Streudiagramme
Einführung in die Datenvisualisierung mit ggplot2

Rick Scavetta
Founder, Scavetta Academy
48 Geometrien
| geom_* | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| abline | contour | dotplot | jitter | pointrange | ribbon | spoke |
| area | count | errorbar | label | polygon | rug | step |
| bar | crossbar | errorbarh | line | segment | text | |
| bin2d | curve | freqpoly | linerange | qq_line | sf | tile |
| blank | density | hex | map | quantile | sf_label | violin |
| boxplot | density2d | histogram | path | raster | sf_text | vline |
| col | density_2d | hline | point | rect | smooth |
Gängige Diagrammtypen
| Diagrammtyp | Mögliche Geome |
|---|---|
| Streudiagramme | points, jitter, abline, smooth, count |
Streudiagramme
- Jedes Geom kann bestimmte Zuordnungen von ästhetischen Elementen akzeptieren, z. B. geom_point():
| Grundlegend |
|---|
| x,y |
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length,
y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point()
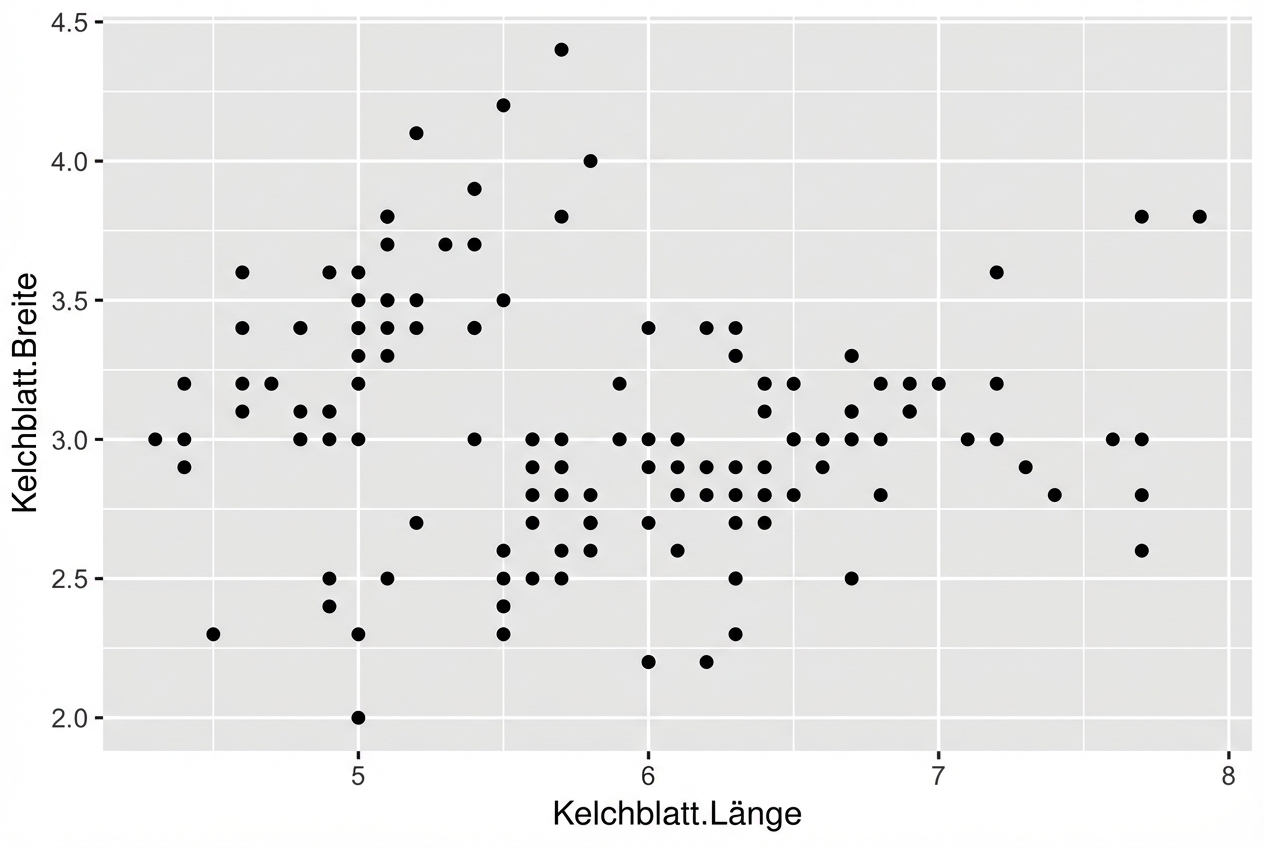
Streudiagramme
- Jedes Geom kann bestimmte Zuordnungen von ästhetischen Elementen akzeptieren, z. B. geom_point():
| Grundlegend | Optional |
|---|---|
| x,y | alpha, color, fill, shape, size, stroke |
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length,
y = Sepal.Width,
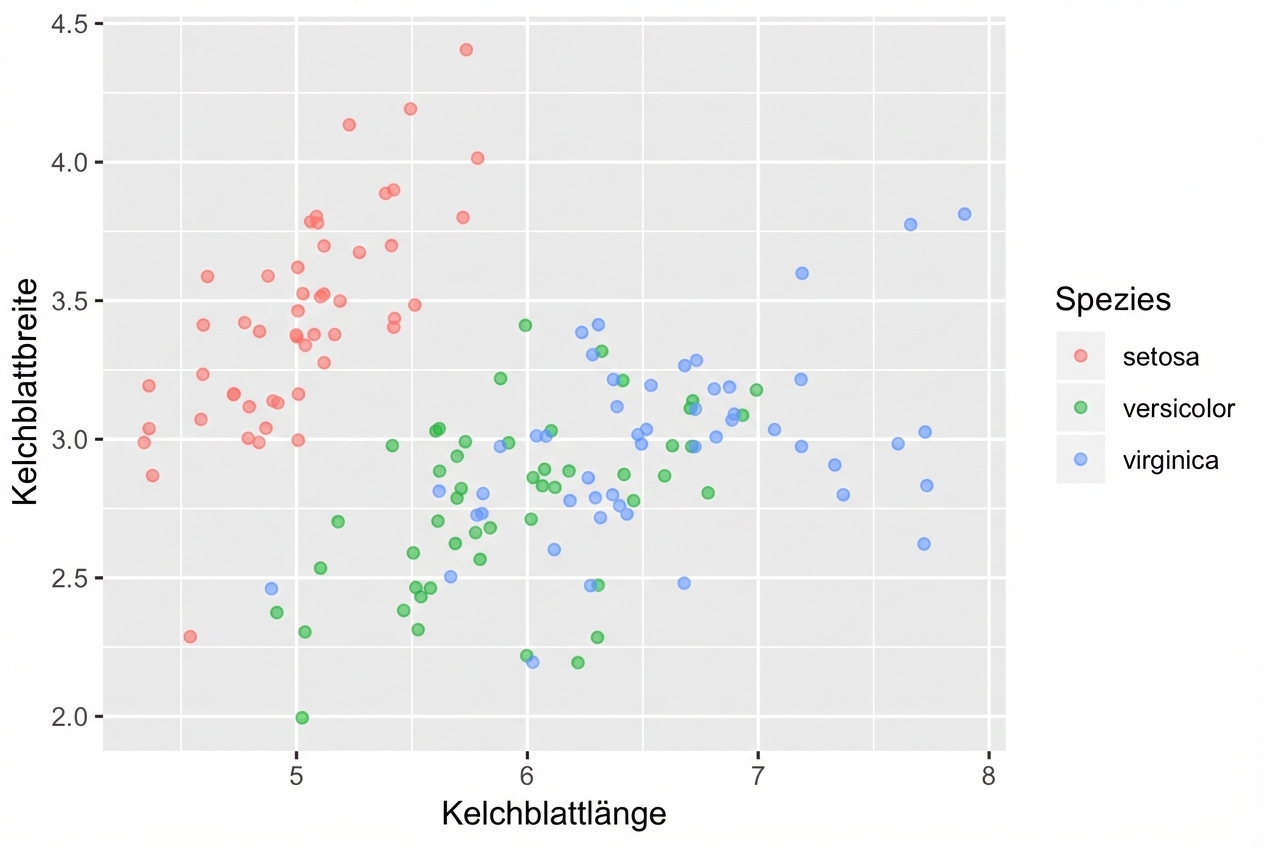
col = Species)) +
geom_point()
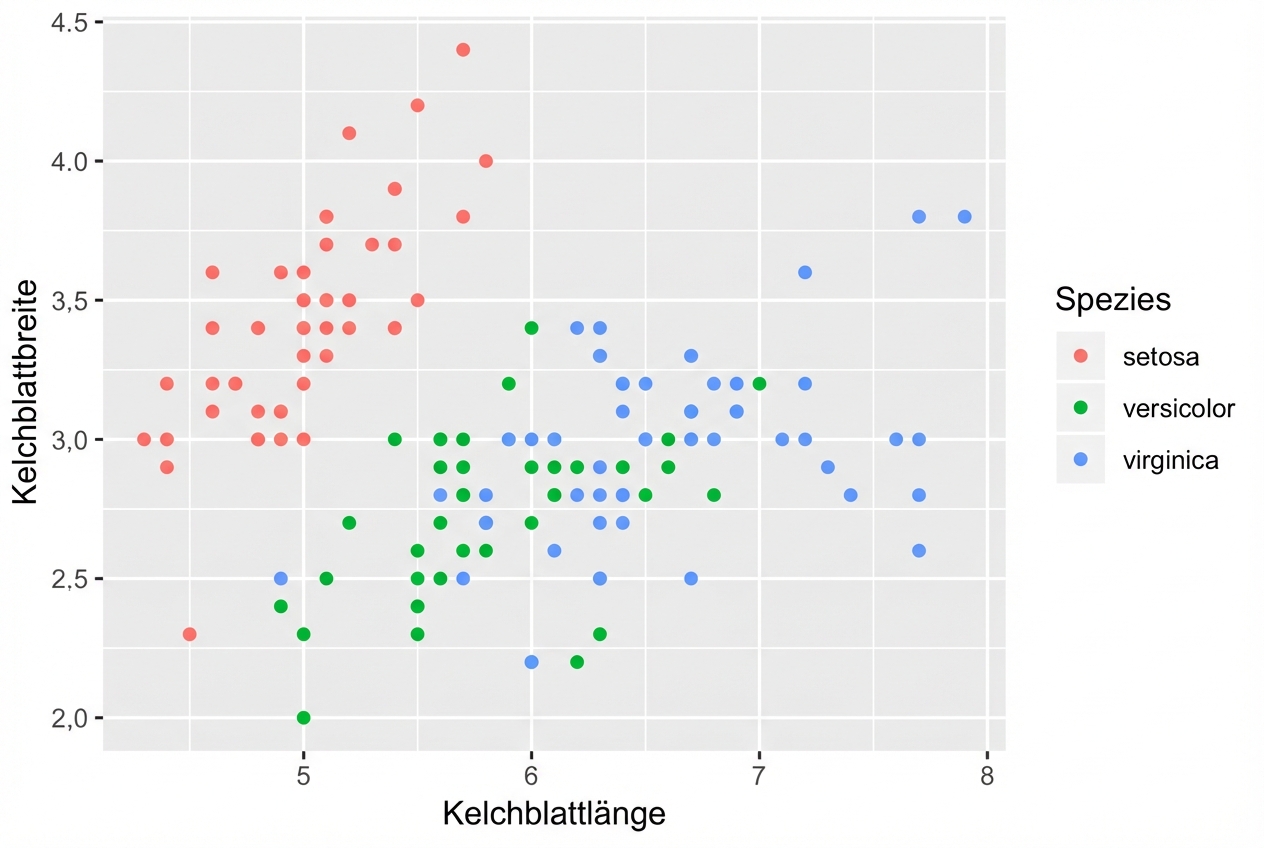
