Customer input to improve your operation
Data-Driven Decision Making for Business

Ted Kwartler
Data Dude
Examine customer survey data
$$

- Data collection: qualitative interviews, online reviews, transactional data
- Use model to explain customer survey data
Survey inputs as a model
- Q1: How satisfied are you overall [1-5]?
- Q2: How do you rate the quality of the product/service [1-5]?
- Q3: How do you rate the product/service options [1-5]?
- Q4: Do you agree that the offering is fairly priced [1-5]?
| Q1 (overall satisfaction) | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer-1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Customer-N | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Survey inputs as a model
| Q1 (overall satisfaction) | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer-1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Customer-N | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
$$
- Target variable
- Q1
- Explanatory variables
- Q2, Q3, Q4
Explanatory models from customer data
| Q1 (overall satisfaction) | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer-1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-2 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Customer-3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| Customer-N | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
$$
Logistic regression model
$f(\text{overall satisfaction}) = \beta_1 * Q2 + \beta_2 * Q3 + \beta_3 * Q4$
Sum of betas to understand impact
Logistic regression model
$f(\text{overall satisfaction}) = \beta_1 * Q2 + \beta_2 * Q3 + \beta_3 * Q4$
Model output
$f(\text{overall satisfaction}) = 0.25 * Q2 + 0.25 * Q3 + 1 * Q4$
Sum of betas
| Beta | Sum of beta | Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q2 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 |
| Q3 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 |
| Q4 | .1 | 0.6 | .16 |
Adding context with frequency
$$
| Beta | Sum of beta | Proportion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q2 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 |
| Q3 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 |
| Q4 | .1 | 0.6 | .16 |
Adding context with frequency
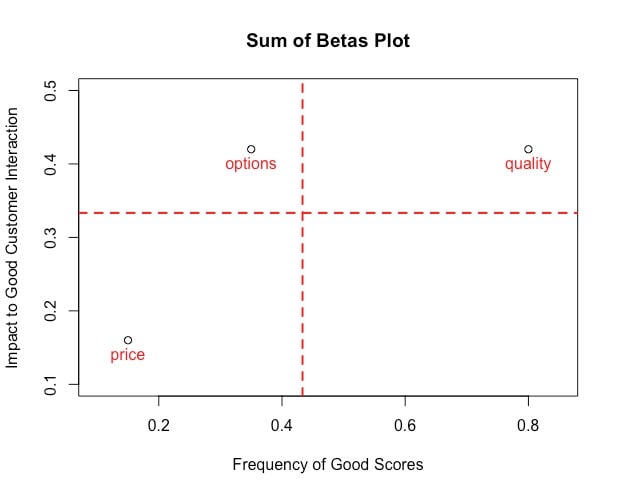
Adding the context of how often the organization does well in a category
| Beta | Sum of beta | Proportion | Frequency of a high score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 | .8 |
| Q3 | .25 | 0.6 | .42 | .35 |
| Q4 | .1 | 0.6 | .16 | .15 |
Off to it!
Data-Driven Decision Making for Business

