CLI Interface
Introduction to Testing in Python

Alexander Levin
Data Scientist
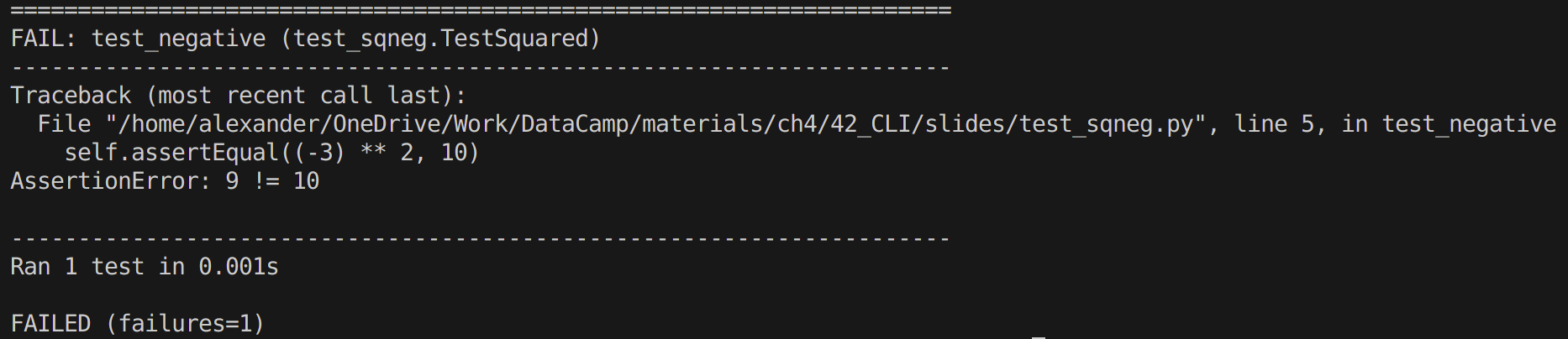
Example: code
Test of the exponentiation operator:
# test_sqneg.py
import unittest
# Declaring the TestCase class
class TestSquared(unittest.TestCase):
# Defining the test
def test_negative(self):
self.assertEqual((-3) ** 2, 9)
CLI command:
python3 -m unittest test_sqneg.py
Run Python script test_sqneg.py using module unittest.
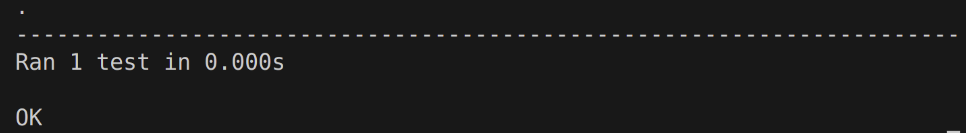
Example: output
The command:
python3 -m unittest test_sqneg.py
The test output:
Keyword argument -k
unittest -k - run test methods and classes that match the pattern or substring
Command:
python3 -m unittest -k "SomeStringOrPattern" test_script.py
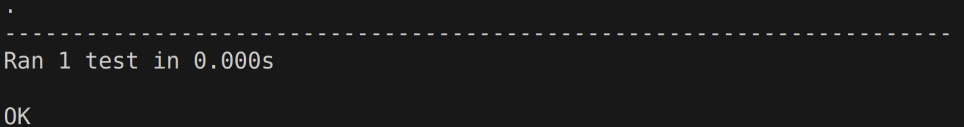
Example:
python3 -m unittest -k "Squared" test_sqneg.py
Output:
Fail fast flag -f
unittest -f - stop the test run on the first error or failure.
Command: python3 -m unittest -f test_script.py
Use case example: when all of tests are crucial, like testing the airplane before a flight.
Catch flag -c
Catch flag unittest -c - lets to interrupt the test by pushing "Ctrl - C".
- If "Ctrl - C"
- is pushed once,
unittestwaits for the current test to end and reports all the results so far. - is pushed twice,
unittestraises theKeyboardInterruptexception.
- is pushed once,
Command: python3 -m unittest -c test_script.py
Use case example: when debugging a big test suite
Verbose flag -v
unittest -v - run tests with more detail
Command: python3 -m unittest -v test_script.py.
Use case example: debugging purposes
Output example: 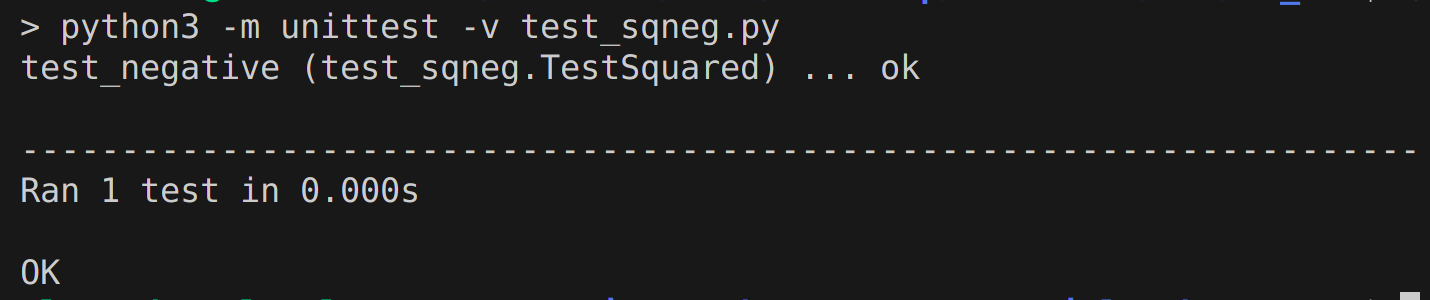
Summary
Basic command without arguments
python3 -m unittest test_script.pyOutput in unittest
Keyword argument:
python3 -m unittest -k "SomeStringOrPattern" test_script.pyFail fast flag:
python3 -m unittest -f test_script.pyCatch flag:
python3 -m unittest -c test_script.pyVerbose flag:
python3 -m unittest -v test_script.py
Let's practice!
Introduction to Testing in Python

