Privacy
Introduction to Data Privacy

Tiffany Lewis
Security and Privacy Instructor
Privacy's origin story
- 1800s conversations about technology and Privacy:
- Individuals' rights
- Sensationalist reporting
- Privacy - The right to be left alone, or freedom from interference or intrusion.

1 Samuel D. Warren and Louis D. Brandeis, "The Right to Privacy," Harvard Law Review, 4 (5), (1890): 193-220, p. 195, citing Judge Cooley in Cooley on Torts, 2nd ed.
Digging into today's definition of Privacy
- Data Privacy - control over how personal data is collected and used.
- "The authorized and valid processing of personal information."

1 Bhajaria, Nishant, and Neil Hunt. Data Privacy: A Runbook for Engineers. Manning Publications Co., 2022.
Personal data
- Personal data - data related to a person or can be used to identify an individual.
- Examples:
- Date of birth (DOB)
- Name
- Geolocation
- Examples:
- Goal to keep personal data safe

Privacy's expanding implications
- Increase discussions in 21st-century due to:
- Internet
- Applications
- Larger data footprint
- Privacy concerns include:
- Surveillance
- Big data analytics
- 3rd party providers

State of Privacy today
- 59%+ of Americans do not know what is being done with their data.
- 81% of Americans say that the risks of collecting data about them outweigh the benefits.
- Potential causes:
- Lack of Privacy knowledge
- Lack of trust
- Lack of standardized regulation

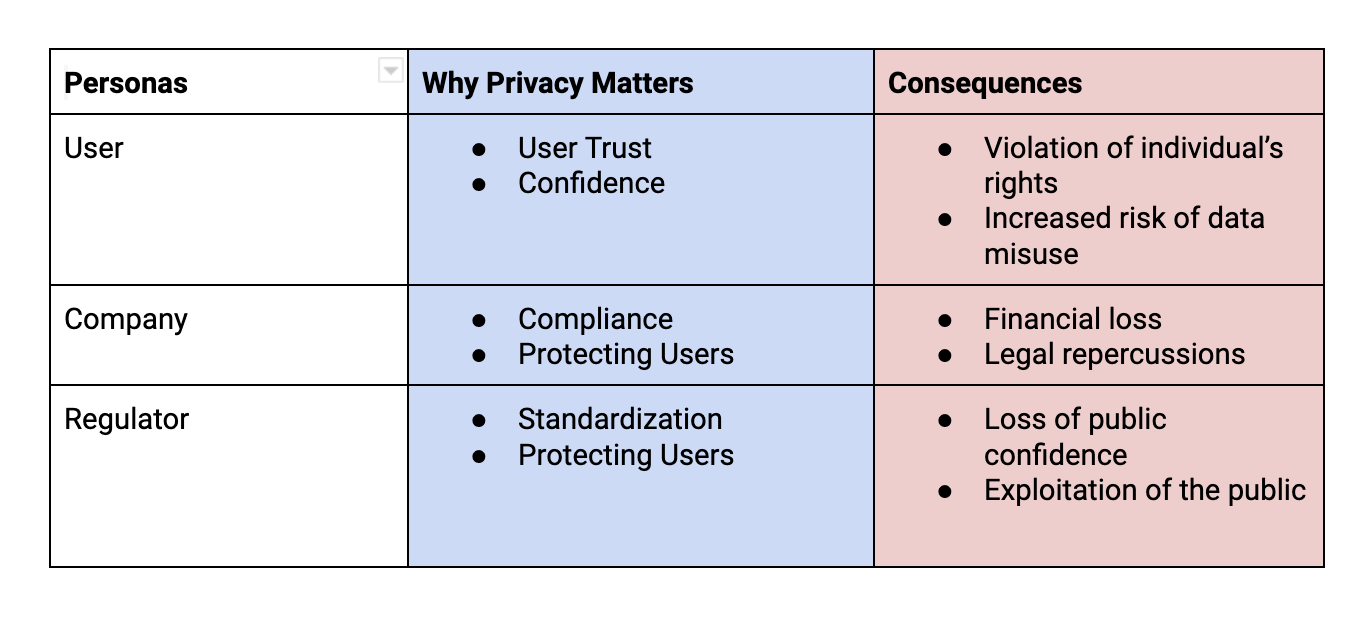
Privacy Implications
Privacy has different implications for different groups
PREACH
- P (Purpose) - Why is the company asking to use your data?
- R (Right to Request) - Do you have the ability to request changes to your information?
- E (Easy to understand) - Is it easy to understand a company's policies?
- A (Alerting) - Will you be alerted if the company mishandles your data?
- C (Consent) - Have you given consent (i.e., permission) for your information to be used?
- H (How) - How is the company or service planning to use your data?
Let's practice!
Introduction to Data Privacy