Geom-spezifische Zuordnungen von ästhetischen Elementen
# These result in the same plot!
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_point()
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(aes(col = Species))
Kontrolliere die ästhetischen Zuordnungen der einzelnen Ebenen unabhängig voneinander:
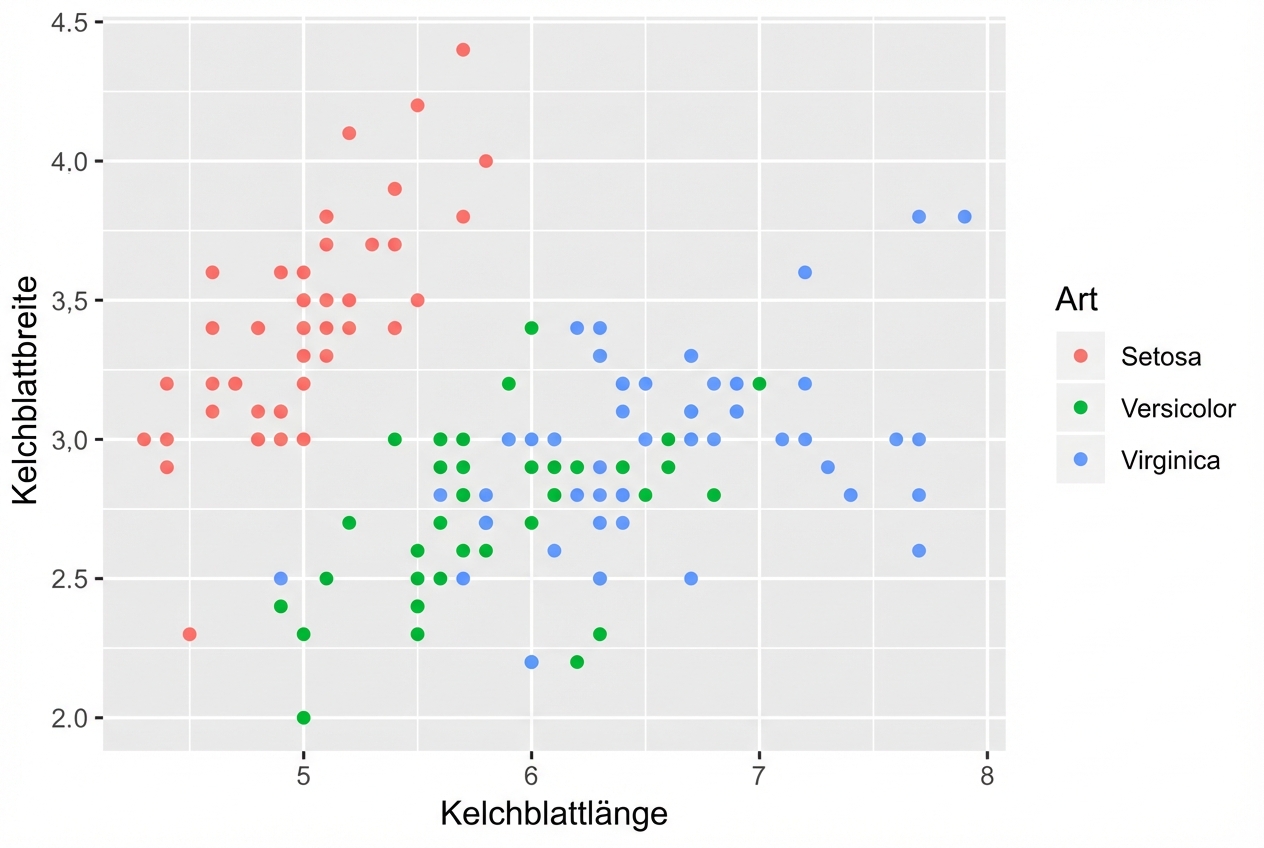
head(iris, 3) # Raw data
Species Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
1 setosa 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2
