Get several stocks & manage a MultiIndex
Importing and Managing Financial Data in Python

Stefan Jansen
Instructor
Get data for several stocks
- Use the listing information to select multiple stocks
- E.g. largest 3 stocks per sector
- Use Yahoo! Finance to retrieve data for several stocks
- Learn how to manage a
pandasMultiIndex, a powerful tool to deal with more complex data sets
Load prices for top 5 companies
nasdaq = pd.read_excel('listings.xlsx', sheet_name='nasdaq', na_values='n/a')nasdaq.set_index('Stock Symbol', inplace=True)top_5 = nasdaq['Market Capitalization'].nlargest(n=5) # Top 5 top_5.div(1000000) # Market Cap in million USD
AAPL 740024.467000
GOOG 569426.124504
... ...
Name: Market Capitalization, dtype: float64
tickers = top_5.index.tolist() # Convert index to list
['AAPL', 'GOOG', 'MSFT', 'AMZN', 'FB']
Load prices for top 5 companies
df = DataReader(tickers, 'yahoo', start=date(2020, 1, 1))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
DatetimeIndex: 712 entries, 2020-01-02 to 2022-10-27
Data columns (total 30 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
-- ------ -------------- -----
0 (Adj Close, AAPL) 712 non-null float64
1 (Adj Close, GOOG) 712 non-null float64
