Kubernetes Architecture
Introduction to Kubernetes

Frank Heilmann
Platform Architect and Freelance Instructor
Kubernetes Overview
- Kubernetes is built from many elements:
- Most important ones, from larger to smaller:
- Clusters and Control Planes
- Nodes
- Pods
- Network connectivity through Services
Kubernetes Cluster and the Control Plane
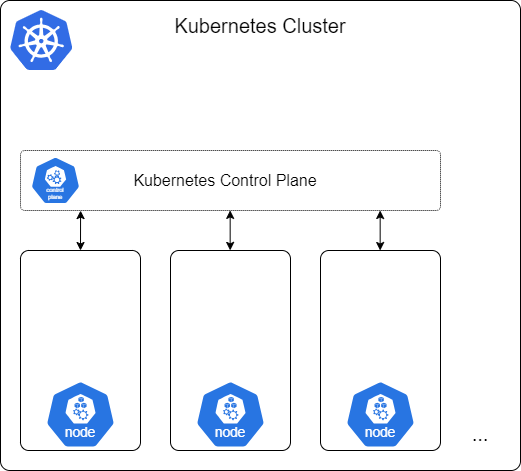
- A Kubernetes Cluster is a set of connected computers (or Nodes)
- Servers in a datacenter, virtual machines in the cloud
- The Kubernetes Control Plane manages these nodes
- consists of many components, that can run on any node in the cluster
Kubernetes Nodes
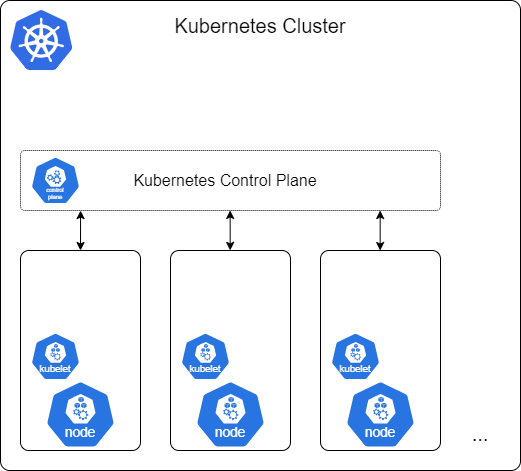
- A Kubernetes Node typically runs Linux + container engine (Docker)
$$
- Nodes are also called worker machines
$$
- Nodes run Kubernetes Kubelet
- ensures containers run in so-called Pods
Kubernetes Pods
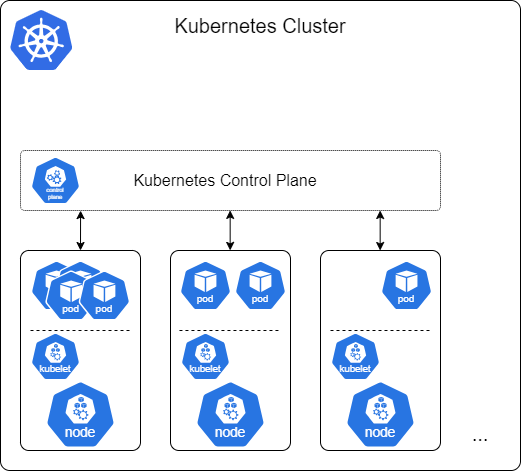
- Kubernetes Pod
- Smallest unit that you can deploy
- A Pod is a set of one or more containers
- The containers in a Pod belong together logically, share storage and network
- Pods are ephemeral:
- Pods can be stopped and recreated and any point in time.
- Pods can moved to other nodes at any point in time.
Kubernetes Services
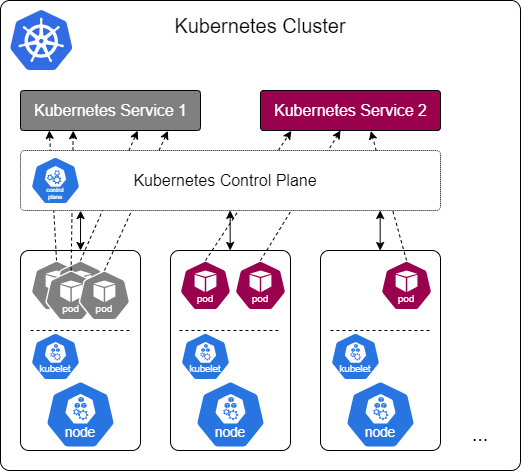
- Kubernetes Service: resource for exposing network connectivity
- Required to connect to Pod from outside, or to communicate between Pods
- Reason: Pods may get re-deployed any time, and will
- Receive a new IP address
- Services are not ephemeral, they offer stable network connectivity
Kubernetes Cheat Sheet
- Kubernetes Cluster: set of connected computers (Nodes) configured to run Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Control Plane: manages the Nodes in a Cluster
- Kubernetes Nodes: also called "worker machines", running Linux and a container engine
- Kubernetes Pods: a set of one or more containers, the smallest deployable unit
- Kubernetes Services: a resource for exposing network connectivity, required to connect to Pods from outside, and for communication between Pods
Let's practice!
Introduction to Kubernetes

