Optimizers
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

Isaiah Hull
Visiting Associate Professor of Finance, BI Norwegian Business School
How to find a minimum

1 Source: U.S. National Park Service
How to find a minimum

1 Source: U.S. National Park Service
How to find a minimum
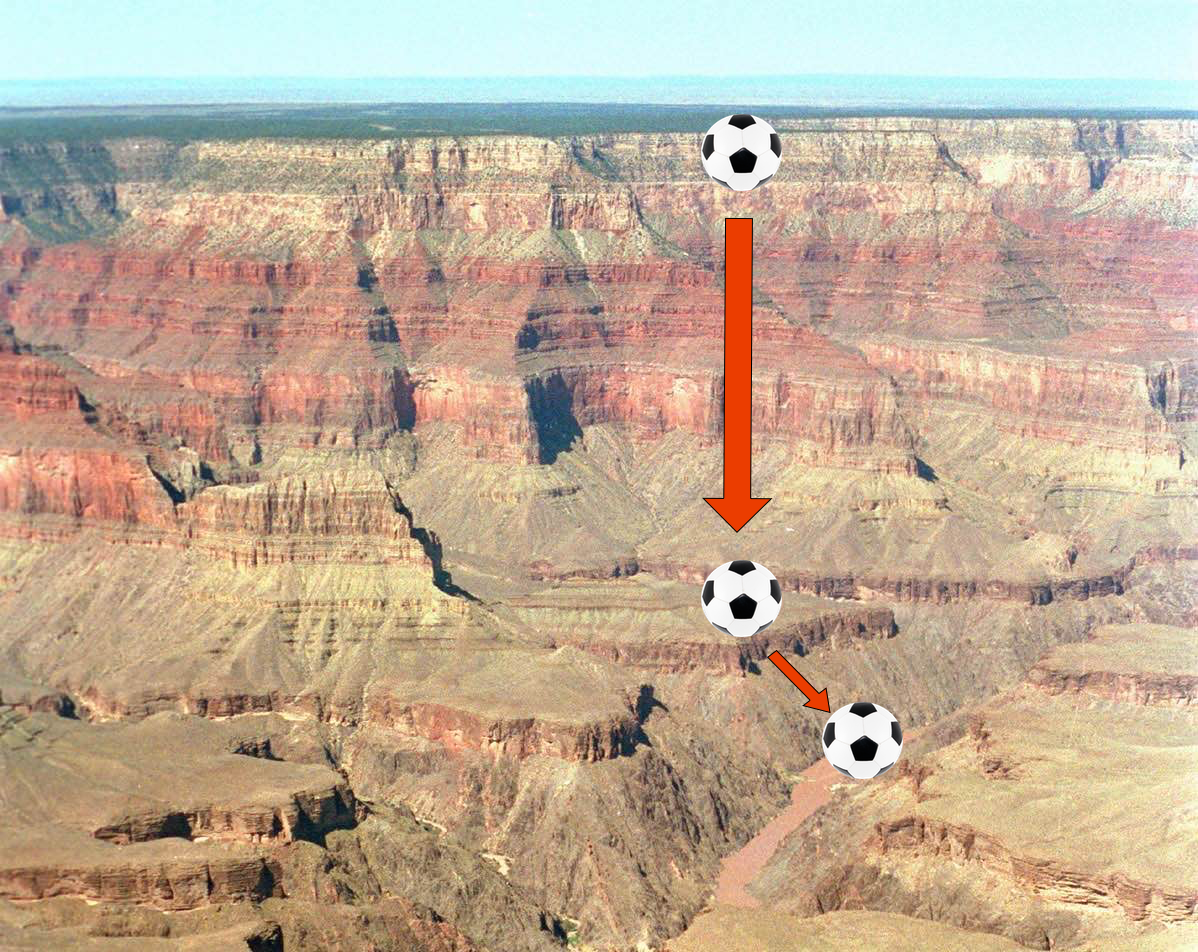
1 Source: U.S. National Park Service
The gradient descent optimizer
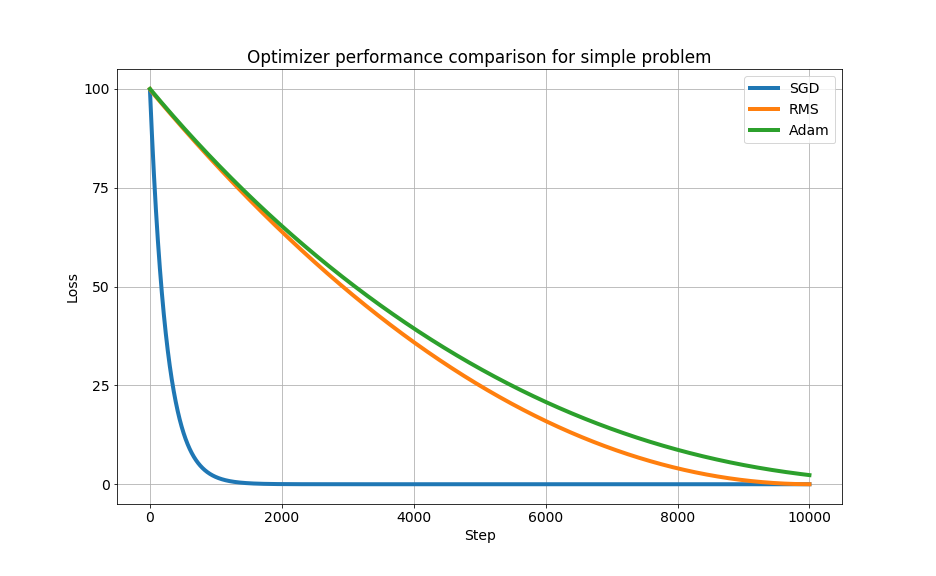
Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizer
tf.keras.optimizers.SGD()learning_rate
Simple and easy to interpret
The RMS prop optimizer
Root mean squared (RMS) propagation optimizer
- Applies different learning rates to each feature
tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop()learning_ratemomentumdecay
Allows for momentum to both build and decay
The adam optimizer
Adaptive moment (adam) optimizer
tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()learning_ratebeta1
Performs well with default parameter values
A complete example
import tensorflow as tf
# Define the model function
def model(bias, weights, features = borrower_features):
product = tf.matmul(features, weights)
return tf.keras.activations.sigmoid(product+bias)
# Compute the predicted values and loss
def loss_function(bias, weights, targets = default, features = borrower_features):
predictions = model(bias, weights)
return tf.keras.losses.binary_crossentropy(targets, predictions)
# Minimize the loss function with RMS propagation
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.9)
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(bias, weights), var_list=[bias, weights])
Let's practice!
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