2 setosa 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2
3 setosa 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2
iris %>%
group_by(Species) %>%
summarise_all(mean) -> iris.summary
iris.summary # Summary statistics
# A tibble: 3 x 5
Species Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 setosa 5.01 3.43 1.46 0.246
2 versicolor 5.94 2.77 4.26 1.33
3 virginica 6.59 2.97 5.55 2.03
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
# Inherits both data and aes from ggplot()
geom_point() +
# Different data, but inherited aes
geom_point(data = iris.summary, shape = 15, size = 5)
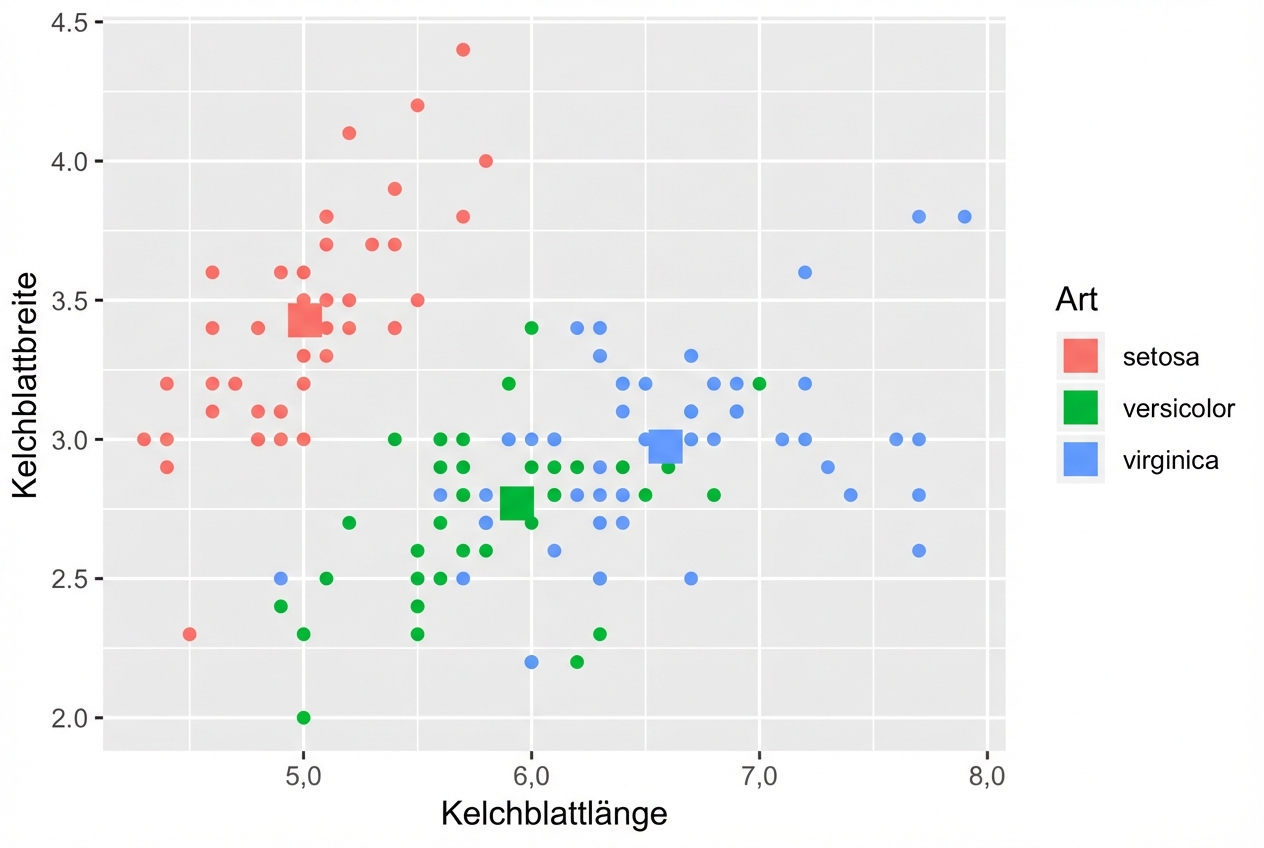
Form Attributwerte
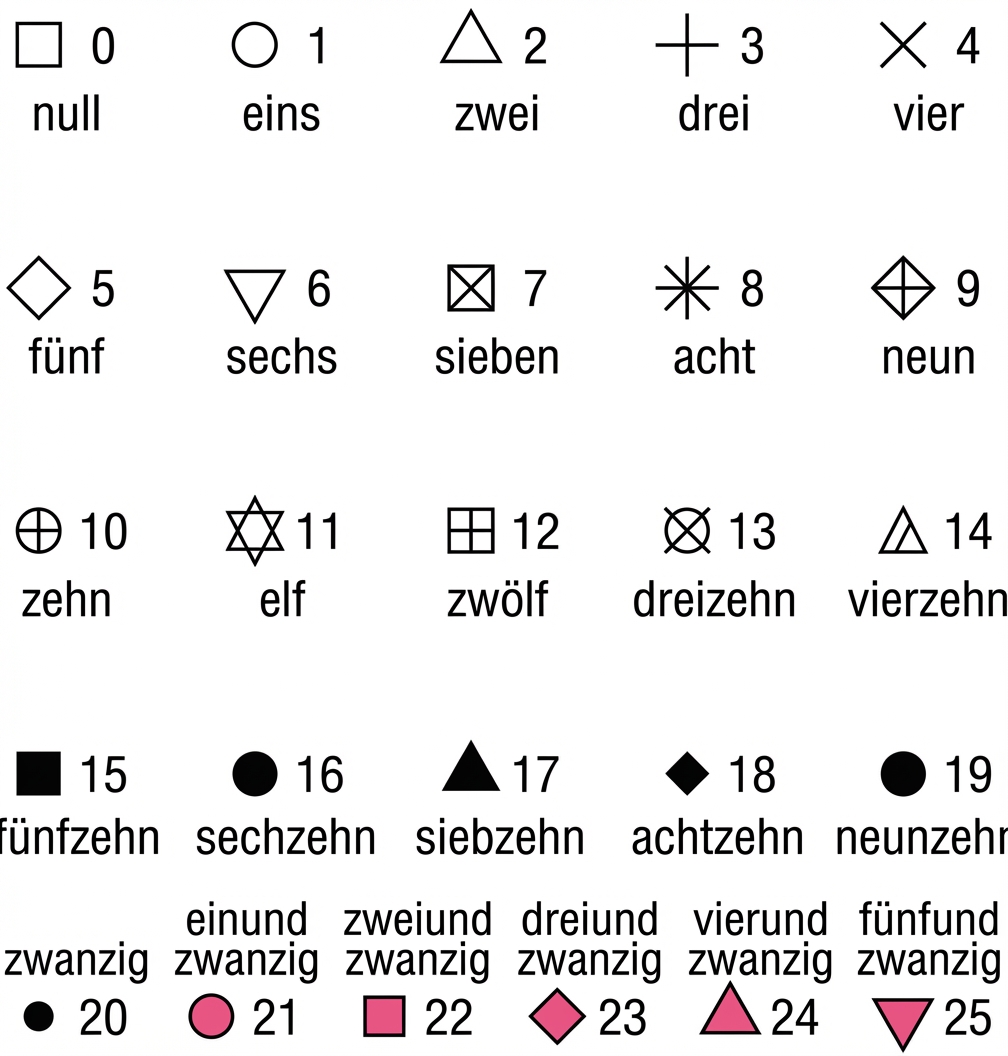
Beispiel
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_point() +
geom_point(data = iris.summary, shape = 21, size = 5,
fill = "black", stroke = 2)
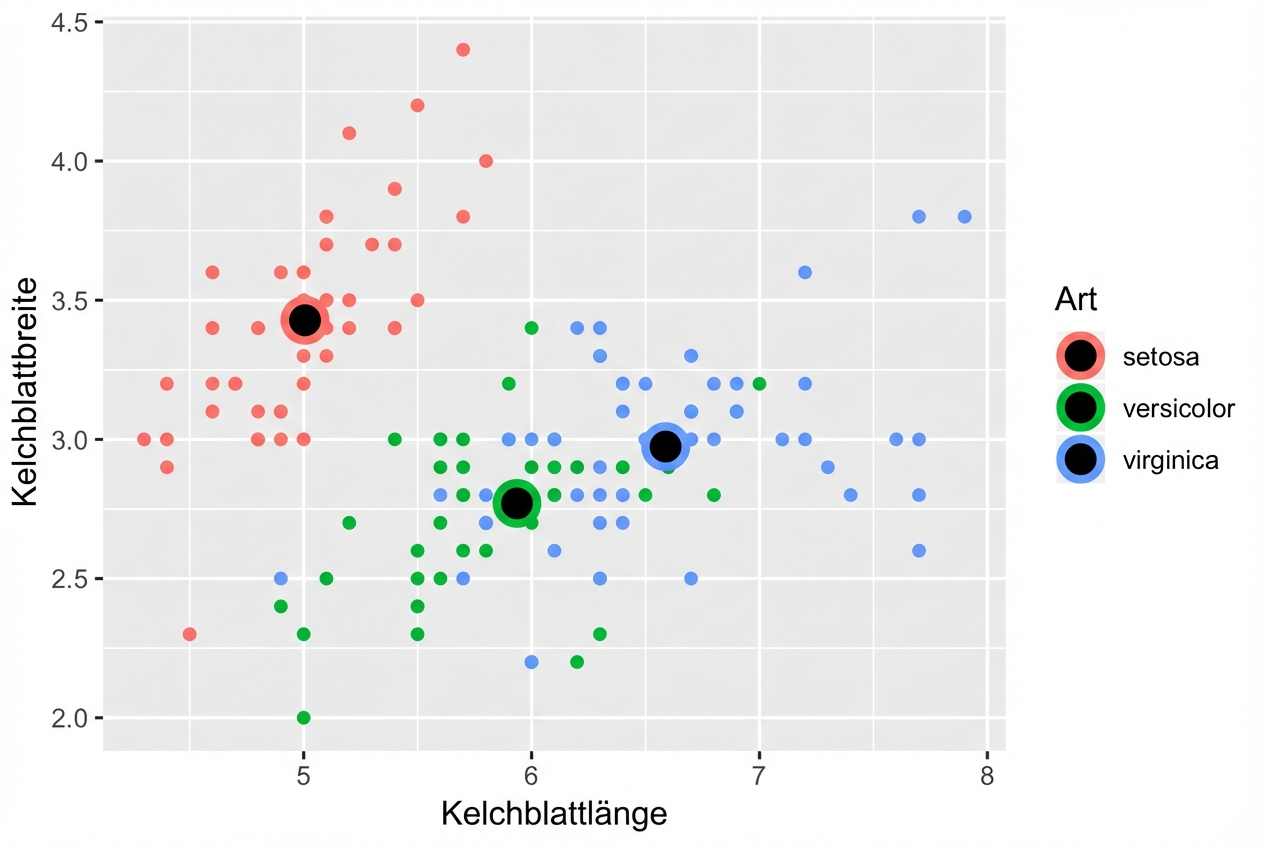
On-the-fly-Statistiken mit ggplot2
