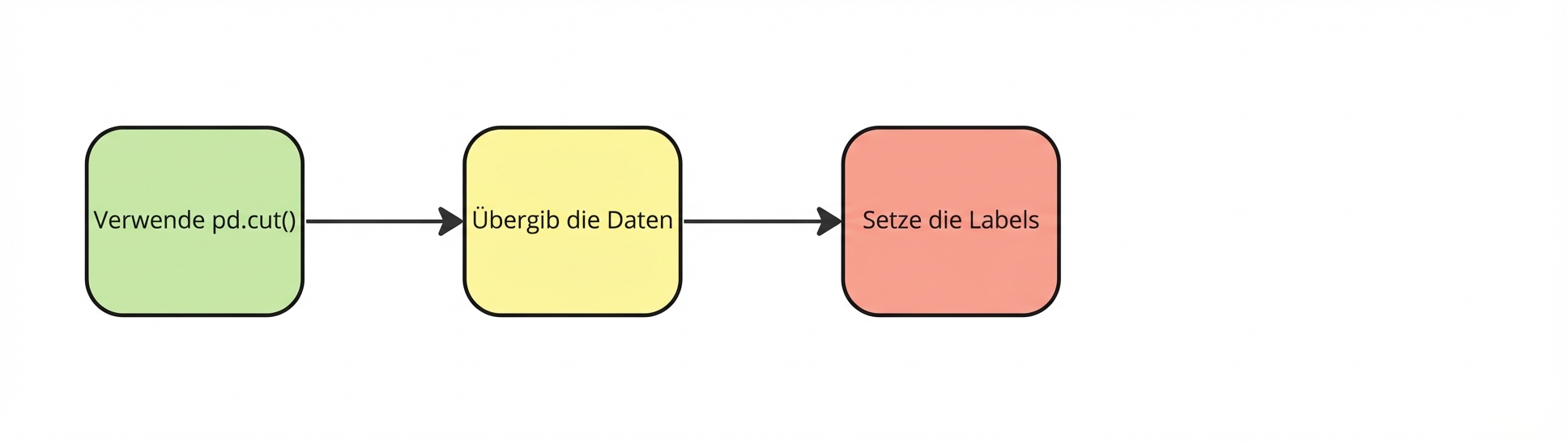
planes["Price_Category"] = pd.cut(planes["Price"],
labels=labels,
pd.cut()
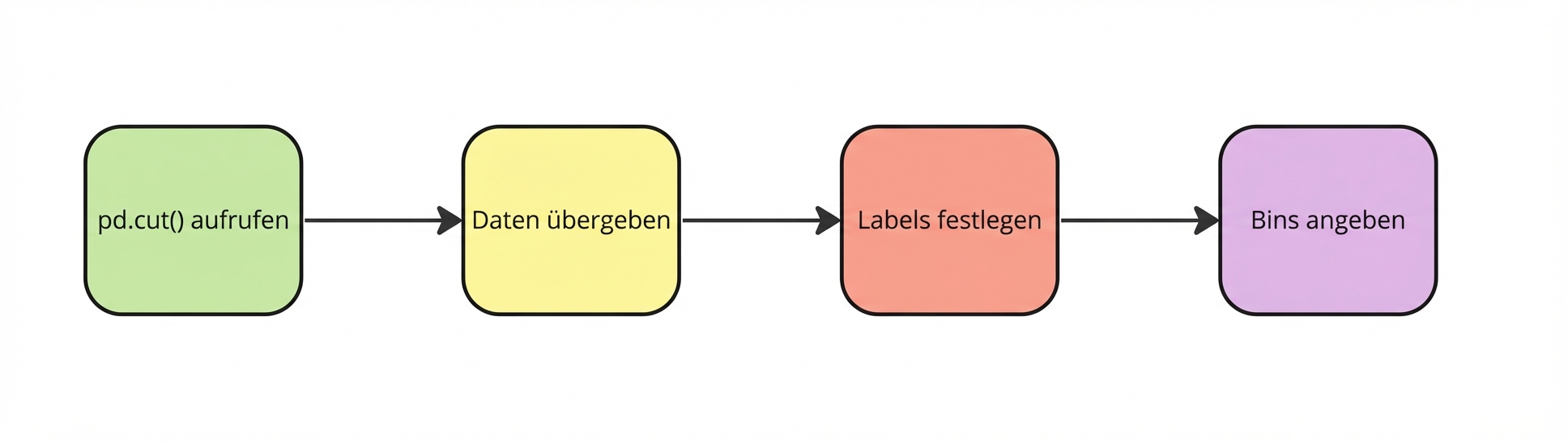
planes["Price_Category"] = pd.cut(planes["Price"],
labels=labels,
bins=bins)
Preiskategorien
print(planes[["Price","Price_Category"]].head())
Price Price_Category
0 13882.0 First Class
