Table Storage
Develop for Azure Storage

Shahzad Mian
Content developer, DataCamp
Table storage
Understanding Table storage
- Identify when to use Azure Table Storage versus Cosmos DB.
- Understand how data is organized using tables, entities, and properties.
- Perform create, read, update, and delete operations in a Table.

What is Table storage?
- Azure Table Storage offers a simple, schema-less way to store structured data.
- It's perfect for lightweight scenarios like:
- Logs
- IoT telemetry
- Configuration settings
- Fast, affordable data store for straightforward lookups.
- No need for complex schema or relationships.
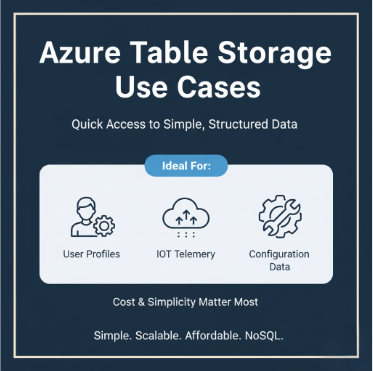
When to use Table storage
- Used for quick, cost-effective access to structured data simple key-value lookups.
- Common use cases include:
- Storing IoT sensor readings.
- Configuration data.
- Best for simplicity and scalability over complex querying.
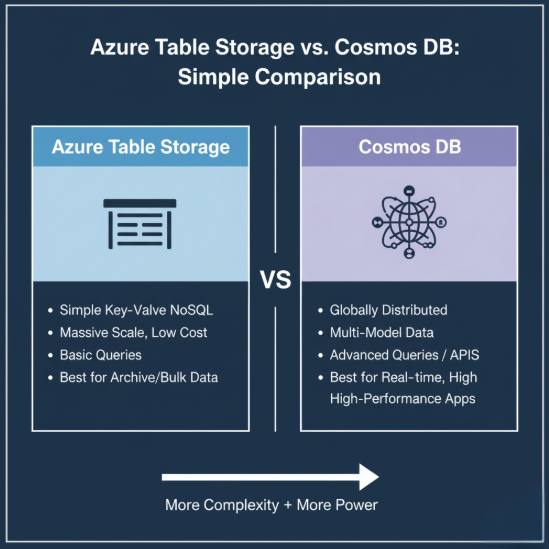
When to use Cosmos DB instead?
- Cosmos DB = advanced querying, global distribution, or multiple APIs.
- Supports global replication with low latency and rich indexing.
- Ideal for applications with large-scale, high-performance requirements.
- Better suited when supporting APIs such as MongoDB or Cassandra.
- The trade-off: more features come at a higher cost.
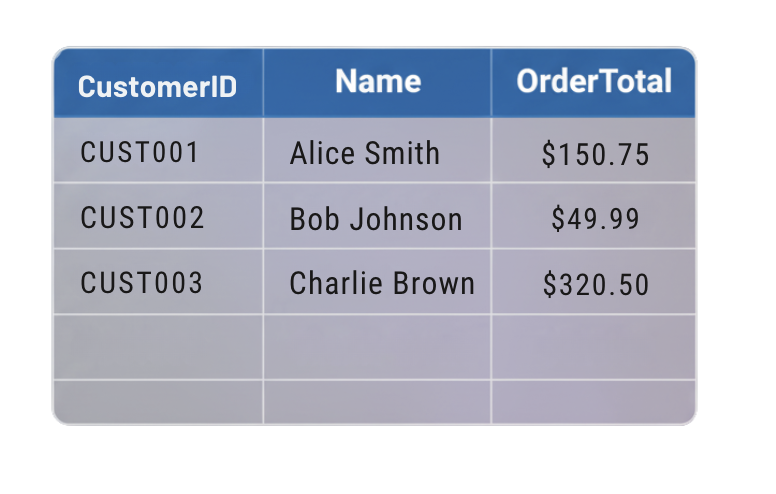
Data organization
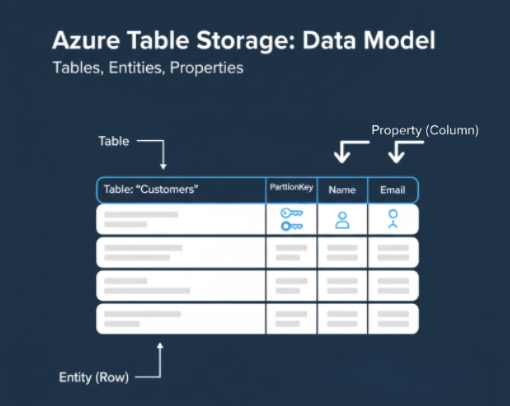
