Glückwunsch!
Entwicklung mit Python für Fortgeschrittene

Jasmin Ludolf
Senior Data Science Content Developer
Kapitel 1 – Zusammenfassung
- Integrierte Funktionen:
print(),help(),type()max(),min(),sum()len(),round(),sorted()
- Module:
string,os
$$
- Pakete:
pandas
Kapitel 2 – Zusammenfassung
# Create a custom function
def average(values):
# Calculate the average
average_value = sum(values) / len(values)
# Round the results
rounded_average = round(average_value, 2)
# Return rounded_average as an output
return rounded_average
Kapitel 2 – Zusammenfassung
# Create a custom function def average(values, rounded=False):# Round average to two decimal places if rounded is True if rounded == True: average_value = sum(values) / len(values) rounded_average = round(average_value, 2) return rounded_average# Otherwise, don't round else: average_value = sum(values) / len(values) return average_value
Kapitel 2 – Zusammenfassung
def average(values): """ Find the mean in a sequence of values and round to two decimal places. Args: values (list): A list of numeric values. Returns: rounded_average (float): The mean of values, rounded to two decimal places. """average_value = sum(values) / len(values) rounded_average = round(average_value, 2) return rounded_average
Kapitel 2 – Zusammenfassung
# Use arbitrary positional arguments def average(*args): average_value = sum(args) / len(args) rounded_average = round(average_value, 2) return rounded_average# Use arbitrary keyword arguments def average(**kwargs): average_value = sum(kwargs.values()) / len(kwargs.values()) rounded_average = round(average_value, 2) return rounded_average
Kapitel 3 – Zusammenfassung
lambda arguments: expression
names = ["john", "sally", "leah"]
# Apply a lambda function inside map()
capitalize = map(lambda x: x.capitalize(), names)
# Convert to a list
print(list(capitalize))
['John', 'Sally', 'Leah']
Kapitel 3 – Zusammenfassung
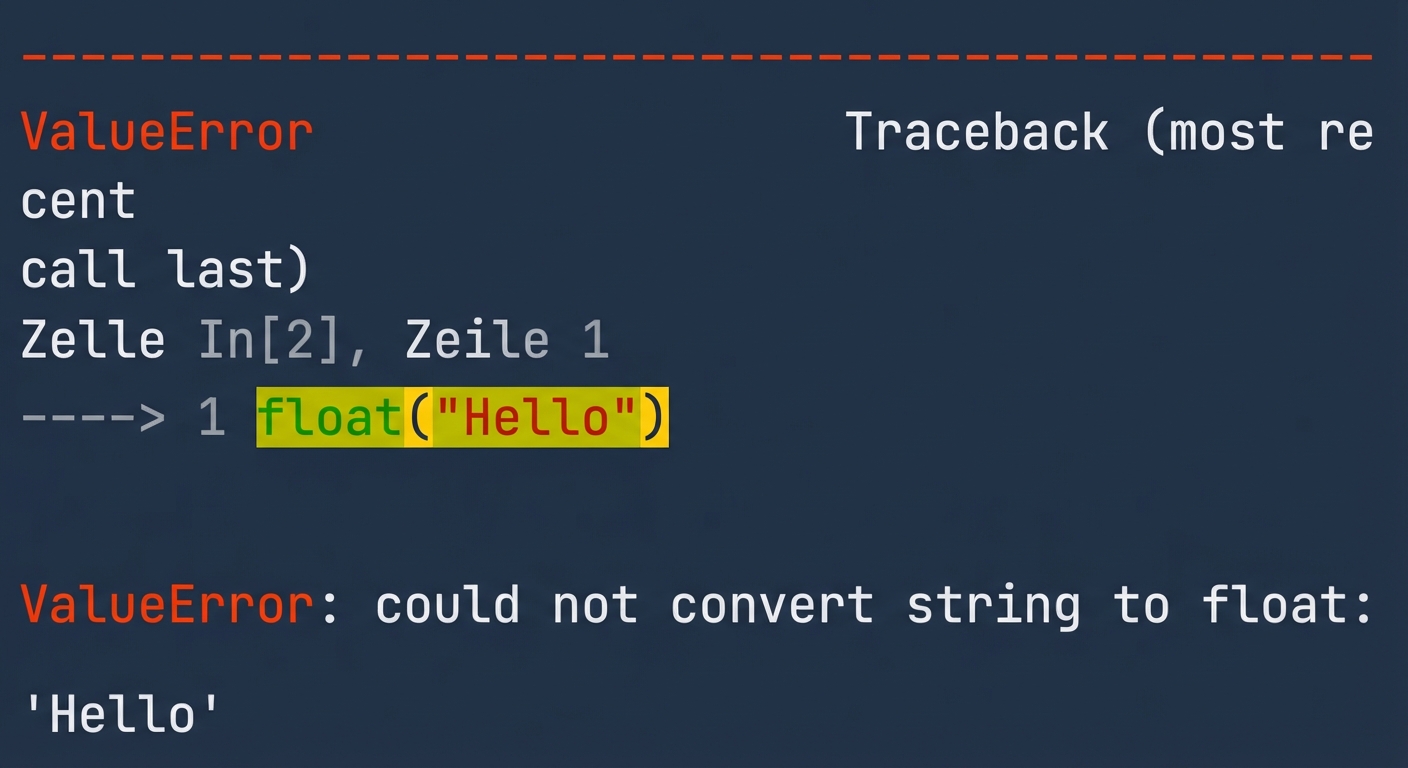
$$
tryexceptraise
Nächste Schritte
Weitere eingebaute Funktionen:
zip()input()reduce()filter()
Weitere Pakete und Module:
timevenvrequestsfastapi
- Essenziell für die Entwicklung von Software in großem Maßstab
Glückwunsch!
Entwicklung mit Python für Fortgeschrittene

