Linear regression
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

Isaiah Hull
Visiting Associate Professor of Finance, BI Norwegian Business School
What is a linear regression?
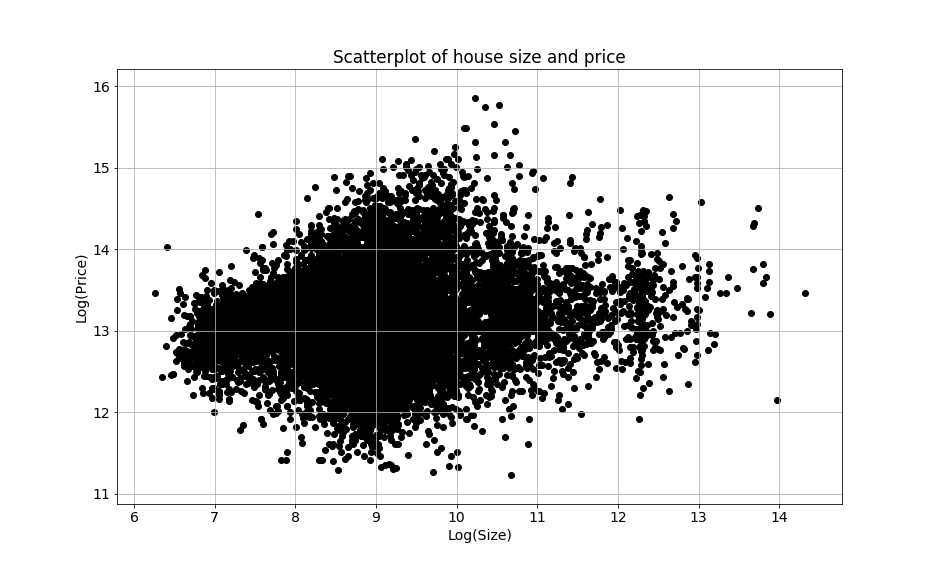
What is a linear regression?
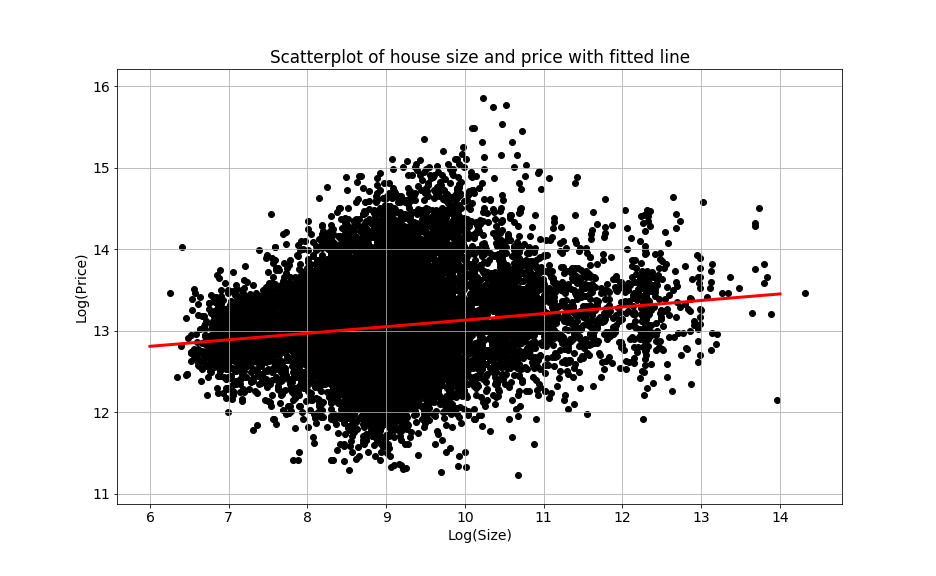
The linear regression model
- A linear regression model assumes a linear relationship:
- $price = intercept + size*slope + error$
- This is an example of a univariate regression.
- There is only one feature,
size.
- There is only one feature,
- Multiple regression models have more than one feature.
- E.g.
sizeandlocation
- E.g.
Linear regression in TensorFlow
# Define the targets and features
price = np.array(housing['price'], np.float32)
size = np.array(housing['sqft_living'], np.float32)
# Define the intercept and slope
intercept = tf.Variable(0.1, np.float32)
slope = tf.Variable(0.1, np.float32)
# Define a linear regression model
def linear_regression(intercept, slope, features = size):
return intercept + features*slope
# Compute the predicted values and loss
def loss_function(intercept, slope, targets = price, features = size):
predictions = linear_regression(intercept, slope)
return tf.keras.losses.mse(targets, predictions)
Linear regression in TensorFlow
# Define an optimization operation
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
# Minimize the loss function and print the loss
for j in range(1000):
opt.minimize(lambda: loss_function(intercept, slope),\
var_list=[intercept, slope])
print(loss_function(intercept, slope))
tf.Tensor(10.909373, shape=(), dtype=float32)
...
tf.Tensor(0.15479447, shape=(), dtype=float32)
# Print the trained parameters
print(intercept.numpy(), slope.numpy())
Let's practice!
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