1 6218.0 Premium Economy
2 13302.0 First Class
3 3873.0 Economy
4 11087.0 Business Class
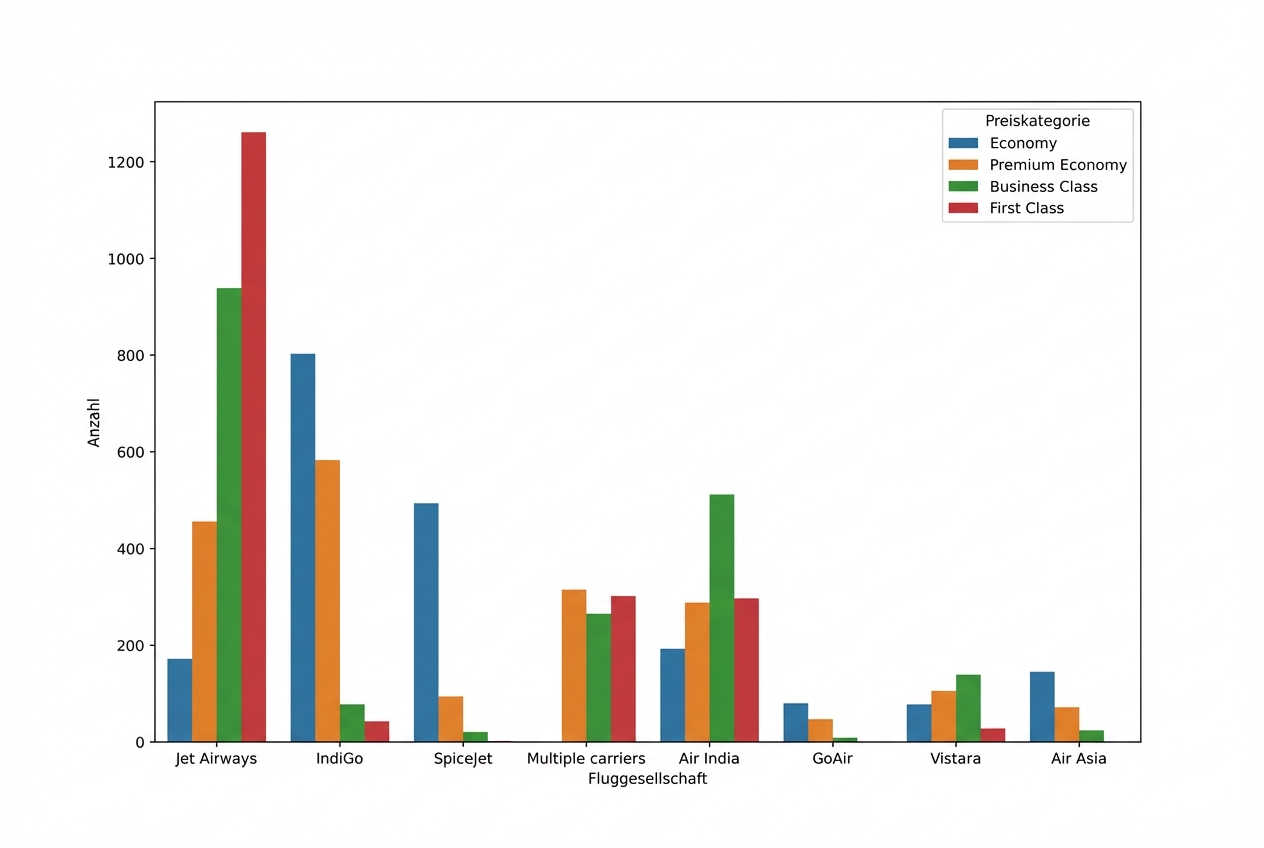
Preisklasse nach Fluggesellschaft
sns.countplot(data=planes, x="Airline", hue="Price_Category")
plt.show()
Preisklasse nach Fluggesellschaft
Lass uns üben!
Explorative Datenanalyse in Python

