Ausreißer, Hebelwirkung und Einfluss
Einführung in Regression mit statsmodels in Python

Maarten Van den Broeck
Content Developer at DataCamp
Rotaugendatensatz
roach = fish[fish['species'] == "Roach"]
print(roach.head())
species mass_g length_cm
35 Roach 40.0 12.9
36 Roach 69.0 16.5
37 Roach 78.0 17.5
38 Roach 87.0 18.2
39 Roach 120.0 18.6

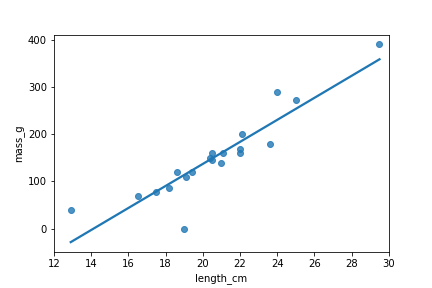
Welche Punkte sind Ausreißer?
sns.regplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
data=roach,
ci=None)
plt.show()
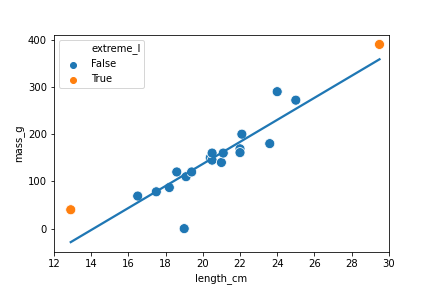
Extreme erklärende Werte
roach["extreme_l"] = ((roach["length_cm"] < 15) |
(roach["length_cm"] > 26))
fig = plt.figure()
sns.regplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
data=roach,
ci=None)
sns.scatterplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
hue="extreme_l",
data=roach)
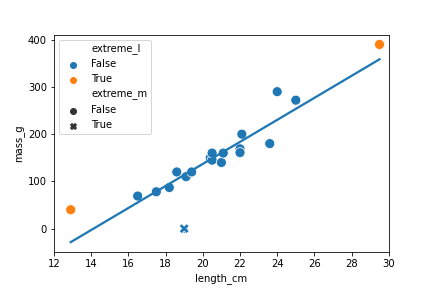
Werte, die von der Regressionsgeraden abweichen
roach["extreme_m"] = roach["mass_g"] < 1
fig = plt.figure()
sns.regplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
data=roach,
ci=None)
sns.scatterplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
hue="extreme_l",
style="extreme_m",
data=roach)
Hebelwirkung und Einfluss
Die Hebelwirkung zeigt, wie extrem die Werte der erklärenden Variablen ausfallen.
Der Einfluss misst, wie stark sich das Modell ändern würde, wenn du die Beobachtung bei der Modellierung aus dem Datensatz weglassen würdest.

.get_influence() und .summary_frame()
mdl_roach = ols("mass_g ~ length_cm", data=roach).fit()summary_roach = mdl_roach.get_influence().summary_frame()roach["leverage"] = summary_roach["hat_diag"] print(roach.head())
species mass_g length_cm leverage
35 Roach 40.0 12.9 0.313729
36 Roach 69.0 16.5 0.125538
37 Roach 78.0 17.5 0.093487
38 Roach 87.0 18.2 0.076283
39 Roach 120.0 18.6 0.068387
Cook-Distanz
Die Cook-Distanz ist das gängigste Maß für den Einfluss.
roach["cooks_dist"] = summary_roach["cooks_d"]
print(roach.head())
species mass_g length_cm leverage cooks_dist
35 Roach 40.0 12.9 0.313729 1.074015
36 Roach 69.0 16.5 0.125538 0.010429
37 Roach 78.0 17.5 0.093487 0.000020
38 Roach 87.0 18.2 0.076283 0.001980
39 Roach 120.0 18.6 0.068387 0.006610
Die einflussreichsten Rotaugen
print(roach.sort_values("cooks_dist", ascending = False))
species mass_g length_cm leverage cooks_dist
35 Roach 40.0 12.9 0.313729 1.074015 # really short roach
54 Roach 390.0 29.5 0.394740 0.365782 # really long roach
40 Roach 0.0 19.0 0.061897 0.311852 # roach with zero mass
52 Roach 290.0 24.0 0.099488 0.150064
51 Roach 180.0 23.6 0.088391 0.061209
.. ... ... ... ... ...
43 Roach 150.0 20.4 0.050264 0.000257
44 Roach 145.0 20.5 0.050092 0.000256
42 Roach 120.0 19.4 0.056815 0.000199
47 Roach 160.0 21.1 0.050910 0.000137
37 Roach 78.0 17.5 0.093487 0.000020
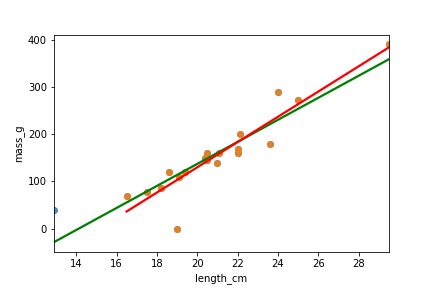
Das einflussreichste Rotauge loswerden
roach_not_short = roach[roach["length_cm"] != 12.9]
sns.regplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
data=roach,
ci=None,
line_kws={"color": "green"})
sns.regplot(x="length_cm",
y="mass_g",
data=roach_not_short,
ci=None,
line_kws={"color": "red"})
Lass uns üben!
Einführung in Regression mit statsmodels in Python