- Siehe den zweiten Kurs für die Statistik-Ebene.
- Hinweis: Vermeide es, nur den Mittelwert ohne ein Maß für die Streuung, z. B. die Standardabweichung, darzustellen.

position = "jitter"
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_point(position = "jitter")
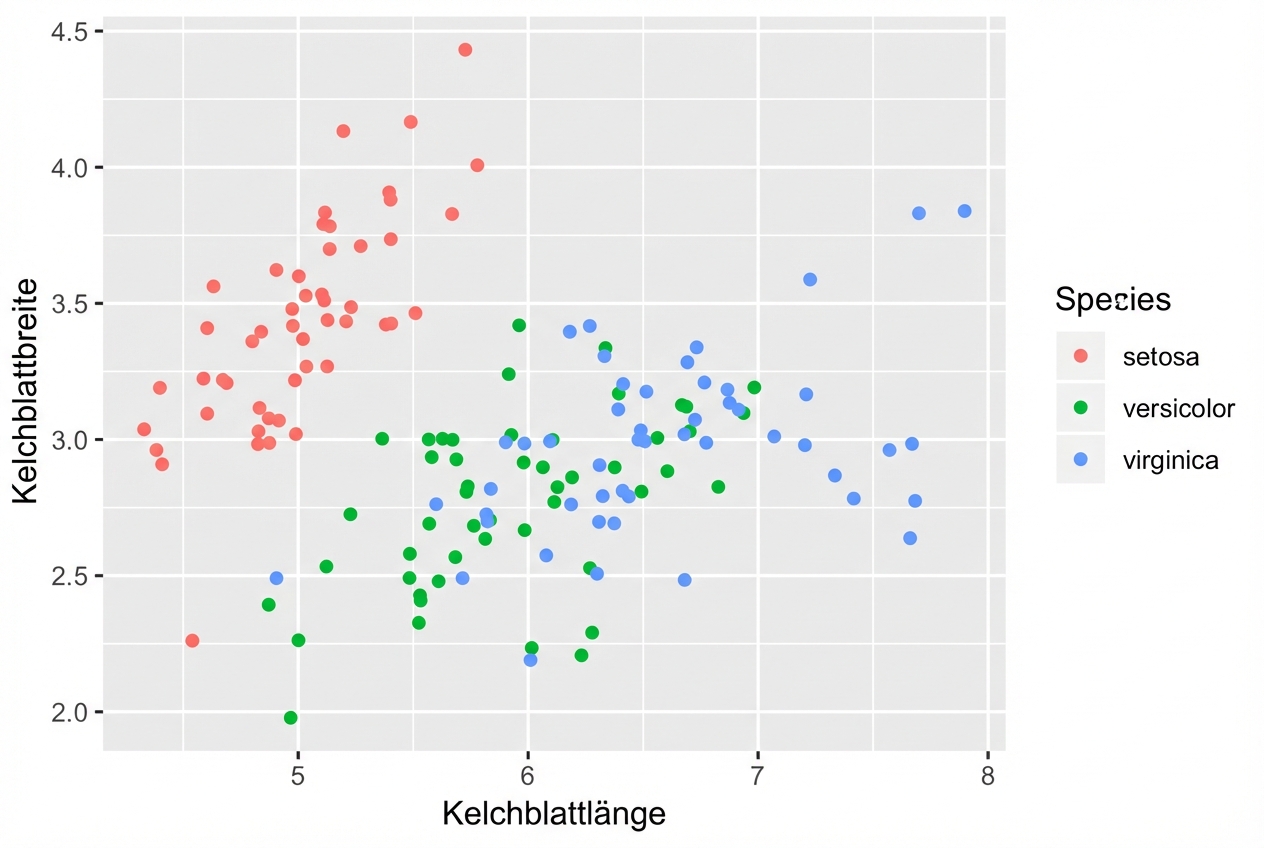
geom_jitter()
Eine Abkürzung zu geom_point(position = "jitter")
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_jitter()
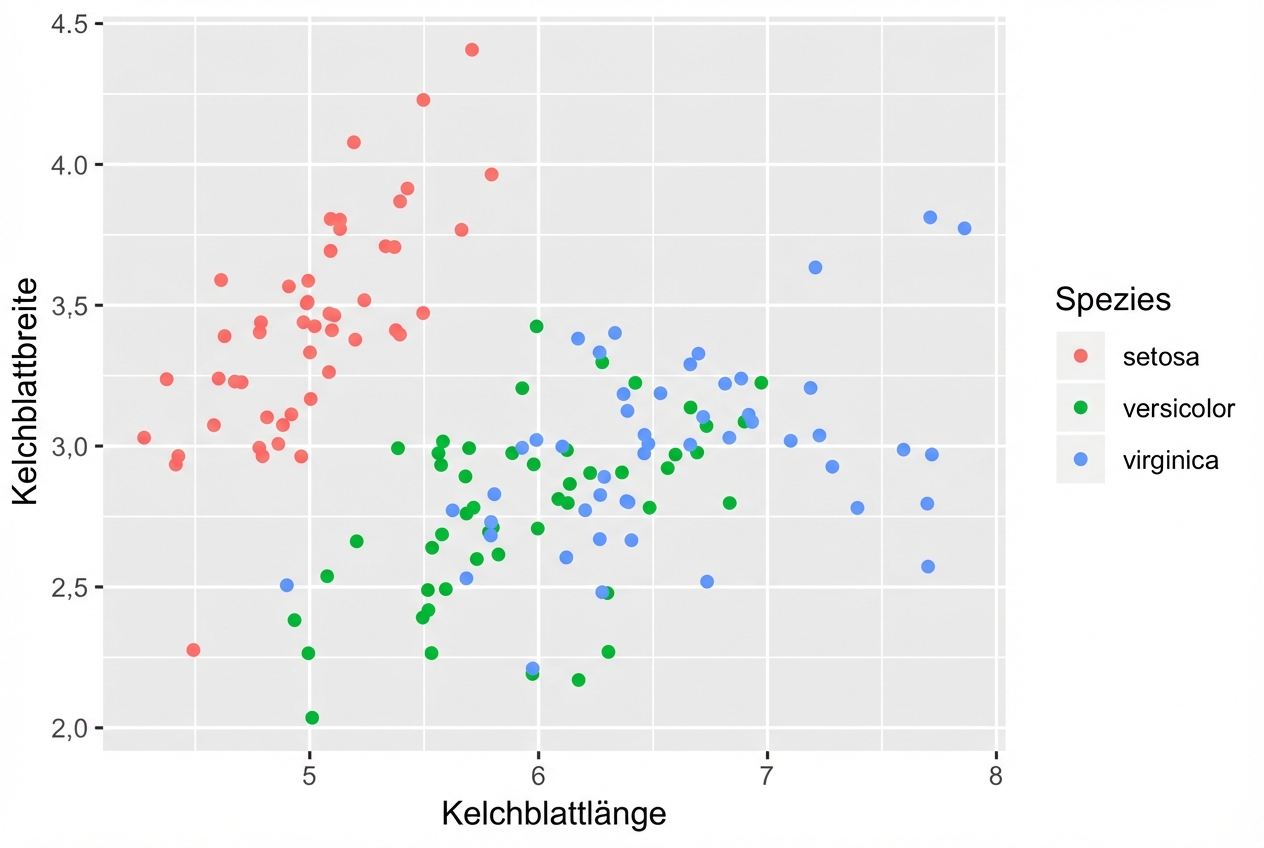