2 (Adj Close, MSFT) 712 non-null float64
...
28 (Volume, AMZN) 712 non-null float64
29 (Volume, FB) 253 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(30)
memory usage: 172.4 KB
df = df.stack()
Load prices for top 5 companies
df.info()
MultiIndex: 3101 entries, (Timestamp('2020-01-02 00:00:00'), 'AAPL') to (Timestamp('2022-10-27 00:00:00'), 'FB')
Data columns (total 6 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
-- ------ -------------- -----
0 Adj Close 3101 non-null float64
...
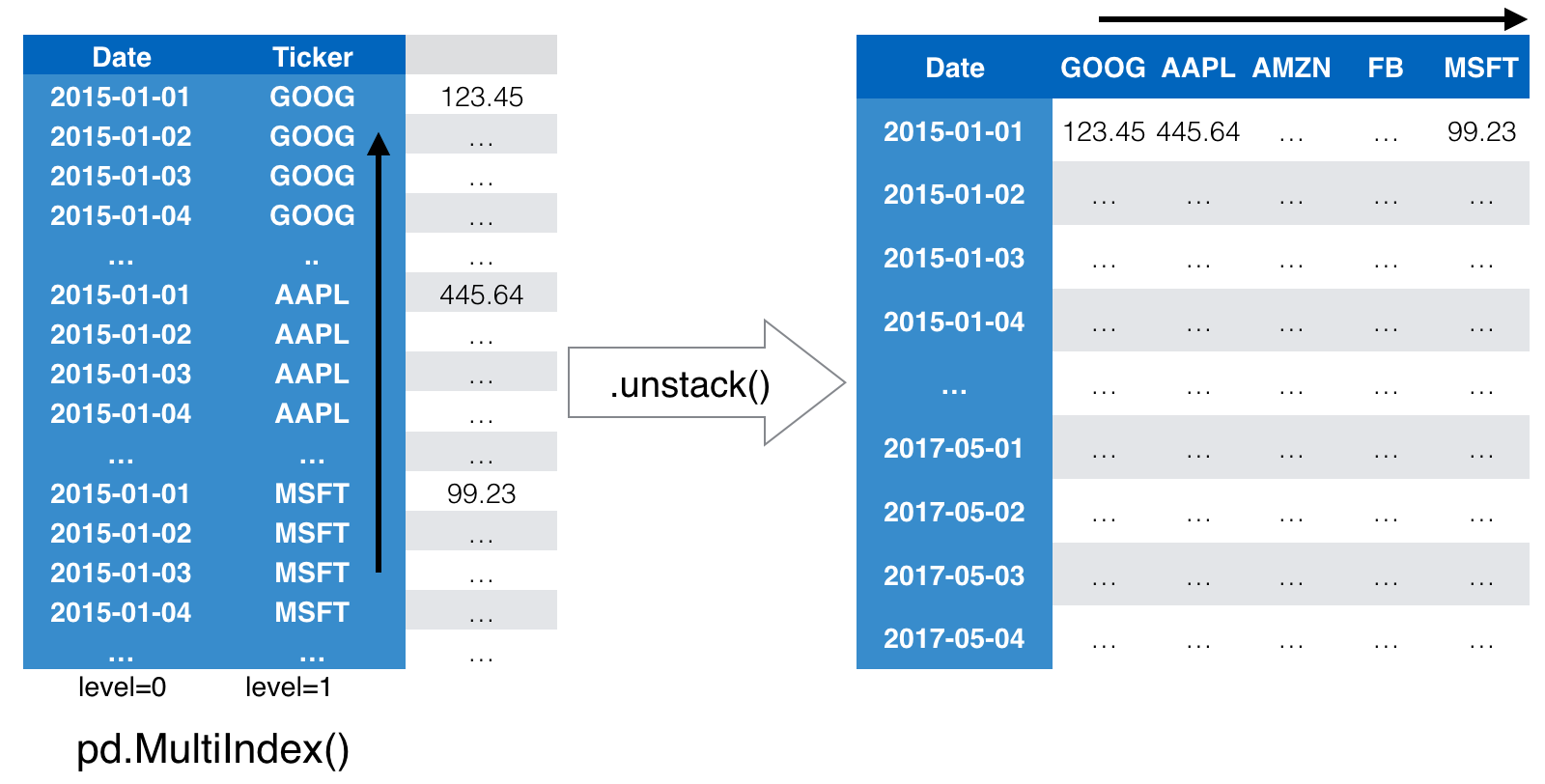
Reshape your data: .unstack()
unstacked = df['Close'].unstack()
unstacked.info()
DatetimeIndex: 712 entries, 2020-01-02 to 2022-10-27
Data columns (total 5 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
-- ------ -------------- -----
0 AAPL 712 non-null float64
1 GOOG 712 non-null float64
2 MSFT 712 non-null float64
3 AMZN 712 non-null float64
4 FB 253 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(5)
memory usage: 33.4 KB
From long to wide format
unstacked = df['Close'].unstack() # Results in DataFrame
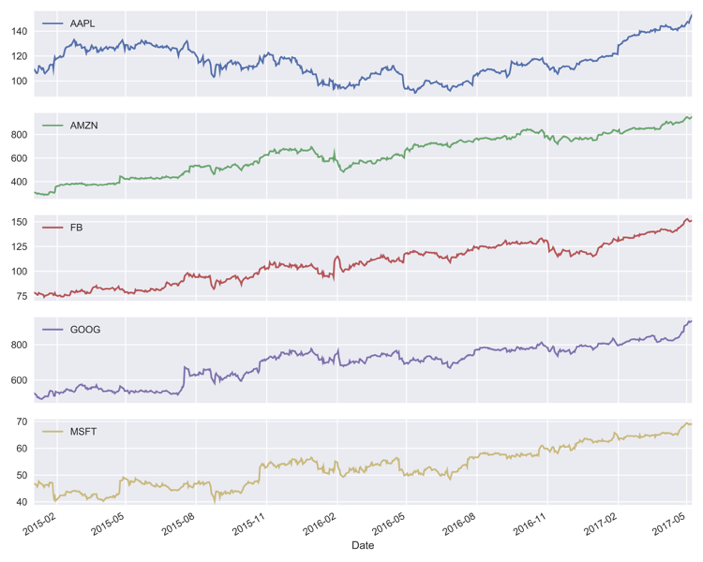
Stock prices: Visualization
unstacked.plot(subplots=True)
plt.tight_layout(); plt.show()
Let's practice!
Importing and Managing Financial Data in Python