- Data in Table Storage is grouped into tables.
- Each table contains entities, similar to rows.
- Each entity includes properties, similar to columns.
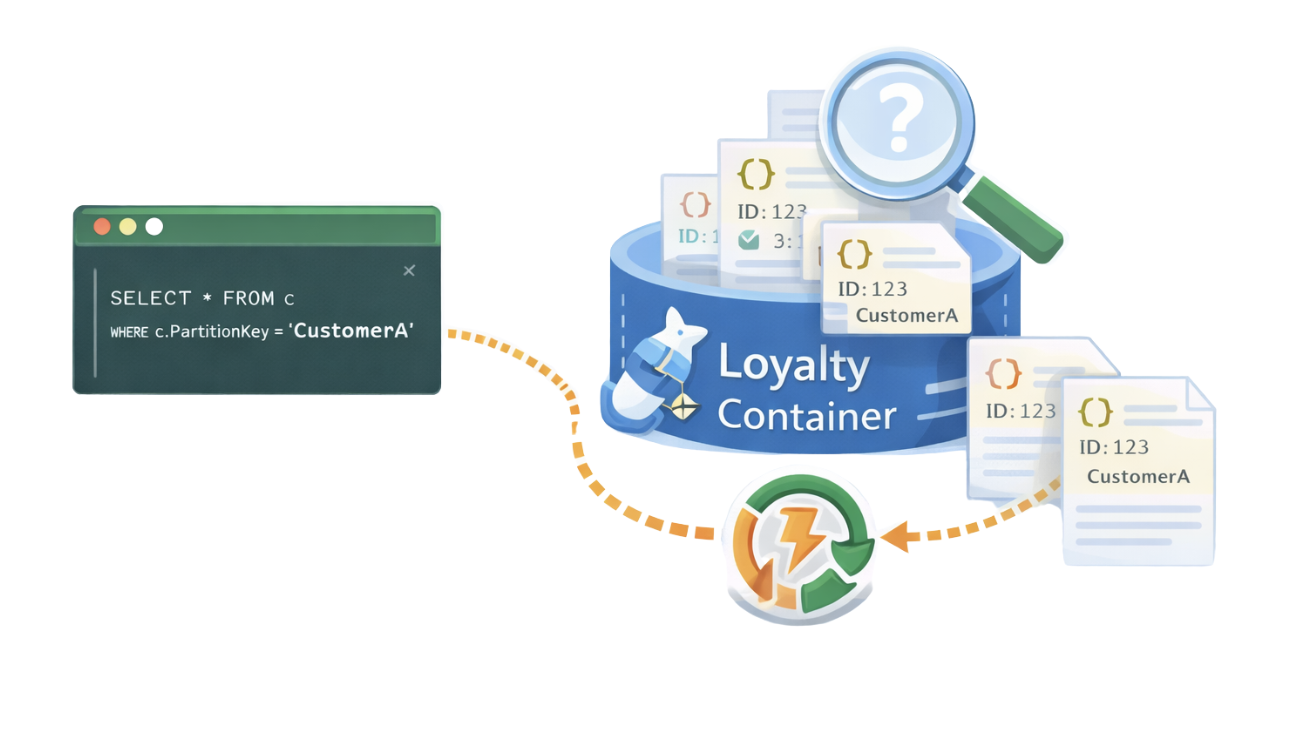
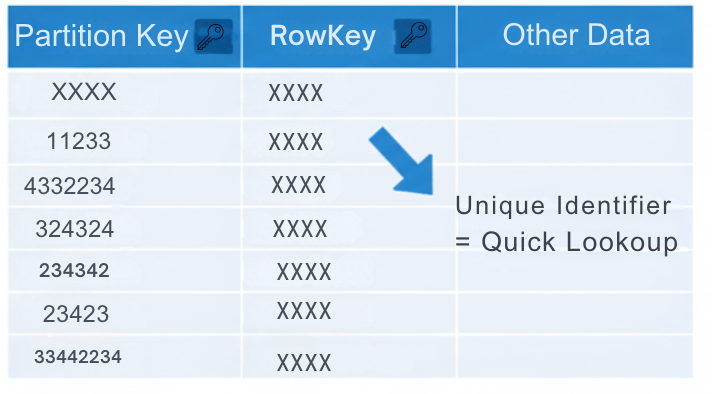
- Every entity must have a PartitionKey and a RowKey to uniquely identify it.
- These keys make queries fast and efficient, even at scale.
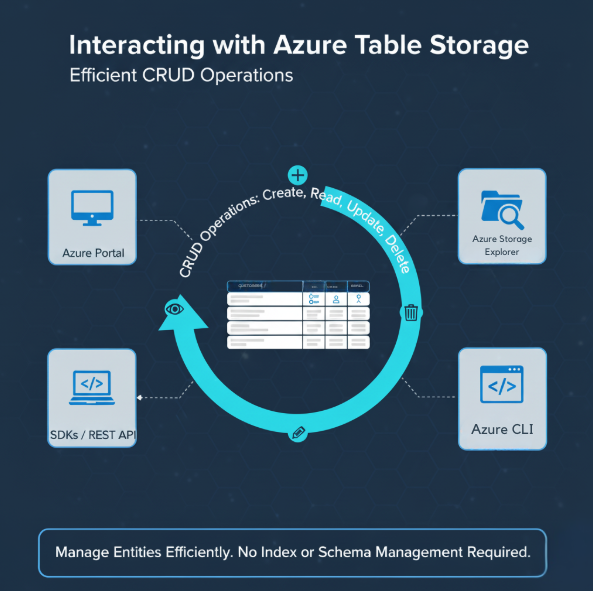
CRUD operations
- You can perform CRUD actions using:
- The Azure Portal.
- SDKs or REST API.
- Azure Storage Explorer.
- Manage data without worrying about indexes or schema updates.
Create example
- To add an entity, define a unique PartitionKey and RowKey.
- Example record for a customer might look like this:
"PartitionKey": "CustomerA",
"RowKey": "1001",
"Name": "Ava",
"Points": 120
Querying
Update and Delete
Updating replaces an entity's properties with new values.
Deleting removes an entity entirely.
Example commands:
table_client.update_entity(entity)
table_client.delete_entity("CustomerA","1001")
- Foundation for working with Table Storage.
Key takeaways
Use Table Storage for simple, scalable, and cost-efficient structured data.
Every record needs a PartitionKey and RowKey.
Use Cosmos DB when you need richer querying, global replication, or multiple data models.
Both services can complement each other in hybrid data architectures.

Let's practice!
Develop for Azure Storage

