Advanced operations
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

Isaiah Hull
Visiting Associate Professor of Finance, BI Norwegian Business School
Overview of advanced operations
- We have covered basic operations in TensorFlow
add(),multiply(),matmul(), andreduce_sum()
- In this lesson, we explore advanced operations
gradient(),reshape(), andrandom()
Overview of advanced operations
| Operation | Use |
|---|---|
gradient() |
Computes the slope of a function at a point |
reshape() |
Reshapes a tensor (e.g. 10x10 to 100x1) |
random() |
Populates tensor with entries drawn from a probability distribution |
Finding the optimum
In many problems, we will want to find the optimum of a function.
- Minimum: Lowest value of a loss function.
- Maximum: Highest value of objective function.
We can do this using the
gradient()operation.- Optimum: Find a point where gradient = 0.
- Minimum: Change in gradient > 0
- Maximum: Change in gradient < 0
Calculating the gradient
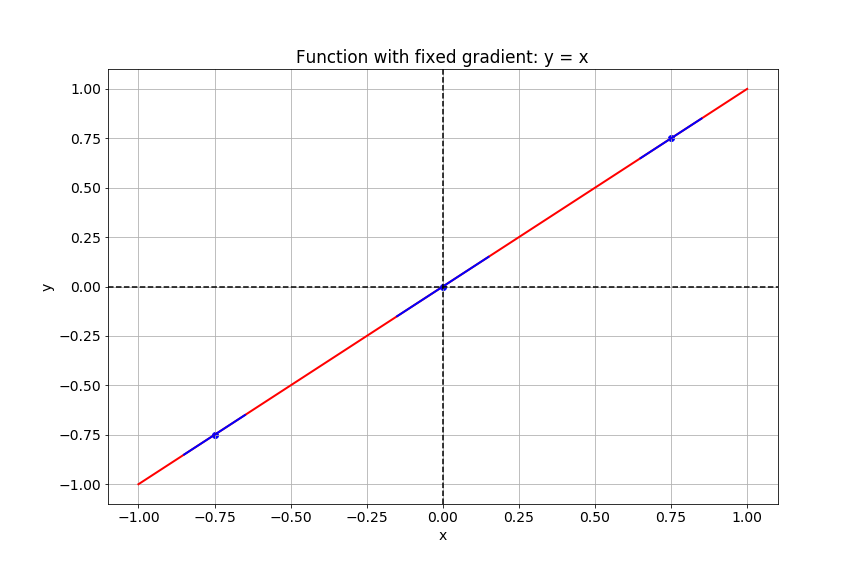
Calculating the gradient
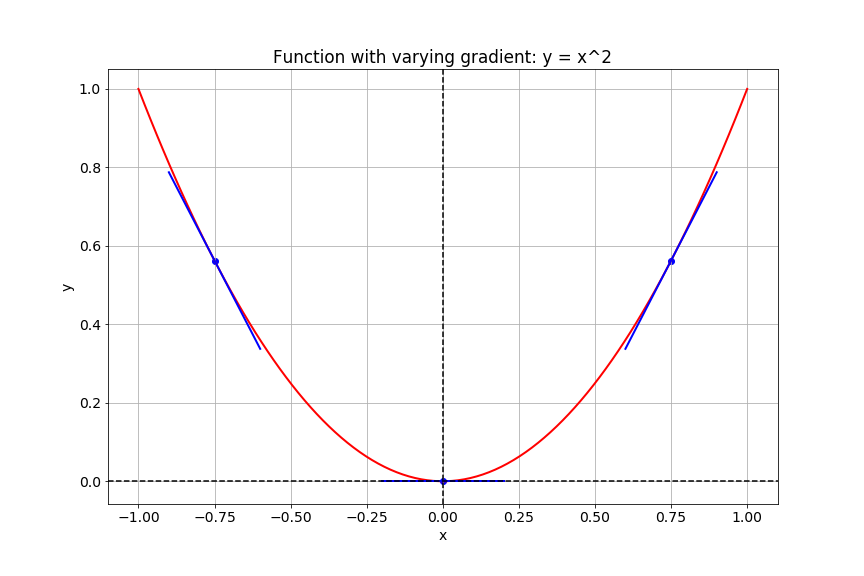
Gradients in TensorFlow
# Import tensorflow under the alias tf
import tensorflow as tf
# Define x
x = tf.Variable(-1.0)
# Define y within instance of GradientTape
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch(x)
y = tf.multiply(x, x)
# Evaluate the gradient of y at x = -1
g = tape.gradient(y, x)
print(g.numpy())
-2.0
Images as tensors
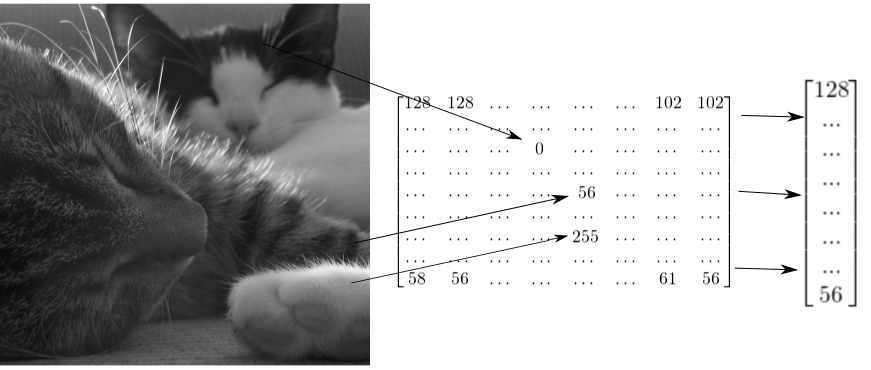
How to reshape a grayscale image
# Import tensorflow as alias tf
import tensorflow as tf
# Generate grayscale image
gray = tf.random.uniform([2, 2], maxval=255, dtype='int32')
# Reshape grayscale image
gray = tf.reshape(gray, [2*2, 1])
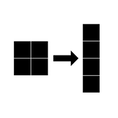
How to reshape a color image
# Import tensorflow as alias tf
import tensorflow as tf
# Generate color image
color = tf.random.uniform([2, 2, 3], maxval=255, dtype='int32')
# Reshape color image
color = tf.reshape(color, [2*2, 3])
Let's practice!
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python