Vergiss nicht, Alpha einzustellen
- Kombiniere Jittering mit Alpha-Blending, wenn nötig
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_jitter(alpha = 0.6)
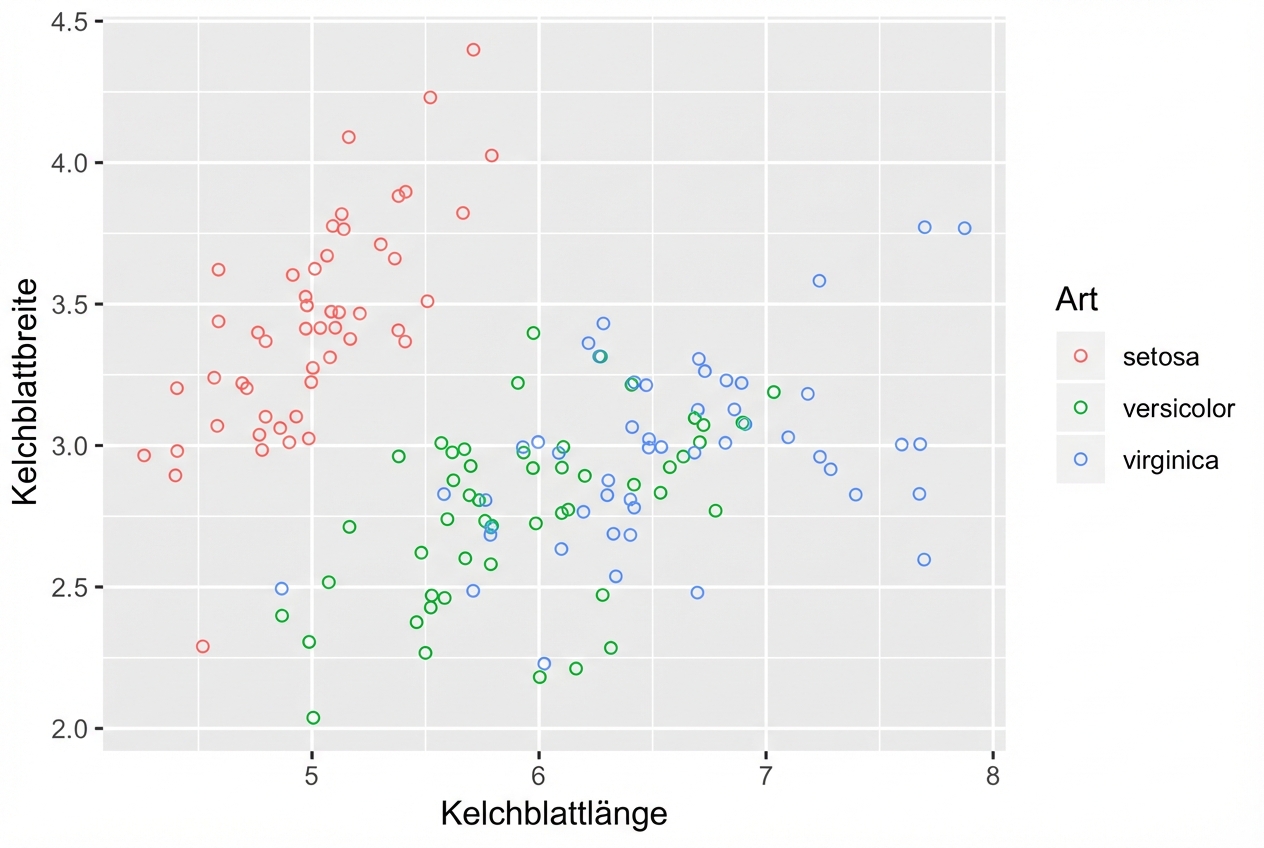
Hohle Kreise helfen auch
shape = 1ist ein hohler Kreis.- Es ist nicht notwendig, auch Alpha-Blending zu verwenden.
ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, col = Species)) +
geom_jitter(shape = 1)
Lass uns üben!
Einführung in die Datenvisualisierung mit ggplot2

